About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 230 results for "Dara Vancea" clear search
Opinions on contested energy infrastructures
Annalisa Stefanelli | Published Thursday, June 23, 2016This ABM simulates opinions on a topic (originally contested infrastructures) through the interactions between paired agents and based on the sociopsychological assumptions of social judgment theory (SJT; Sherif & Hovland, 1961).
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
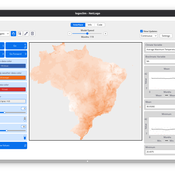
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
Retention in Higher Education: An Agent-Based Model of Social Interactions and Motivated Agent Behavior
Andrew Crooks Amira Al-Khulaidy Stine | Published Wednesday, October 23, 2024Educational attainment and student retention in higher education are two of the main focuses of higher education research. Institutions in the U.S. are constantly looking for ways to identify areas of improvement across different aspects of the student experience on university campuses. This paper combines Department of Education data, U.S. Census data, and higher education theory on student retention, to build an agent-based model of student behavior.
A Simulation of Arab Spring Protests Informed by Qualitative Evidence
Bruce Edmonds Stephanie Dornschneider | Published Monday, April 29, 2019 | Last modified Friday, May 24, 2019The purpose of the simulation was to explore and better understand the process of bridging between an analysis of qualitative data and the specification of a simulation. This may be developed for more serious processes later but at the moment it is merely an illustration.
This exercise was done by Stephanie Dornschneider (School of Politics and International Relations, University College Dublin) and Bruce Edmonds to inform the discussion at the Lorentz workshop on “Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data using Social Simulation” at Leiden in April 2019. The qualitative data was collected and analysed by SD. The model specification was developed as the result of discussion by BE & SD. The model was programmed by BE. This is described in a paper submitted to Social Simulation 2019 and (to some extent) in the slides presented at the workshop.
Agent-based model of sexual partnership
Andrea Knittel | Published Monday, December 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013In this model agents meet, evaluate one another, decide whether or not to date, if and when to become sexual partners, and when to break up.
Irrigation game
Marco Janssen | Published Monday, July 23, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Irrigation game calibrated on experimental data
Spatiotemporal Visualization of Emotional and Emotional-related Mental States
Luis Macedo | Published Monday, November 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A system that receives from an agent-based social simulation the agent’s emotional data, their emotional-related data such as motivations and beliefs, as well as their location, and visualizes of all this information in a two dimensional map of the geographic region the agents inhabit as well as on graphs along the time dimension.
An adaptive model of homing pigeons: A genetic algorithm approach
Gudrun Wallentin Francis Oloo | Published Friday, January 27, 2017In this model, we simulate the navigation behavior of homing pigeons. Specifically we use genetic algorithms to optimize the navigation and flocking parameters of pigeon agents.
Hohokam Water Management Simulation (HWM)
John Murphy | Published Wednesday, August 31, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Simulation of irrigation system management using archaeological data from southern Arizona
Peer reviewed Hohokam Trade Networks Model
Joshua Watts | Published Sunday, October 26, 2014The Hohokam Trade Networks Model focuses on key features of the Hohokam economy to explore how differences in trade network topologies may show up in the archaeological record. The model is set in the Phoenix Basin of central Arizona, AD 200-1450.
Displaying 10 of 230 results for "Dara Vancea" clear search