About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 11 results temperature clear search
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Peer reviewed The Indus Village's Weather model: procedural generation of daily weather
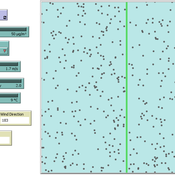
Andreas Angourakis | Published Tuesday, May 13, 2025Overview
The Weather model is a procedural generation model designed to create realistic daily weather data for socioecological simulations. It generates synthetic weather time series for solar radiation, temperature, and precipitation using algorithms based on sinusoidal and double logistic functions. The model incorporates stochastic variation to mimic unpredictable weather patterns and aims to provide realistic yet flexible weather inputs for exploring diverse climate scenarios.
The Weather model can be used independently or integrated into larger models, providing realistic weather patterns without extensive coding or data collection. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, enabling users to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and have greater confidence in their applications.
…
Peer reviewed WaDemEsT-Water Demand Estimation Tool for Residential Areas
Kamil Aybuğa | Published Tuesday, February 18, 2025This model simulates household water consumption patterns in an urban environment. Its current setup compares monthly water consumption data, and the results of a daily heuristic water demand model with the simulation results produced by household demographics that is fine tuned via some base demand model. It’s designed to estimate and analyze water demand based on various factors including household demographics, daily routines of residents (working, weekending, vacation patterns), weather conditions (temperature and precipitation), appliance usage patterns, seasonal variations, and special periods such as weekends and holidays. The model aims to help understand how different factors influence residential water consumption and can be used for water demand forecasting and management.
GenoScope
Kristin Crouse | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, April 09, 2025GenoScope is a modular agent-based model designed to simulate how cells respond to environmental stressors or other treatment conditions across species. Genes, treatment conditions, and cell physiology outcomes are represented as interacting agents that influence each other’s behavior over time. Rather than imposing fixed interaction rules, GenoScope initializes with randomized regulatory logic and calibrates rule sets based on empirical data. Calibration is grounded in a common-garden experiment involving 16 mammalian species—including humans, dolphins, bats, and camels—exposed to varying levels of temperature, glucose, and oxygen. This comparative approach enables the identification of mechanisms by which animal cells achieve robustness under extreme environmental conditions.
Absorption of particulate matter by leafs
Georg Jäger Chiara Letter | Published Monday, November 12, 2018 | Last modified Monday, November 12, 2018This model aims to understand the interaction between particulate matter and leaves of trees. The particles collide with the leaf and can either be absorbed with a certain probability, otherwise they bounce off it. The absorptions are detected in a counter.
The movement of the particles depends mainly on the strength and direction of the wind and the air temperature. They also show a certain random movement, but the proportion is negligible.
In a collision with the leaf, the particles are absorbed with a certain probability (absorption-probability), otherwise repelled.
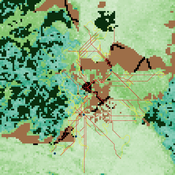
RaMDry - Rangeland Model in Drylands
Pascal Fust Eva Schlecht | Published Friday, January 05, 2018 | Last modified Friday, April 01, 2022RaMDry allows to study the dynamic use of forage ressources by herbivores in semi-arid savanna with an emphasis on effects of change of climate and management. Seasonal dynamics affects the amount and the nutritional values of the available forage.
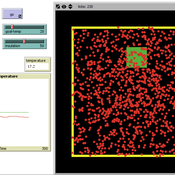
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
SpeciesWorld
Tony Lawson | Published Friday, March 16, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013How can species evolve a cooperative network to keep the environment suitable for life?
Displaying 10 of 11 results temperature clear search