About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 240 results for "Marcel Volosin" clear search
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
Peer reviewed Green Consumption Tipping Point
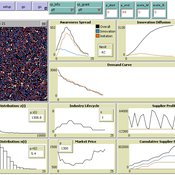
Mario | Published Thursday, February 26, 2026This model is a minimal agent-based model (ABM) of green consumption and market tipping dynamics in a stylised two-firm economy. It is designed as an existence proof to illustrate how weak individual preferences, when combined with habit formation, social influence, and firm price adaptation, can generate non-linear transitions (tipping points) in market outcomes.
The economy consists of:
1) Two firms, each supplying a differentiated consumption bundle that differs in its fixed green share (one relatively greener, one less green).
2) Many households, each consuming a unit mass per period and allocating consumption between the two firms.
…
Firm explore-exploit of knowledge
Rosanna Garcia | Published Monday, March 28, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The basic premise of the model is to simulate several ‘agents’ going through build-buy cycles: Build: Factories follow simple rules of strategy in the allocation of resources between making exploration and exploitation type products. Buy: Each of two types of Consumers, early-adopters and late adopters, follow simple purchase decision rules in deciding to purchase a product from one of two randomly chosen factories. Thus, the two working ‘agents’ of the model are ‘factories’ and […]
(Policy induced) Diffusion of Innovations - An integrated demand-supply Model based on Cournot Competition
Martin Rixin | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Objective is to simulate policy interventions in an integrated demand-supply model. The underlying demand function links both sides. Diffusion proceeds if interactions distribute awareness (Epidemic effect) and rivalry reduces the market price (Probit effect). Endogeneity is given due to the fact that consumer awareness as well as their willingness-to-pay drives supply-side rivalry. Firm´s entry and exit decisions as well as quantity and price settings are driven by Cournot competition.
FNNR-ABM
Judy Mak | Published Thursday, February 28, 2019 | Last modified Saturday, December 07, 2019FNNR-ABM is an agent-based model that simulates human activity, Guizhou snub-nosed monkey movement, and GTGP-enrolled land parcel conversion in the Fanjingshan National Nature Reserve in Guizhou, China.
Quick-start guide:
1. Install Python and set environmental path variables.
2. Install the mesa, matplotlib (optional), and pyshp (optional) Python libraries.
3. Configure fnnr_config_file.py.
…
Agent-based model of power dynamics in agri-food systems
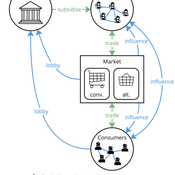
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, October 27, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, June 12, 2025This is a stylised agent-based model designed to explore the conditions that lead to lock-ins and transitions in agri-food systems.
The model represents interactions between four different types of agents: farmers, consumers, markets, and the state. Farmers and consumers are heterogeneous, and at each time step decide whether to trade with one of two market agents: the conventional or alternative. The state agent provides subsidies to the farmers at each time step.
The key emergent outcome is the fraction of trade in each time step that flows through the alternative market agent. This arises from the distributed decisions of farmer and consumer agents. A “sustainability transition” is defined as a shift in the dominant practices (and associated balance of power) towards the alternative paradigm.
…
Competitive Arousal Agent Based Model
Zoé Chollet | Published Friday, May 13, 2022What is it?
This model demonstrates a very simple bidding market where buyers try to acquire a desired item at the best price in a competitive environment
…
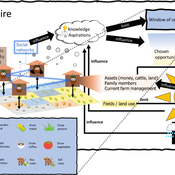
3spire: an agent-based model for exploring aspiration adaptation theory and its implications on smallholder farmers in Ethiopia
ateeuw Yue Dou Markus A Meyer Andrew Nelson | Published Sunday, February 16, 20253spire is an ABM where farming households make management decisions aimed at satisficing along the aspirational dimensions: food self-sufficiency, income, and leisure. Households decision outcomes depend on their social networks, knowledge, assets, household needs, past management, and climate/market trends
Replicating the Macy & Sato Model: Trust, Cooperation and Market Formation in the U.S. and Japan
Oliver Will | Published Saturday, August 29, 2009 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A replication of the model “Trust, Cooperation and Market Formation in the U.S. and Japan” by Michael W. Macy and Yoshimichi Sato.
Shared Norms and the Evolution of Ethnic Markers
Nathan Rollins | Published Friday, January 22, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The publication and mathematical model upon which this ABM is based shows one mechanism that can lead to stable behavioral and cultural traits between groups.
Displaying 10 of 240 results for "Marcel Volosin" clear search