Reduced Mobility Transition Model (R-MoTMo) 1.0.0
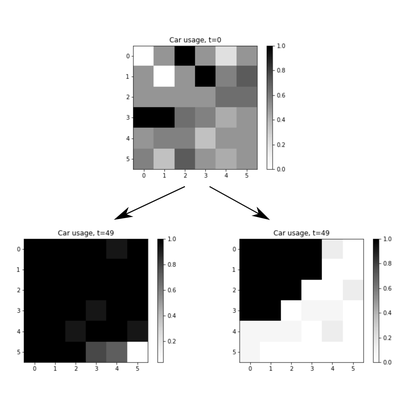
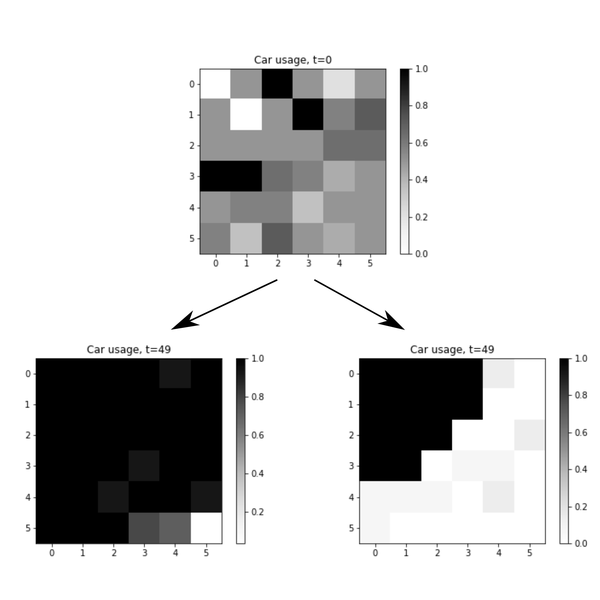
The Mobility Transition Model (MoTMo) is a large scale agent-based model to simulate the private mobility demand in Germany until 2035. Here, we publish a very much reduced version of this model (R-MoTMo) which is designed to demonstrate the basic modelling ideas; the aim is by abstracting from the (empirical, technological, geographical, etc.) details to examine the feed-backs of individual decisions on the socio-technical system.
Release Notes
In the file run.py, the simulation parameters can be set in lines 13-20.
The simulation name (part of the name of the saved result files) is created from the input parameters (line 22-24).
Run the file run.py to start a simulation.
If “plotResults” is set “True” (line 33), the plots specified in lines 35-42 are done after the simulation is finished. (To plot results from saved files without a new simulation use the file justPlot.py.)