About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 180 results for "Robin D Fink" clear search
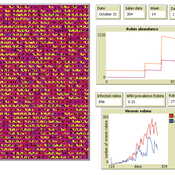
Peer reviewed AMRO_CULEX_WNV
Aniruddha Belsare Jennifer Owen | Published Saturday, February 27, 2021 | Last modified Thursday, March 11, 2021An agent-based model simulating West Nile Virus dynamics in a one host (American robin)-one vector (Culex spp. mosquito) system. ODD improved and code cleaned.
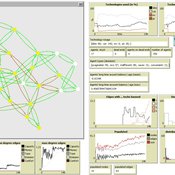
Simulation of the Governance of Complex Systems
Fabian Adelt Johannes Weyer Robin D Fink Andreas Ihrig | Published Monday, December 18, 2017 | Last modified Friday, March 02, 2018Simulation-Framework to study the governance of complex, network-like sociotechnical systems by means of ABM. Agents’ behaviour is based on a sociological model of action. A set of basic governance mechanisms helps to conduct first experiments.
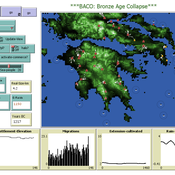
The Bronze Age Collapse model (BACO model)
Marco Vidal-Cordasco | Published Friday, October 09, 2020The Bronze Age Collapse model (BACO model) is written using free NetLogo software v.6.0.3. The purpose of using the BACO model is to develop a tool to identify and analyse the main factors that made the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age socio-ecological system resilient or vulnerable in the face of the environmental aridity recorded in the Aegean. The model explores the relationship between dependent and independent variables. Independent variables are: a) inter-annual rainfall variability for the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age in the eastern Mediterranean, b) intensity of raiding, c) percentage of marine, agricultural and other calorie sources included in the diet, d) soil erosion processes, e) farming assets, and d) storage capacity. Dependent variables are: a) human pressure for land, b) settlement patterns, c) number of commercial exchanges, d) demographic behaviour, and e) number of migrations.
Peer reviewed An extended replication of Abelson's and Bernstein's community referendum simulation
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Friday, October 25, 2019 | Last modified Friday, August 25, 2023This is an extended replication of Abelson’s and Bernstein’s early computer simulation model of community referendum controversies which was originally published in 1963 and often cited, but seldom analysed in detail. This replication is in NetLogo 6.3.0, accompanied with an ODD+D protocol and class and sequence diagrams.
This replication replaces the original scales for attitude position and interest in the referendum issue which were distributed between 0 and 1 with values that are initialised according to a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1 to make simulation results easier compatible with scales derived from empirical data collected in surveys such as the European Value Study which often are derived via factor analysis or principal component analysis from the answers to sets of questions.
Another difference is that this model is not only run for Abelson’s and Bernstein’s ten week referendum campaign but for an arbitrary time in order that one can find out whether the distributions of attitude position and interest in the (still one-dimensional) issue stabilise in the long run.
Individual Heights and Phase Transition under Emergences: Agent-Based Modeling from 2D to 3D
zhuo zhang | Published Saturday, August 27, 2022We use an agent-based 3D model to reveal the behavioral dynamics of real-world cases. The target of the simulation is the Peshawar massacre. The previous 2-D model has three main problems which can be solved by our 3-D model. Under the key action rules, our model matches the real target case exactly. Based on the optimal solution, we precisely match the results of the real cases, such as the number of deaths and injuries. We also explore the importance of adding height (constructed as a 3D model) to the model.
The uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Monday, August 31, 2020The agent-based simulation is set to work on information that is either (a) functional, (b) pseudo-functional, (c) dysfunctional, or (d) irrelevant. The idea is that a judgment on whether information falls into one of the four categories is based on the agent and its network. In other words, it is the agents who interprets a particular information as being (a), (b), (c), or (d). It is a decision based on an exchange with co-workers. This makes the judgment a socially-grounded cognitive exercise. The uFUNK 1.0.2 Model is set on an organization where agent-employee work on agent-tasks.
The Effect of Individual and Collective Characteristics on Team Performance: A Model of Networked Agents Engaged in Collective Problem Solving
Amin Boroomand | Published Tuesday, March 16, 2021 | Last modified Monday, July 26, 2021This code is for an agent-based model of collective problem solving in which agents with different behavior strategies, explore the NK landscape while they communicate with their peers agents. This model is based on the famous work of Lazer, D., & Friedman, A. (2007), The network structure of exploration and exploitation.
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
Exploring the Effects of Link Recommendations on Social Networks
Andrew Crooks Ciara Sibley | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020The purpose of this model is explore how “friend-of-friend” link recommendations, which are commonly used on social networking sites, impact online social network structure. Specifically, this model generates online social networks, by connecting individuals based upon varying proportions of a) connections from the real world and b) link recommendations. Links formed by recommendation mimic mutual connection, or friend-of-friend algorithms. Generated networks can then be analyzed, by the included scripts, to assess the influence that different proportions of link recommendations have on network properties, specifically: clustering, modularity, path length, eccentricity, diameter, and degree distribution.
Peer reviewed B3GET
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, November 14, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, September 20, 2022B3GET simulates populations of virtual organisms evolving over generations, whose evolutionary outcomes reflect the selection pressures of their environment. The model simulates several factors considered important in biology, including life history trade-offs, investment in fighting ability and aggression, sperm competition, infanticide, and competition over access to food and mates. Downloaded materials include starting genotype and population files. Edit the these files and see what changes occur in the behavior of virtual populations!
View the B3GET user manual here.
Displaying 10 of 180 results for "Robin D Fink" clear search