About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search
Peer reviewed A Macroeconomic Model of a Closed Economy
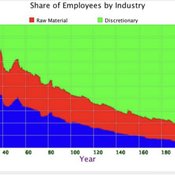
Ian Stuart | Published Saturday, May 08, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, June 23, 2021This model/program presents a “three industry model” that may be particularly useful for macroeconomic simulations. The main purpose of this program is to demonstrate a mechanism in which the relative share of labor shifts between industries.
Care has been taken so that it is written in a self-documenting way so that it may be useful to anyone that might build from it or use it as an example.
This model is not intended to match a specific economy (and is not calibrated to do so) but its particular minimalist implementation may be useful for future research/development.
…
RBM - A Relation-based model - a fishery implementation
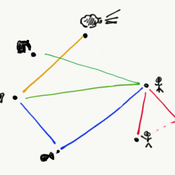
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Anja Klein Tilman Hertz | Published Monday, March 17, 2025The Relation-Based Model (RBM) purpose is to operationalise (a form of) process-relational (PR) thinking to serve as a thinking tool for process-relational thinking among social-ecological system (SES) researchers. The development of this model itself has been a ‘Proof of concept’- exercise to see whether we actually represent process-relational thinking in a methodology that is entity-based (ABM).
The target of the agent-based model is to show the emergence, change and disappearance of fishing assemblages (focusing on processes of self-organisation) in a Mexican fishery using a process-relational view. From this view, a fishery is regarded as an assemblage in which fishing can be enabled, fishing can occur, and fish can be bought/sold. These core doings - or sub-assemblages or capacities - maintain the assemblage. Each (sub)assemblage reflects different actualisations of constellations of relations and elements (buyers, fishers, fuel, permits, vessels and wind). The RBM thereby reflects an artificial fishery in which agents (elements) and their links (relations) engage in (enabling) fishing and buying/selling.
Peer reviewed An IBM of a fishing fleet exploiting a pelagic resource and with a fisher management system. A preliminary version.
Paul Hart | Published Tuesday, March 19, 2024A fisher directed management system was describeded by Hart (2021). It was proposed that fishers should only be allowed to exploit a resource if they collaborated in a resource management system for which they would own and be collectively responsible for. As part of the system fishers would need to follow the rules of exploitation set by the group and provide a central unit with data with which to monitor the fishery. Any fisher not following the rules would at first be fined but eventually expelled from the fishery if he/she continued to act selfishly. This version of the model establishes the dynamics of a fleet of vessels and controls overfishing by imposing fines on fishers whose income is low and who are tempted to keep fishing beyond the set quota which is established each year depending on the abundance of the fish stock. This version will later be elaborated to have interactions between the fishers including pressure to comply with the norms set by the group and which could lead to a stable management system.
A Diffusion Study
Diego Leal | Published Sunday, April 21, 2024This ABM
Landscape connectivity and predator–prey population dynamics
Jacopo A. Baggio | Published Thursday, November 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A simple model to assess the effect of connectivity on interacting species (i.e. predator-prey type)
Social model of a Team Developing a Planning-Methodology
Oswaldo Terán Christophe Sibertin | Published Monday, November 18, 2013 | Last modified Sunday, November 16, 2014The model represents a team intended at designing a methodology for Institutional Planning. Included in ICAART’14 to exemplify how emotions can be identified in SocLab; and in ESSA’14 to show the Efficiency of Organizational Withdrawal vs Commitment.
We propose here a computational model of school segregation that is aligned with a corresponding Schelling-type model of residential segregation. To adapt the model for application to school segregation, we move beyond previous work by combining two preference arguments in modeling parents’ school choice, preferences for the ethnic composition of a school and preferences for minimizing the travelling distance to the school.
Simulating the Ridesharing Economy: The Individual Agent Metro-Washington Area Ridesharing Model (IAMWARM)
Joseph A. E. Shaheen | Published Thursday, January 27, 2022This is a ridesharing model (Uber/Lyft) of the larger Washington DC metro area. The model can be modified (Netlogo 6.x) relatively easily and be adapted to any metro area. Please cite generously (this was a lot of work) and please cite the paper, not the comses model.
Link to the paper published in “Complex Adaptive Systems” here: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-20309-2_7
Citation: Shaheen J.A.E. (2019) Simulating the Ridesharing Economy: The Individual Agent Metro-Washington Area Ridesharing Model (IAMWARM). In: Carmichael T., Collins A., Hadžikadić M. (eds) Complex Adaptive Systems. Understanding Complex Systems. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20309-2_7
Foragers to Farmers
Nick Gauthier Elske van der Vaart Michael Storozum Tim Dorscheidt | Published Monday, July 22, 2024This model is represents an effort to replicate one of the first attempts (van der Vaart 2006) to develop an agent based model of agricultural origins using principles and equations drawn from human behavioral ecology. We have taken one theory of habitat choice (Ideal Free Distribution) and applied it to human behavioral adaptations to differences in resource quality of different habitats.
A Model of Making
Bruce Edmonds | Published Friday, January 29, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, December 07, 2016This models provides the infrastructure to model the activity of making. Individuals use resources they find in their environment plus those they buy, to design, construct and deconstruct items. It represents plans and complex objects explicitly.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search