About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 3 of 3 results sugarscape clear search
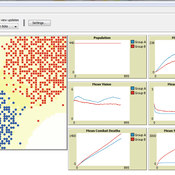
This model was developed to test the usability of evolutionary computing and reinforcement learning by extending a well known agent-based model. Sugarscape (Epstein & Axtell, 1996) has been used to demonstrate migration, trade, wealth inequality, disease processes, sex, culture, and conflict. It is on conflict that this model is focused to demonstrate how machine learning methodologies could be applied.
The code is based on the Sugarscape 2 Constant Growback model, availble in the NetLogo models library. New code was added into the existing model while removing code that was not needed and modifying existing code to support the changes. Support for the original movement rule was retained while evolutionary computing, Q-Learning, and SARSA Learning were added.
Sugarscape with spice
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Friday, September 18, 2020This is a variation of the Sugarspace model of Axtell and Epstein (1996) with spice and trade of sugar and spice. The model is not an exact replication since we have a somewhat simpler landscape of sugar and spice resources included, as well as a simple reproduction rule where agents with a certain accumulated wealth derive an offspring (if a nearby empty patch is available).
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/
SugarscapeCW
Christopher Watts | Published Saturday, August 01, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, April 12, 2023A replication in Netlogo 5.2 of the classic model, Sugarscape (Epstein & Axtell, 1996).