About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 101 results #R clear search
Peer reviewed Population Genetics
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, September 09, 2020This model simulates the mechanisms of evolution, or how allele frequencies change in a population over time.
Peer reviewed Dawkins Weasel
Kristin Crouse | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Wednesday, January 28, 2026Dawkins’ Weasel is a NetLogo model that illustrates the principle of evolution by natural selection. It is inspired by a thought experiment presented by Richard Dawkins in his book The Blind Watchmaker (1996).
Network formation on a two-layer multiplex with shocks
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, November 27, 2017A dynamic model of social network formation on single-layer and multiplex networks with structural incentives that vary over time.
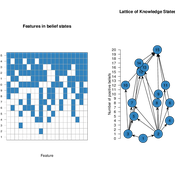
Knowledge Space Model for Opinion Dynamics
Shane Mueller | Published Thursday, September 28, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, September 20, 2018Knowledge Space model of Opinion Dynamics.
Harvesting daisies in Daisyworld
Marco Janssen | Published Saturday, July 22, 2017Comparing impact of alternative behavioral theories in a simple social-ecological system.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
Success bias imitation increases the probability of effectively dealing with ecological disturbances
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018This model aims to investigate how different type of learning (social system) and disturbance specific attributes (ecological system) influence adoption of treatment strategies to treat the effects of ecological disturbances.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
Increased costs of cooperation help cooperators in the long run
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, March 01, 2017A spatial prisoner’s dilemma model with mobile agents, de-coupled birth-death events, and harsh environments.
Displaying 10 of 101 results #R clear search