About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1259 results
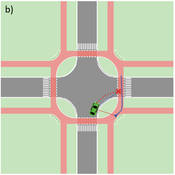
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
Multi-Hazard Coastal Agent-Based Model (MHCABM)
Andrew Allison | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021MHCABM is an agent-based, multi-hazard risk interaction model with an integrated applied dynamic adaptive pathways planning component. It is designed to explore the impacts of climate change adaptation decisions on the form and function of a coastal human-environment system, using as a case study an idealised patch based representation of the Mount North-Omanu area of Tauranga city, New Zealand. The interacting hazards represented are erosion, inundation, groundwater intrusion driven by intermittent heavy rainfall / inundations (storm) impacts, and sea level rise.
Simulating changing traffic flow caused by new bus route in Augsburg
Eduard | Published Wednesday, August 04, 2021This is a Netlogo model which simulates car and bus/tram traffic in Augsburg, specifically between the districts Stadtbergen, Göggingen and the Königsplatz. People either use their cars or public transport to travel to one of their random destinations (Stadtbergen or Göggingen), performing some activity and then returning to their home. Attributes such as travel and waiting time as well as their happiness upon arriving are stored and have an impact on individuals on whether they would consider changing their mode of transport or not.
Style_Net_01
Andrew White | Published Tuesday, August 03, 2021Style_Net_01 is a spatial agent-based model designed to serve as a platform for exploring geographic patterns of tool transport and discard among seasonally mobile hunter-gatherer populations. The model has four main levels: artifact, person, group, and system. Persons make, use, and discard artifacts. Persons travel in groups within the geographic space of the model. The movements of groups represent a seasonal pattern of aggregation and dispersal, with all groups coalescing at an aggregation site during one point of the yearly cycle. The scale of group mobility is controlled by a parameter. The creation, use, and discard of artifacts is controlled by several parameters that specify how many tools each person carries in a personal inventory, how many times each tool can be used before it is discarded, and the frequency of tool usage. A lithic source (representing a geographically-specific, recognizable source of stone for tools) can be placed anywhere in the geographic space of the model.
Model of Rental Evictions in Phoenix During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Sean Bergin J M Applegate | Published Saturday, July 31, 2021 | Last modified Friday, October 15, 2021The purpose of this model is to explore the dynamics of residency and eviction for households renting in the greater Phoenix (Arizona) metropolitan area. The model uses a representative population of renters modified from American Community Survey (ACS) data that includes demographic, housing and economic information. Each month, households pay their subsistence, rental and utility bills. If a household is unable to pay their monthly rent or utility bill they apply for financial assistance. This model provides a platform to understand the impact of various economic shock upon households. Also, the model includes conditions that occurred as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic which allows for the study of eviction mitigation strategies that were employed, such as the eviction moratorium and stimulus payments. The model allows us to make preliminary predictions concerning the number of households that may be evicted once the moratorium on evictions ends and the long-term effects on the number of evicted households in the greater Phoenix area going forward.
SiFlo: An Agent-based Model to simulate inhabitants’ behavior during a flood event
Patrick Taillandier Franck Taillandier Pascal Di Maiolo Rasool Mehdizadeh | Published Thursday, July 29, 2021SiFlo is an ABM dedicated to simulate flood events in urban areas. It considers the water flowing and the reaction of the inhabitants. The inhabitants would be able to perform different actions regarding the flood: protection (protect their house, their equipment and furniture…), evacuation (considering traffic model), get and give information (considering imperfect knowledge), etc. A special care was taken to model the inhabitant behavior: the inhabitants should be able to build complex reasoning, to have emotions, to follow or not instructions, to have incomplete knowledge about the flood, to interfere with other inhabitants, to find their way on the road network. The model integrates the closure of roads and the danger a flooded road can represent. Furthermore, it considers the state of the infrastructures and notably protection infrastructures as dyke. Then, it allows to simulate a dyke breaking.
The model intends to be generic and flexible whereas provide a fine geographic description of the case study. In this perspective, the model is able to directly import GIS data to reproduce any territory. The following sections expose the main elements of the model.
Peer reviewed Small-Trade Model
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Blanca Gonzalez-Mon Örjan Bodin | Published Wednesday, July 28, 2021The purpose of this model is to understand the role of trade networks and their interaction with different fish resources, for fish provision. The model is developed based on a multi-methods approach, combining agent-based modeling, network analysis and qualitative data based on a small-scale fisheries study case. The model can be used to investigate both how trade network structures are embedded in a social-ecological context and the trade processes that occur within them, to analyze how they lead to emergent outcomes related to the resilience of fish provision. The model processes are informed by qualitative data analysis, and the social network analysis of an empirical fish trade network. The network analysis can be used to investigate diverse network structures to perform model experiments, and their influence on model outcomes.
The main outcomes we study are 1) the overexploitation of fish resources and 2) the availability and variability of fish provision to satisfy different market demands, and 3) individual traders’ fish supply at the micro-level. The model has two types of trader agents, seller and dealer. The model reveals that the characteristics of the trade networks, linked to different trader types (that have different roles in those networks), can affect the resilience of fish provision.
Bid-rigging Norms Game Model
HIDEYUKI MOROFUJI | Published Tuesday, July 27, 2021 | Last modified Friday, May 12, 2023In this simulation, we modify the norms game model to bid-rigging (collusion) model, while we can simulate also the norms game model.
Cultural Dissemination: An Agent-Based Model with Social Influence
nhnguyen98 | Published Monday, July 26, 2021We study cultural dissemination in the context of an Axelrod-like agent-based model describing the spread of cultural traits across a society, with an added element of social influence. This modification produces absorbing states exhibiting greater variation in number and size of distinct cultural regions compared to the original Axelrod model, and we identify the mechanism responsible for this amplification in heterogeneity. We develop several new metrics to quantitatively characterize the heterogeneity and geometric qualities of these absorbing states. Additionally, we examine the dynamical approach to absorbing states in both our Social Influence Model as well as the Axelrod Model, which not only yields interesting insights into the differences in behavior of the two models over time, but also provides a more comprehensive view into the behavior of Axelrod’s original model. The quantitative metrics introduced in this paper have broad potential applicability across a large variety of agent-based cultural dissemination models.
SAFARI: Simulating Agroforestry Adoption in Rural Indonesia
Beatrice Nöldeke Etti Winter Yves Laumonier Trifosa Simamora | Published Tuesday, July 20, 2021The Simulating Agroforestry Adoption in Rural Indonesia (SAFARI) model aims at exploring the adoption of illipe rubber agroforestry systems by farming households in the case study region in rural Indonesia. Thereby, the ABM simulates the interdependencies of agroforestry systems and local livelihoods, income, land use, biodiversity, and carbon fixation. The model contrasts development paths without agroforestry (business as usual (BAU) scenario), corresponding to a scenario where the government promotes rubber monoculture, with the introduction of illipe rubber agroforestry systems (IRA scenario) as an alternative. It aims to support policy-makers to assess the potential of IRA over larger temporal and spatial scales.
Displaying 10 of 1259 results