About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1256 results
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
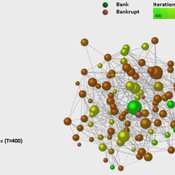
Dynamic Interbank Network Simulator
Valentina Guleva | Published Wednesday, November 23, 2016 | Last modified Monday, April 13, 2020The model provides instruments for the simulation of interbank network evolution. There are tools for dynamic network analysis, allowing to evaluate graph topological invariants, thermodynamic network features and combinational node-based features.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
Cooperation Under Resources Pressure (CURP)
María Pereda José Manuel Galán Ordax José Santos | Published Monday, November 21, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018This is an agent-based model designed to explore the evolution of cooperation under changes in resources availability for a given population
Peer reviewed AgentEx
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Caroline Schill Therese Lindahl | Published Sunday, November 13, 2016AgentEx aims to advance understanding of group processes for sustainable management of a common pool resource (CPR). By supporting the development and test explanations of cooperation and sustainable exploitation.
Peninsula_Iberica 1.0
Carolina Cucart-Mora Sergi Lozano Javier Fernández-López De Pablo | Published Friday, November 04, 2016 | Last modified Monday, November 27, 2017This model was build to explore the bio-cultural interaction between AMH and Neanderthals during the Middle to Upper Paleolithic Transition in the Iberian Peninsula
Urban Sprawl and Income segregation with effect from income level and inequality
Nina Schwarz Cheng Guo Carsten M Buchmann | Published Tuesday, November 01, 2016 | Last modified Friday, May 26, 2017This is a stylized model based on Alonso’s model investigating the relationship between urban sprawl and income segregation.
Bicycle encounter model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
Salzburg Bicycle model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016An ABM to simulate the spatio-temporal distribution of cyclists across the road network of the city of Salzburg.
Homing pigeon model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016This model represents the flight paths of a flock of homing pigeons according to their flocking-, orientation- and leadership behaviour.
Displaying 10 of 1256 results