About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 113 results random clear search
Seasonal Social Networks and Learning Opportunities Under Unbiased Cultural Transmission
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Monday, May 18, 2015This agent-based model examines the impact of seasonal aggregation, dispersion, and learning opportunities on the richness and evenness of artifact styles under random social learning (unbiased transmission).
Environmental uncertainty affects the optimal structure of information-sharing networks
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt | Published Monday, March 16, 2015We used a computer simulation to measure how well different network structures (fully connected, small world, lattice, and random) find and exploit resource peaks in a variable environment.
Netlogo Profiler code example
Colin Wren | Published Wednesday, March 04, 2015This is a very simple foraging model used to illustrate the features of Netlogo’s Profiler extension.
A Model of Iterated Ultimatum game
Andrea Scalco | Published Tuesday, February 24, 2015 | Last modified Monday, March 09, 2015The simulation generates two kinds of agents, whose proposals are generated accordingly to their selfish or selfless behaviour. Then, agents compete in order to increase their portfolio playing the ultimatum game with a random-stranger matching.
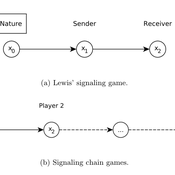
Lewis' Signaling Chains
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
Demographic microsimulation for individuals and couples
Sabine Zinn | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015The simulation model conducts fine-grained population projection by specifying life course dynamics of individuals and couples by means of traditional demographic microsimulation and by using agent-based modeling for mate matching.
Effect of communication in irrigation games
Jacopo A. Baggio Marco Janssen | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, August 09, 2017The model includes different formulations how agents make decisions in irrigation games and this is compared with empirical data. The aim is to test different theoretical models, especially explaining effect of communication.
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
In-group favoritism due to friend selection strategies based on fixed tag and within-group reputation
Yutaka Nakai | Published Friday, March 28, 2014 | Last modified Friday, March 28, 2014An agent-based model simulates emergence of in-group favoritism. Agents adopt friend selection strategies using an invariable tag and reputations meaning how cooperative others are to a group. The reputation can be seen as a kind of public opinion.
Opinion Dynamics Under Intergroup Conflict Escalation
Meysam Alizadeh Alin Coman Michael Lewis Katia Sycara | Published Friday, March 14, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, October 29, 2014We develop an agent-based model to explore the effect of perceived intergroup conflict escalation on the number of extremists. The proposed model builds on the 2D bounded confidence model proposed by Huet et al (2008).
Displaying 10 of 113 results random clear search