About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 120 results for "Brandon Velasco" clear search
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
Ageing and Spending
Tony Lawson | Published Tuesday, October 06, 2015How natural population ageing affects UK household spending patterns.
Peer reviewed Multilevel Group Selection I
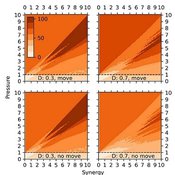
Wayne W. Wakeland Thaddeus Shannon Garry Sotnik | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Saturday, July 03, 2021New theoretical agent-based model of population-wide adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior with four parameters (initial percent of adopters, pressure to change behavior, synergy from behavior, and population density); dynamics in behavior, movement, freeriding, and group composition and size; and emergence of multilevel group selection. Theoretical analysis of model’s dynamics identified six regions in model’s parameter space, in which pressure-synergy combinations lead to different outcomes: extinction, persistence, and full adoption. Simulation results verified the theoretical analysis and demonstrated that increases in density reduce number of pressure-synergy combinations leading to population-wide adoption; initial percent of contributors affects underlying behavior and final outcomes, but not size of regions or transition zones between them; and random movement assists adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior.
An agent-based simulation model simulating the problem solving process of tournament-based crowdsourcing
wiseyanjie | Published Friday, May 04, 2018 | Last modified Friday, July 06, 2018A series of studies show the applicability of the NK model in the crowdsourcing research, but it also exposes a problem that the application of the NK model is not tightly integrated with crowdsourcing process, which leads to lack of a basic crowdsourcing simulation model. Accordingly, by introducing interaction relationship among task decisions to define three tasks of different structure: local task, small-world task and random task, and introducing bounded rationality and its two dimensions are taken into account: bounded rationality level that used to distinguish industry types and bounded rationality bias that used to differentiate professional users and ordinary users, an agent-based model that simulates the problem-solving process of tournament-based crowdsourcing is constructed by combining the NK fitness landscapes and the crowdsourcing framework of “Task-Crowd-Process-Evaluation”.
An agent-based simulation model simulating the problem solving process of tournament-based crowdsourcing
wiseyanjie | Published Friday, July 06, 2018A series of studies show the applicability of the NK model in the crowdsourcing research, but it also exposes a problem that the application of the NK model is not tightly integrated with crowdsourcing process, which leads to lack of a basic crowdsourcing simulation model. Accordingly, by introducing interaction relationship among task decisions to define three tasks of different structure: local task, small-world task and random task, and introducing bounded rationality and its two dimensions are taken into account: bounded rationality level that used to distinguish industry types and bounded rationality bias that used to differentiate professional users and ordinary users, an agent-based model that simulates the problem-solving process of tournament-based crowdsourcing is constructed by combining the NK fitness landscapes and the crowdsourcing framework of “Task-Crowd-Process-Evaluation”.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
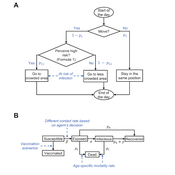
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Seasonal Social Networks and Learning Opportunities Under Unbiased Cultural Transmission
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Monday, May 18, 2015This agent-based model examines the impact of seasonal aggregation, dispersion, and learning opportunities on the richness and evenness of artifact styles under random social learning (unbiased transmission).
Machine Learning simulates Agent-based Model
Bernardo Furtado | Published Wednesday, March 07, 2018This is an initial exploratory exercise done for the class @ http://thiagomarzagao.com/teaching/ipea/ Text available here: https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.04429v1
The program:
Reads output from an ABM model and its parameters’ configuration
Creates a socioeconomic optimal output based on two ABM results of the modelers choice
Organizes the data as X and Y matrices
Trains some Machine Learning algorithms
…
Biodiversity and Adoption of Small-scale Agroforestry in Rwanda (BASAR)
Beatrice Nöldeke Etti Winter Elisée Bahati Ntawuhiganayo | Published Friday, July 15, 2022The BASAR model aims to investigate different approaches to describe small-scale farmers’ decision-making in the context of diversified agroforestry adoption in rural Rwanda. Thereby, it compares random behaviour with perfect rationality (non-discounted and discounted utility maximization), bounded rationality (satisficing and fast and frugal decision tree heuristics), Theory of Planned Behaviour, and a probabilistic regression-based approach. It is aimed at policy-makers, extension agents, and cooperatives to better understand how rural farmers decide about implementing innovative agricultural practices such as agroforestry and at modelers to support them in selecting an approach to represent human decision-making in ABMs of Social-Ecological Systems. The overall objective is to identify a suitable approach to describe human decision-making and therefore improve forecasts of adoption rates and support the development and implementation of interventions that aim to raise low adoption rates.
Displaying 10 of 120 results for "Brandon Velasco" clear search