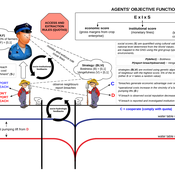
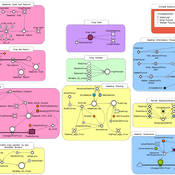
About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1120 results for "Joan A Barceló" clear search
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
GODS: Gossip-Oriented Dilemma Simulator
Jan Majewski | Published Wednesday, September 04, 2024 | Last modified Monday, September 29, 2025Model of influence of access to social information spread via social network on decisions in a two-person game.
Resource distribution effects on optimal foraging theory
Marco Janssen Kim Hill | Published Friday, January 27, 2017The original Ache model is used to explore different distributions of resources on the landscape and it’s effect on optimal strategies of the camps on hunting and camp movement.
Cascades across networks are sufficient for the formation of echo chambers: An agent-based model
Jan-Philipp Fränken | Published Monday, January 11, 2021An agent-based model of echo chamber formation employing a Bayesian Source Credibility cognitive architecture limiting interactions to a single cascade.
THE STATUS ARENA
Gert Jan Hofstede Jillian Student Mark R Kramer | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, January 09, 2018Status-power dynamics on a playground, resulting in a status landscape with a gender status gap. Causal: individual (beauty, kindness, power), binary (rough-and-tumble; has-been-nice) or prior popularity (status). Cultural: acceptability of fighting.
Perspectives on the Information-Based Economy
Vladimir Gazda Jana Zausinova Marcel Volosin | Published Monday, October 24, 2022This is the agent-based model of information market evolution. It simulates the influences of the transition from material to electronic carriers of information, which is modelled by the falling price of variable production factor. It demonstrates that due to zero marginal production costs, the competition increases, the market becomes unstable, and experience various phases of evolution leading to market monopolization.
Peer reviewed BAM: The Bottom-up Adaptive Macroeconomics Model
Alejandro Platas López Alejandro Guerra-Hernández | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 26, 2020Overview
Purpose
Modeling an economy with stable macro signals, that works as a benchmark for studying the effects of the agent activities, e.g. extortion, at the service of the elaboration of public policies..
…
A Model of the Gender Cliff in the Relative Contribution to the Household Income
André Grow Jan Van Bavel | Published Wednesday, December 18, 2019In Western countries, the distribution of relative incomes within marriages tends to be skewed in a remarkable way. Husbands usually do not only earn more than their female partners, but there also is a striking discontinuity in their relative contributions to the household income at the 50/50 point: many wives contribute just a bit less than or as much as their husbands, but few contribute more. Our model makes it possible to study a social mechanism that might create this ‘cliff’: women and men differ in their incomes (even outside marriage) and this may differentially affect their abilities to find similar- or higher-income partners. This may ultimately contribute to inequalities within the households that form. The model and associated files make it possible to assess the merit of this mechanism in 27 European countries.
Soil microbe-predator model with enzymes
Randall Boone John C Moore Akihiro Koyama Kirstin Holfelder | Published Thursday, November 21, 2013We seek to improve understanding of roles enzyme play in soil food webs. We created an agent-based simulation of a simple food web that includes enzymatic activity. The model was used in a publication, Moore et al. (in press; Biochemistry).
Impact of Seasonal Forecast Use on Agricultural Income in a System with Varying Crop Costs and Returns
Thushara Gunda Josh T Bazuin John Nay Kam L Yeung | Published Tuesday, February 07, 2017The objective of the model is to evaluate the impact of seasonal forecasts on a farmer’s net agricultural income when their crop choices have different and variable costs and returns.
Displaying 10 of 1120 results for "Joan A Barceló" clear search