About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 15 results sociology clear search
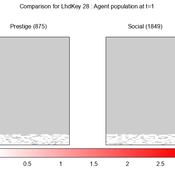
We provide a theory-grounded, socio-geographic agent-based model to present a possible explanation for human movement in the Adriatic region within the Cetina phenomenon.
Focusing on ideas of social capital theory from Piere Bordieu (1986), we implement agent mobility in an abstract geography based on cultural capital (prestige) and social capital (social position). Agents hold myopic representations of social (Schaff, 2016) and geographical networks and decide in a heuristic way on moving (and where) or staying.
The model is implemented in a fork of the Laboratory for Simulation Development (LSD), appended with GIS capabilities (Pereira et. al. 2020).
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
Peer reviewed COMMONSIM: Simulating the utopia of COMMONISM
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Ernest Aigner Stefan Meretz Jens Schröter Hanno Pahl Annette Schlemm Simon Sutterlütti | Published Sunday, November 05, 2023This research article presents an agent-based simulation hereinafter called COMMONSIM. It builds on COMMONISM, i.e. a large-scale commons-based vision for a utopian society. In this society, production and distribution of means are not coordinated via markets, exchange, and money, or a central polity, but via bottom-up signalling and polycentric networks, i.e. ex-ante coordination via needs. Heterogeneous agents care for each other in life groups and produce in different groups care, environmental as well as intermediate and final means to satisfy sensual-vital needs. Productive needs decide on the magnitude of activity in groups for a common interest, e.g. the production of means in a multi-sectoral artificial economy. Agents share cultural traits identified by different behaviour: a propensity for egoism, leisure, environmentalism, and productivity. The narrative of this utopian society follows principles of critical psychology and sociology, complexity and evolution, the theory of commons, and critical political economy. The article presents the utopia and an agent-based study of it, with emphasis on culture-dependent allocation mechanisms and their social and economic implications for agents and groups.
Schelling Model of the City of Salzburg
Andreas Schlagbauer | Published Monday, December 05, 2022The purpose of the model is to better understand, how different factors for human residential choices affect the city’s segregation pattern. Therefore, a Schelling (1971) model was extended to include ethnicity, income, and affordability and applied to the city of Salzburg. So far, only a few studies have tried to explore the effect of multiple factors on the residential pattern (Sahasranaman & Jensen, 2016, 2018; Yin, 2009). Thereby, models using multiple factors can produce more realistic results (Benenson et al., 2002). This model and the corresponding thesis aim to fill that gap.
Cellular automata model of social networks
Rubens de Almeida Zimbres | Published Tuesday, August 02, 2022This project was developed during the Santa Fe course Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling 2022. The origin is a Cellular Automata (CA) model to simulate human interactions that happen in the real world, from Rubens and Oliveira (2009). These authors used a market research with real people in two different times: one at time zero and the second at time zero plus 4 months (longitudinal market research). They developed an agent-based model whose initial condition was inherited from the results of the first market research response values and evolve it to simulate human interactions with Agent-Based Modeling that led to the values of the second market research, without explicitly imposing rules. Then, compared results of the model with the second market research. The model reached 73.80% accuracy.
In the same way, this project is an Exploratory ABM project that models individuals in a closed society whose behavior depends upon the result of interaction with two neighbors within a radius of interaction, one on the relative “right” and other one on the relative “left”. According to the states (colors) of neighbors, a given cellular automata rule is applied, according to the value set in Chooser. Five states were used here and are defined as levels of quality perception, where red (states 0 and 1) means unhappy, state 3 is neutral and green (states 3 and 4) means happy.
There is also a message passing algorithm in the social network, to analyze the flow and spread of information among nodes. Both the cellular automaton and the message passing algorithms were developed using the Python extension. The model also uses extensions csv and arduino.
Open Peer Review Model
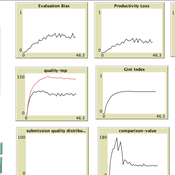
Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, May 24, 2021This is an agent-based model of a population of scientists alternatively authoring or reviewing manuscripts submitted to a scholarly journal for peer review. Peer-review evaluation can be either ‘confidential’, i.e. the identity of authors and reviewers is not disclosed, or ‘open’, i.e. authors’ identity is disclosed to reviewers. The quality of the submitted manuscripts vary according to their authors’ resources, which vary according to the number of publications. Reviewers can assess the assigned manuscript’s quality either reliably of unreliably according to varying behavioural assumptions, i.e. direct/indirect reciprocation of past outcome as authors, or deference towards higher-status authors.
Introducing two extensions of Schelling's segregation model
Andreas Flache Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Monday, January 25, 2021Schelling famously proposed an extremely simple but highly illustrative social mechanism to understand how strong ethnic segregation could arise in a world where individuals do not necessarily want it. Schelling’s simple computational model is the starting point for our extensions in which we build upon Wilensky’s original NetLogo implementation of this model. Our two NetLogo models can be best studied while reading our chapter “Agent-based Computational Models” (Flache and de Matos Fernandes, 2021). In the chapter, we propose 10 best practices to elucidate how agent-based models are a unique method for providing and analyzing formally precise, and empirically plausible mechanistic explanations of puzzling social phenomena, such as segregation, in the social world. Our chapter addresses in particular analytical sociologists who are new to ABMs.
In the first model (SegregationExtended), we build on Wilensky’s implementation of Schelling’s model which is available in NetLogo library (Wilensky, 1997). We considerably extend this model, allowing in particular to include larger neighborhoods and a population with four groups roughly resembling the ethnic composition of a contemporary large U.S. city. Further features added concern the possibility to include random noise, and the addition of a number of new outcome measures tuned to highlight macro-level implications of the segregation dynamics for different groups in the agent society.
In SegregationDiscreteChoice, we further modify the model incorporating in particular three new features: 1) heterogeneous preferences roughly based on empirical research categorizing agents into low, medium, and highly tolerant within each of the ethnic subgroups of the population, 2) we drop global thresholds (%-similar-wanted) and introduce instead a continuous individual-level single-peaked preference function for agents’ ideal neighborhood composition, and 3) we use a discrete choice model according to which agents probabilistically decide whether to move to a vacant spot or stay in the current spot by comparing the attractiveness of both locations based on the individual preference functions.
…
Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model
Szymon Talaga Andrzej Nowak | Published Tuesday, September 17, 2019This is code repository for the paper “Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model”.
It provides all information, code and data necessary to replicate all the simulations and analyses presented in the paper.
This document contains the overall instruction as well as description of the content of the repository.
Details regarding particular stages are documented within source files as comments.
Models for assessing empowerment through public policies in rural areas in Brazil
Marcos Aurélio Santos da Silva | Published Monday, April 08, 2019Brazil has initiated two territorial public policies for a rural sustainable development, the National Program for Sustainable Development of the Rural Territories (PRONAT) and Citizenship Territory Program (PTC). These public policies aims, as a condition for its effectiveness, the equilibrium of the power relations between actors which participate in the Collegiate for Territorial Development (CODETER) of each Rural Territory. Our research studies the hypotheses that, in the Rural Territories submitted to the PRONAT and PTC public policies, the power and reciprocity relations between actors engaged in the CODETER effectively have evolved in favor of the civil society representatives to the detriment of the public powers, notably the mayors.
The SocLab approach has been applied in two case studies and four models representing the Southern Rural Territory of Sergipe (TRSS) and the São Francisco Rural Territory (TRBSF) were designed for two referential periods, 2008-2012 and 2013-2017. These models were developed to evaluate the empowerment of the civil society in these rural territories due to thes two public policies, PRONAT and PTC.
Peer Review Game
Giangiacomo Bravo Flaminio Squazzoni Francisco Grimaldo Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, April 30, 2018NetLogo software for the Peer Review Game model. It represents a population of scientists endowed with a proportion of a fixed pool of resources. At each step scientists decide how to allocate their resources between submitting manuscripts and reviewing others’ submissions. Quality of submissions and reviews depend on the amount of allocated resources and biased perception of submissions’ quality. Scientists can behave according to different allocation strategies by simply reacting to the outcome of their previous submission process or comparing their outcome with published papers’ quality. Overall bias of selected submissions and quality of published papers are computed at each step.
Displaying 10 of 15 results sociology clear search