About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 473 results # Agent Based model clear search
Location Analysis Hybrid ABM
Lukasz Kowalski | Published Friday, February 08, 2019The purpose of this hybrid ABM is to answer the question: where is the best place for a new swimming pool in a region of Krakow (in Poland)?
The model is well described in ODD protocol, that can be found in the end of my article published in JASSS journal (available online: http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/22/1/1.html ). Comparison of this kind of models with spatial interaction ones, is presented in the article. Before developing the model for different purposes, area of interest or services, I recommend reading ODD protocol and the article.
I published two films on YouTube that present the model: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iFWG2Xv20Ss , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tDTtcscyTdI&t=1s
…
Imperfect knowledge and stable governance in democracies
Carlos M Fernández-Márquez Francisco Jose Vazquez Luis Fernando Medina | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019In this paper we introduce an agent-based model of elections and government formation where voters do not have perfect knowledge about the parties’ ideological position. Although voters are boundedly rational, they are forward-looking in that they try to assess the likely impact of the different parties over the resulting government. Thus, their decision rules combine sincere and strategic voting: they form preferences about the different parties but deem some of them as inadmissible and try to block them from office. We find that the most stable and durable coalition governments emerge at intermediate levels of informational ambiguity. When voters have very poor information about the parties, their votes are scattered too widely, preventing the emergence of robust majorities. But also, voters with highly precise perceptions about the parties will cluster around tiny electoral niches with a similar aggregate effect.
Contract farming in the Mekong Delta's rice supply chain
Hung Nguyen | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We study three obstacles of the expansion of contract rice farming in the Mekong Delta (MKD) region. The failure of buyers in building trust-based relationship with small-holder farmers, unattractive offered prices from the contract farming scheme, and limited rice processing capacity have constrained contractors from participating in the large-scale paddy field program. We present an agent-based model to examine the viability of contract farming in the region from the contractor perspective.
The model focuses on financial incentives and trust, which affect the decision of relevant parties on whether to participate and honor a contract. The model is also designed in the context of the MKD’s rice supply chain with two contractors engaging in the contract rice farming scheme alongside an open market, in which both parties can renege on the agreement. We then evaluate the contractors’ performances with different combinations of scenarios related to the three obstacles.
Our results firstly show that a fully-equipped contractor who opportunistically exploits a relatively small proportion (less than 10%) of the contracted farmers in most instances can outperform spot market-based contractors in terms of average profit achieved for each crop. Secondly, a committed contractor who offers lower purchasing prices than the most typical rate can obtain better earnings per ton of rice as well as higher profit per crop. However, those contractors in both cases could not enlarge their contract farming scheme, since either farmers’ trust toward them decreases gradually or their offers are unable to compete with the benefits from a competitor or the spot market. Thirdly, the results are also in agreement with the existing literature that the contract farming scheme is not a cost-effective method for buyers with limited rice processing capacity, which is a common situation among the contractors in the MKD region.
Replication of an agent-based model using the Replication Standard
Derek Robinson Jiaxin Zhang | Published Sunday, January 20, 2019 | Last modified Saturday, July 18, 2020This model is a replication model which is constructed based on the existing model used by the following article:
Brown, D.G. and Robinson, D.T., 2006. Effects of heterogeneity in residential preferences on an agent-based model of urban sprawl. Ecology and society, 11(1).
The original model is called SLUCE’s Original Model for Experimentation (SOME). In Brown and Robinson (2006)’s article, the SOME model was used to explore the impacts of heterogeneity in residential location selections on the research of urban sprawl. The original model was constructed using Objective-C language based on SWARM platform. This replication model is built by NetLogo language on NetLogo platform. We successfully replicate that model and demonstrated the reliability and replicability of it.
Agent Based model exploring relationship between ethnic density and health.
Frensis Bras | Published Tuesday, January 15, 2019The model explores the relationship between ethnic density and health. It does this through exploring the potential pathway between racism, segregation, area deprivation and income.
Bicycle model
Gudrun Wallentin Dana Kaziyeva Martin Loidl | Published Thursday, January 10, 2019 | Last modified Monday, February 22, 2021The purpose of the model is to generate the spatio-temporal distribution of bicycle traffic flows at a regional scale level. Disaggregated results are computed for each network segment with the minute time step. The human decision-making is governed by probabilistic rules derived from the mobility survey.
Resisting hostility
Sylvie Huet | Published Thursday, December 20, 2018We propose an agent-based model leading to a decrease or an increase of hostility between agents after a major cultural threat such as a terrorist attack. The model is inspired from the Terror Management Theory and the Social Judgement Theory. An agent has a cultural identity defined through its acceptance segments about each of three different cultural worldviews (i.e., Atheist, Muslim, Christian) of the considered society. An agent’s acceptance segment is composed from its acceptable positions toward a cultural worldview, including its most acceptable position. An agent forms an attitude about another agent depending on the similarity between their cultural identities. When a terrorist attack is perpetrated in the name of an extreme cultural identity, the negatively perceived agents from this extreme cultural identity point of view tend to decrease the width of their acceptance segments in order to differentiate themselves more from the threatening cultural identity
Gentrilab
Adrian Lara | Published Monday, December 17, 2018Development of a Multiagent System for the Analysis of Gentrification in Latin America, an Agent-Based Model
Modeling Personal Carbon Trading with ABM
Roman Seidl | Published Friday, December 07, 2018 | Last modified Thursday, July 29, 2021A simulated approach for Personal Carbon Trading, for figuring out what effects it might have if it will be implemented in the real world. We use an artificial population with some empirical data from international literature and basic assumptions about heterogeneous energy demand. The model is not to be used as simulating the actual behavior of real populations, but a toy model to test the effects of differences in various factors such as number of agents, energy price, price of allowances, etc. It is important to adapt the model for specific countries as carbon footprint and energy demand determines the relative success of PCT.
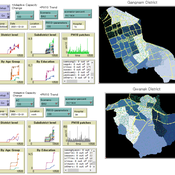
An Agent-based Assessment of Health Vulnerability to Long-term particulate exposure in Seoul Districts
Hyesop Shin Mike Bithell | Published Monday, November 05, 2018 | Last modified Monday, December 03, 2018This model aims to understand the cumulative effects on the population’s vulnerability as represented by exposure to PM10 (particulate matter with diameter less than 10 micrometres) by different age and educational groups in two Seoul districts, Gangnam and Gwanak. Using this model, readers can explore individual’s daily commuting routine, and its health loss when the PM10 concentration of the current patch breaches the national limit of 100µg/m3.
Displaying 10 of 473 results # Agent Based model clear search