About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 289 results for "Jieun Seo" clear search
SMILI-T: Small-scale fisheries institutions and local interactions for transformations
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Tuesday, January 09, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 26, 2021This model examines how financial and social top-down interventions interplay with the internal self-organizing dynamics of a fishing community. The aim is to transform from hierarchical fishbuyer-fisher relationship into fishing cooperatives.
BEEHAVE Extension: Varroa mite control within Good Beekeeping Practice in Germany
Volker Grimm Jürgen Groeneveld Isabel Schödl | Published Wednesday, May 25, 2022 | Last modified Monday, November 07, 2022The western honey bee Apis mellifera is the most important pollinator in the world. The biggest threat to managed honey bees is the ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor and the viruses DWV (Deformed Wing Virus) and APV (Acute Paralysis Virus) it transmits. Untreated honey bee colonies are expected to die within one to three years. This led to the development of strategies for beekeepers to control the Varroa mite in honey bee colonies and ensure the health and survival of their bee colonies, so called Good Beekeeping Practice. The aim of the extension of BEEHAVE was to represent the Good Beekeeping Practice of Varroa control in Germany. The relevant measures within the Varroa control strategies are drone brood removal as a Varroa trap and the treatment of bee colonies with organic acaricides (formic and oxalic acid) to kill the mites. This extension improves BEEHAVE and builds a bridge between beekeepers in practice and in the modelling world. It vastly contributes to the future use of BEEHAVE in beekeeping education in Germany.
A Simulation of Entrepreneurial Spawning
Mark Bagley | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Friday, June 30, 2017Industrial clustering patterns are the result of an entrepreneurial process where spinoffs inherit the ideas and attributes of their parent firms. This computational model maps these patterns using abstract methodologies.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
Friendship Games Rev 1.0
David Dixon | Published Friday, October 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A friendship game is a kind of network game: a game theory model on a network. This is a NetLogo model of an agent-based adaptation of “‘Friendship-based’ Games” by PJ Lamberson. The agents reach an equilibrium that depends on the strategy played and the topology of the network.
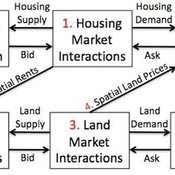
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
A land-use model to illustrate ambiguity in design
Julia Schindler | Published Monday, October 15, 2012 | Last modified Friday, January 13, 2017This is an agent-based model that allows to test alternative designs for three model components. The model was built using the LUDAS design strategy, while each alternative is in line with the strategy. Using the model, it can be shown that alternative designs, though built on the same strategy, lead to different land-use patterns over time.
An Agent-Based Model of Insurance Customer Behaviour with Word of Mouth Network in C#
Rei England Iqbal Owadally Douglas Wright | Published Friday, March 04, 2022This is an agent-based model with two types of agents: customers and insurers. Insurers are price-takers who choose how much to spend on their service quality, and customers evaluate insurers based on premium, brand preference, and their perceived service quality. Customers are also connected in a small-world network and may share their opinions with their network.
The ABM contains two types of agents: insurers and customers. These act within the environment of a motor insurance market. At each simulation, the model undergoes the following steps:
- Network generation: At the start of the simulation, the model generates a small world network of social links between the customers, and randomly assigns each customer to an initial insurer ...
Residents planned behaviour of waste sorting to explore urban situations
Jonathan Edgardo Cohen | Published Wednesday, June 07, 2023 | Last modified Thursday, March 14, 2024Municipal waste management (MWM) is essential for urban development. Efficient waste management is essential for providing a healthy and clean environment, for reducing GHGs and for increasing the amount of material recycled. Waste separation at source is perceived as an effective MWM strategy that relays on the behaviour of citizens to separate their waste in different fractions. The strategy is straightforward, and many cities have adopted the strategy or are working to implement it. However, the success of such strategy depends on adequate understanding of the drivers of the behaviour of proper waste sorting. The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) has been extensively applied to explain the behaviour of waste sorting and contributes to determining the importance of different psychological constructs. Although, evidence shows its validity in different contexts, without exploring how urban policies and the built environment affect the TPB, its application to urban challenges remains unlocked. To date, limited research has focused in exposing how different urban situations such as: distance to waste bins, conditions of recycling facilities or information campaigns affect the planned behaviour of waste separation. To fill this gap, an agent-based model (ABM) of residents capable of planning the behaviour of waste separation is developed. The study is a proof of concept that shows how the TPB can be combined with simulations to provide useful insights to evaluate different urban planning situations. In this paper we depart from a survey to capture TPB constructs, then Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) is used to validate the TPB hypothesis and extract the drivers of the behaviour of waste sorting. Finally, the development of the ABM is detailed and the drivers of the TPB are used to determine how the residents behave. A low-density and a high-density urban scenario are used to extract policy insights. In conclusion, the integration between the TPB into ABMs can help to bridge the knowledge gap between can provide a useful insight to analysing and evaluating waste management scenarios in urban areas. By better understanding individual waste sorting behaviour, we can develop more effective policies and interventions to promote sustainable waste management practices.
Displaying 10 of 289 results for "Jieun Seo" clear search