About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 244 results for "Curtis W Marean" clear search
OMOLAND-CA: An Agent-Based Modeling of Rural Households’ Adaptation to Climate Change
Atesmachew Hailegiorgis Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, July 25, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, July 10, 2018The purpose of the OMOLAND-CA is to investigate the adaptive capacity of rural households in the South Omo zone of Ethiopia with respect to variation in climate, socioeconomic factors, and land-use at the local level.
ACT: Agent-based model of Critical Transitions
Igor Nikolic Oscar Kraan Steven Dalderop Gert Jan Kramer | Published Wednesday, October 18, 2017 | Last modified Monday, August 27, 2018ACT is an ABM based on an existing conceptualisation of the concept of critical transitions applied to the energy transition. With the model we departed from the mean-field approach simulated relevant actor behaviour in the energy transition.
Peer reviewed HUMLAND2: HUMan impact on LANDscapes agent-based model
Fulco Scherjon Anastasia Nikulina Anhelina Zapolska Maria Antonia Serge Marco Davoli Dave van Wees Katharine MacDonald Elena A. Pearce | Published Friday, August 30, 2024The HUMan Impact on LANDscapes (HUMLAND) 2.0.0 is an enhanced version of HUMLAND 1.0.0, developed to track and quantify the intensity of various impacts on landscapes at a continental scale. The model is designed to identify the most influential factors in the transformation of interglacial vegetation, with a particular focus on the burning practices of hunter-gatherers. HUMLAND 2.0.0 incorporates a wide range of spatial datasets as both inputs and targets (expected modelling results) for simulations across Last Interglacial (~130,000–116,000 BP) and Early Holocene (~11,700–8,000 BP).
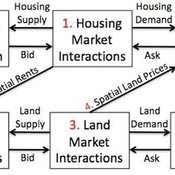
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Correlated random walk
Thibault Fronville | Published Friday, April 01, 2022 | Last modified Monday, April 25, 2022The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
This model is implemented in python and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
An Agent-Based Model of Insurance Customer Behaviour with Word of Mouth Network in C#
Rei England Iqbal Owadally Douglas Wright | Published Friday, March 04, 2022This is an agent-based model with two types of agents: customers and insurers. Insurers are price-takers who choose how much to spend on their service quality, and customers evaluate insurers based on premium, brand preference, and their perceived service quality. Customers are also connected in a small-world network and may share their opinions with their network.
The ABM contains two types of agents: insurers and customers. These act within the environment of a motor insurance market. At each simulation, the model undergoes the following steps:
- Network generation: At the start of the simulation, the model generates a small world network of social links between the customers, and randomly assigns each customer to an initial insurer ...
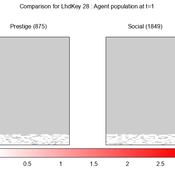
We provide a theory-grounded, socio-geographic agent-based model to present a possible explanation for human movement in the Adriatic region within the Cetina phenomenon.
Focusing on ideas of social capital theory from Piere Bordieu (1986), we implement agent mobility in an abstract geography based on cultural capital (prestige) and social capital (social position). Agents hold myopic representations of social (Schaff, 2016) and geographical networks and decide in a heuristic way on moving (and where) or staying.
The model is implemented in a fork of the Laboratory for Simulation Development (LSD), appended with GIS capabilities (Pereira et. al. 2020).
Epidemic Simulation with Transportation Simulation
FG Econophysics FG Econophysics | Published Monday, March 01, 2021The Episim framework builds upon the established transportation simulation MATSim and is capable of tracking agents’ movements within a network and thus computing infection chains. Several characteristics of the virus and the environment can be parametred, whilst the infection dynamics is computed based upon a compartment model. The spread of the virus can be mitigated by restricting the agents’ activity in certain places.
Quality uncertainty and market failure
David Poza José Manuel Galán María Pereda José Santos | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018Quality uncertainty and market failure: an interactive model to conduct classroom experiments
Displaying 10 of 244 results for "Curtis W Marean" clear search