About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 97 results for "Ricardo Del Olmo" clear search
Cellular automata model of social networks
Rubens de Almeida Zimbres | Published Tuesday, August 02, 2022This project was developed during the Santa Fe course Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling 2022. The origin is a Cellular Automata (CA) model to simulate human interactions that happen in the real world, from Rubens and Oliveira (2009). These authors used a market research with real people in two different times: one at time zero and the second at time zero plus 4 months (longitudinal market research). They developed an agent-based model whose initial condition was inherited from the results of the first market research response values and evolve it to simulate human interactions with Agent-Based Modeling that led to the values of the second market research, without explicitly imposing rules. Then, compared results of the model with the second market research. The model reached 73.80% accuracy.
In the same way, this project is an Exploratory ABM project that models individuals in a closed society whose behavior depends upon the result of interaction with two neighbors within a radius of interaction, one on the relative “right” and other one on the relative “left”. According to the states (colors) of neighbors, a given cellular automata rule is applied, according to the value set in Chooser. Five states were used here and are defined as levels of quality perception, where red (states 0 and 1) means unhappy, state 3 is neutral and green (states 3 and 4) means happy.
There is also a message passing algorithm in the social network, to analyze the flow and spread of information among nodes. Both the cellular automaton and the message passing algorithms were developed using the Python extension. The model also uses extensions csv and arduino.
Shellmound Mobility
Henrique de Sena Kozlowski | Published Saturday, June 15, 2024Least Cost Path (LCP) analysis is a recurrent theme in spatial archaeology. Based on a cost of movement image, the user can interpret how difficult it is to travel around in a landscape. This kind of analysis frequently uses GIS tools to assess different landscapes. This model incorporates some aspects of the LCP analysis based on GIS with the capabilities of agent-based modeling, such as the possibility to simulate random behavior when moving. In this model the agent will travel around the coastal landscape of Southern Brazil, assessing its path based on the different cost of travel through the patches. The agents represent shellmound builders (sambaquieiros), who will travel mainly through the use of canoes around the lagoons.
How it works?
When the simulation starts the hiker agent moves around the world, a representation of the lagoon landscape of the Santa Catarina state in Southern Brazil. The agent movement is based on the travel cost of each patch. This travel cost is taken from a cost surface raster created in ArcMap to represent the different cost of movement around the landscape. Each tick the agent will have a chance to select the best possible patch to move in its Field of View (FOV) that will take it towards its target destination. If it doesn’t select the best possible patch, it will randomly choose one of the patches to move in its FOV. The simulation stops when the hiker agent reaches the target destination. The elevation raster file and the cost surface map are based on a 1 Arc-second (30m) resolution SRTM image, scaled down 5 times. Each patch represents a square of 150m, with an area of 0,0225km². The dataset uses a UTM Sirgas 2000 22S projection system. There are four different cost functions available to use. They change the cost surface used by the hikers to navigate around the world.
Shellmound Trade
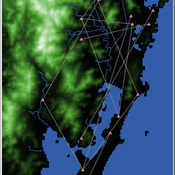
Henrique de Sena Kozlowski | Published Saturday, June 15, 2024This model simulates different trade dynamics in shellmound (sambaqui) builder communities in coastal Southern Brazil. It features two simulation scenarios, one in which every site is the same and another one testing different rates of cooperation. The purpose of the model is to analyze the networks created by the trade dynamics and explore the different ways in which sambaqui communities were articulated in the past.
How it Works?
There are a few rules operating in this model. In either mode of simulation, each tick the agents will produce an amount of resources based on the suitability of the patches inside their occupation-radius, after that the procedures depend on the trade dynamic selected. For BRN? the agents will then repay their owed resources, update their reputation value and then trade again if they need to. For GRN? the agents will just trade with a connected agent if they need to. After that the agents will then consume a random amount of resources that they own and based on that they will grow (split) into a new site or be removed from the simulation. The simulation runs for 1000 ticks. Each patch correspond to a 300x300m square of land in the southern coast of Santa Catarina State in Brazil. Each agent represents a shellmound (sambaqui) builder community. The data for the world were made from a SRTM raster image (1 arc-second) in ArcMap. The sites can be exported into a shapefile (.shp) vector to display in ArcMap. It uses a UTM Sirgas 2000 22S projection system.
Generic servicising model (SPREE project)
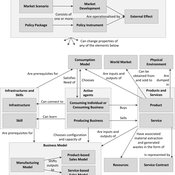
Igor Nikolic Reinier Van Der Veen Kasper H Kisjes | Published Wednesday, August 26, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, September 28, 2016This generic agent-based model allows the user to simulate and explore the influence of servicising policies on the uptake of servicising and on economic, environmental and social effects, notably absolute decoupling.
AMMA: Agent-based Model of the Media Arena
Annie Waldherr | Published Tuesday, February 11, 2014The AMMA simulates how news waves emerge in the mass media. Drawing on the ideas of public arena models and issue-attention cycles, it represents fundamental principles of public communication in a virtual media system.
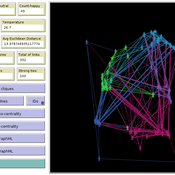
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
Recycling behavior of Chinese households
Igor Nikolic B Dijkhuizen M Van Den Hoven M Minderhoud N Wäckerlin | Published Monday, June 19, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, March 29, 2018The model represents empirically observed recycling behaviour of Chinese citizens, based on the theory of reasoned action (TRA), the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) and the theory of planned behaviour extended with situational factors (TPB+).
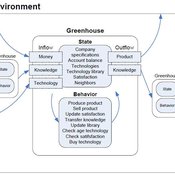
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
MCR Model
Davide Secchi Nuno R Barros De Oliveira | Published Friday, July 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, January 23, 2021The aim of the model is to define when researcher’s assumptions of dependence or independence of cases in multiple case study research affect the results — hence, the understanding of these cases.
Demographic microsimulation for individuals and couples
Sabine Zinn | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015The simulation model conducts fine-grained population projection by specifying life course dynamics of individuals and couples by means of traditional demographic microsimulation and by using agent-based modeling for mate matching.
Displaying 10 of 97 results for "Ricardo Del Olmo" clear search