About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 97 results for "Evelyn Sperber" clear search
This project attempts to model how social media platforms recommend a user followers based on their interests, and how those individual interests change as a result of the influences from those they follow/are followed by.
We have three types of users on the platform:
Consumers (🔴), who update their interests based on who they’re following.
Creators (⬛), who update their interests based on who’s following them.
…
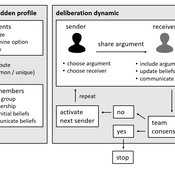
Agent-based model of team decision-making in hidden profile situations
Andreas Flache Jonas Stein Vincenz Frey | Published Thursday, April 20, 2023 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2023The model presented here is extensively described in the paper ‘Talk less to strangers: How homophily can improve collective decision-making in diverse teams’ (forthcoming at JASSS). A full replication package reproducing all results presented in the paper is accessible at https://osf.io/76hfm/.
Narrative documentation includes a detailed description of the model, including a schematic figure and an extensive representation of the model in pseudocode.
The model develops a formal representation of a diverse work team facing a decision problem as implemented in the experimental setup of the hidden-profile paradigm. We implement a setup where a group seeks to identify the best out of a set of possible decision options. Individuals are equipped with different pieces of information that need to be combined to identify the best option. To this end, we assume a team of N agents. Each agent belongs to one of M groups where each group consists of agents who share a common identity.
The virtual teams in our model face a decision problem, in that the best option out of a set of J discrete options needs to be identified. Every team member forms her own belief about which decision option is best but is open to influence by other team members. Influence is implemented as a sequence of communication events. Agents choose an interaction partner according to homophily h and take turns in sharing an argument with an interaction partner. Every time an argument is emitted, the recipient updates her beliefs and tells her team what option she currently believes to be best. This influence process continues until all agents prefer the same option. This option is the team’s decision.
University Connectivity
Rachel Wozniak Nick Glover Chris English Juan Cisneros | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021This model is designed to show the effects of personality types and student organizations have on ones chance to making friendships in a university setting. As known from psychology studies, those that are extroverted have an easier chance making friendships in comparison to those that are introverted.
Once every tick a pair of students (nodes) will be randomly selected they will then have the chance to either be come friends or not (create an edge or not) based on their personality type (you are able to change what the effect of each personality is) and whether or not they are in the same club (you can change this value) then the model triggers the next tick cycle to begin.
Scientific disagreements and the diagnosticity of evidence
Matteo Michelini | Published Wednesday, December 13, 2023The present model is an abstract ABM designed for theoretical exploration and hypotheses generation. Its main aim is to explore the relationship between disagreement over the diagnostic value of evidence and the formation of polarization in scientific communities.
The model represents a scientific community in which scientists aim to determine whether hypothesis H is true, and we assume that agents are in a world in which H is indeed true. To this end, scientists perform experiments, interpret data and exchange their views on how diagnostic of H the obtained evidence is. Based on how the scientists conduct the inquiry, the community may reach a correct consensus (i.e. a situation in which every scientist agrees that H is correct) or not.
BarterNet is a platform for modeling early barter networks with the aim of learning how supply and demand for a good determine if traders will learn to use that good as a form of money. Traders use a good as money when they offer to trade for it even if they can’t consume it, but believe that they can subsequently trade it for a good they can consume in the near future.
TransportVarese
Elena Vallino Elena Maggi | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2017 | Last modified Friday, August 04, 2017This ABM deals with commuting choices in the Italian city of Varese. Empirical data inform agents’ attitudes and modal choices costs and emissions. We evaluate ex ante the impact of policies for less polluting commuting choices.
Forest Logging and Ecosystem Degradation
Carla Guerrero | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026This model simulates a forest ecosystem affected by human logging. We explore different kind of approaches and their possible consequences for the ecosystem. Loggers can either be responsible or irresponsible, they will either take care to cut trees or not. In turn their actions will have consequences on the quality of the soil, the atmosphere as well as their profit made from logging. In this model we see that even careful management cannot prevent the degradation of the forest ecosystem.
REHAB: A Role Playing Game to Explore the Influence of Knowledge and Communication on Natural Resources Management
Christophe Le Page Anne Dray Pascal Perez Claude Garcia | Published Monday, July 13, 2015 | Last modified Monday, July 13, 2015REHAB has been designed as an ice-breaker in courses dealing with ecosystem management and participatory modelling. It helps introducing the two main tools used by the Companion Modelling approach, namely role-playing games and agent-based models.
External shocks, agent interactions, and endogenous feedbacks--investigating system resilience with a stylized land use model
Yang Chen | Published Tuesday, March 06, 2018The purpose of the presented ABM is to explore how system resilience is affected by external disturbances and internal dynamics by using the stylized model of an agricultural land use system.
We explore land system resilience with a stylized land use model in which agents’ land use activities are affected by external shocks, agent interactions, and endogenous feedbacks. External shocks are designed as yield loss in crops, which is ubiquitous in almost every land use system where perturbations can occur due to e.g. extreme weather conditions or diseases. Agent interactions are designed as the transfer of buffer capacity from farmers who can and are willing to provide help to other farmers within their social network. For endogenous feedbacks, we consider land use as an economic activity which is regulated by markets — an increase in crop production results in lower price (a negative feedback) and an agglomeration of a land use results in lower production costs for the land use type (a positive feedback).
An Agent-Based Model to Assess Possible Interventions for Large Shigellosis Outbreaks
Erez Hatna Jeewoen Shin Sharon Greene | Published Wednesday, June 12, 2024Large outbreaks of Shigella sonnei among children in Haredi Jewish (ultra-Orthodox) communities in Brooklyn, New York have occurred every 3–5 years since at least the mid-1980s. These outbreaks are partially attributable to large numbers of young children in these communities, with transmission highest in child care and school settings, and secondary transmission within households. As these outbreaks have been prolonged and difficult to control, we developed an agent-based model of shigellosis transmission among children in these communities to support New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene staff. Simulated children were assigned an initial susceptible, infectious, or recovered (immune) status and interacted and moved between their home, child care program or school, and a community site. We calibrated the model according to observed case counts as reported to the Health Department. Our goal was to better understand the efficacy of existing interventions and whether limited outreach resources could be focused more effectively.
Displaying 10 of 97 results for "Evelyn Sperber" clear search