About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 949 results for "P Van Geert" clear search
Spatial rangeland model
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 22, 2019 | Last modified Friday, March 04, 2022Spatial explicit model of a rangeland system, based on Australian conditions, where grass, woody shrubs and fire compete fore resources. Overgrazing can cause the system to flip from a healthy state to an unproductive shrub state. With the model one can explore the consequences of different movement rules of the livestock on the resilience of the system.
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/.
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Pandemic package
Peter Cotton | Published Friday, April 24, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 08, 2020Pandemic (pip install pandemic)
An agent model in which commuting, compliance, testing and contagion parameters drive infection in a population of thousands of millions. Agents follow Ornstein-Uhlenbeck processes in the plane and collisions drive transmission. Results are stored at SwarmPrediction.com for further analysis, and can be retrieved by anyone.
This is a very simple simulation that in a special case can be shown to be approximated by a compartmental model with time varying infection rate.
A preliminary extension of the Hemelrijk 1996 model of reciprocal behavior to include feeding
Sean Barton | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A more complete description of the model can be found in Appendix I as an ODD protocol. This model is an expansion of the Hemelrijk (1996) that was expanded to include a simple food seeking behavior.
FOUR SEASONS
Lars G Spang | Published Tuesday, March 28, 2017Butterflies (turtles) goes through metamorphism and moves to corresponding patches each season of the year. The number of years and seasons are monitored.
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
Peer reviewed MIOvPOP
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Wednesday, September 18, 2019An ABM simulating white-tailed deer population dynamics for selected Michigan counties. The model yields pre-harvest and post-harvest realistic population snapshots that can be used to initialize the surveillance model (MIOvPOPsurveillance) and the CWD transmission dynamics model (MIOvCWD) respectively.
Thoughtless conformity and spread of norms in an artificial society (Grid Model)
Muhammad Azfar Nisar | Published Tuesday, May 27, 2014This model is a small extension (rectangular layout) of Joshua Epstein’s (2001) model on development of thoughtless conformity in an artificial society of agents.
Endogenous dynamics of firms made up by networked agents: an exploratory analysis
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Wednesday, March 23, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, October 05, 2016This is an adaptation and extension of Robert Axtell’s model (2013) of endogenous firms, in Python 3.4
An Agent-Based DSS for Word-of-Mouth Programs in Freemium Apps
Manuel Chica | Published Monday, September 05, 2016An agent-based framework that aggregates social network-level individual interactions to run targeting and rewarding programs for a freemium social app. Git source code in https://bitbucket.org/mchserrano/socialdynamicsfreemiumapps
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
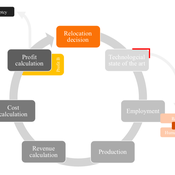
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
Displaying 10 of 949 results for "P Van Geert" clear search