About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 810 results for "Jon Solera" clear search
MERCURY extension: transport-cost
Tom Brughmans | Published Monday, July 23, 2018This is extended version of the MERCRUY model (Brughmans 2015) incorporates a ‘transport-cost’ variable, and is otherwise unchanged. This extended model is described in this publication: Brughmans, T., 2019. Evaluating the potential of computational modelling for informing debates on Roman economic integration, in: Verboven, K., Poblome, J. (Eds.), Structural Determinants in the Roman World.
Brughmans, T., 2015. MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East. CoMSES Comput. Model Libr. URL https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/
FeedUS - A global food trade model
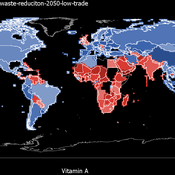
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, February 26, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the impact of global food trade on food and nutrition security in countries around the world. It will incorporate three main aspects of trade between countries, including a country’s wealth, geographic location, and its trade relationships with other countries (past and ongoing), and can be used to study food and nutrition security across countries in various scenarios, such as climate change, sustainable intensification, waste reduction and dietary change.
Introductory SIR Model
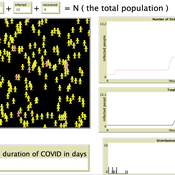
Kit Martin Amber Cesare Matthew Johnson | Published Tuesday, September 28, 2021This is a basic Susceptible, Infected, Recovered (SIR) model. This model explores the spread of disease in a space. In particular, it explores how changing assumptions about the number of susceptible people, starting number of infected people, as well as the disease’s infection probability, and average duration of infection. The model shows that the interactions of agents can drastically affect the results of the model.
We used it in our course on COVID-19: https://www.csats.psu.edu/science-of-covid19
Toward Market Structure as a Complex System: A Web Based Simulation Assignment Implemented in Netlogo
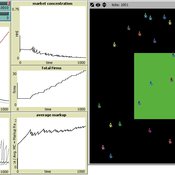
Timothy Kochanski | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the model for a paper that is based on a simulation model, programmed in Netlogo, that demonstrates changes in market structure that occur as marginal costs, demand, and barriers to entry change. Students predict and observe market structure changes in terms of number of firms, market concentration, market price and quantity, and average marginal costs, profits, and markups across the market as firms innovate. By adjusting the demand growth and barriers to entry, students can […]
FOUR SEASONS
Lars G Spang | Published Tuesday, March 28, 2017Butterflies (turtles) goes through metamorphism and moves to corresponding patches each season of the year. The number of years and seasons are monitored.
word-of-mouth dynamics with information seeking
Samuel Thiriot | Published Wednesday, October 24, 2018Studies on word-of-mouth identify two behaviors leading to transmission of information between individuals: proactive transmission of information, and information seeking. Individuals who are aware might be curious of it and start seeking for information; they might find around them the expertise held by another individual. Field studies indicate individuals do not adopt an innovation if they don’t hold the corresponding expertise. This model describes this information seeking behavior, and enables the exploration of the dynamics which emerges out of it.
PowerGen-ABM
Muhammad Indra Al Irsyad Anthony Halog Rabindra Nepal Deddy Priatmodjo Koesrindartoto | Published Sunday, August 04, 2019PowerGen-ABM is an optimisation model for power plant expansions from 2010 to 2025 with Indonesian electricity systems as the case study. PowerGen-ABM integrates three approaches: techno-economic analysis (TEA), linear programming (LP), and input-output analysis (IOA) and environmental analysis. TEA is based on the revenue requirement (RR) formula by UCDavis (2016), and the environmental analysis accounts for resource consumption (i.e., steel, concrete, aluminium, and energy) and carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions during the construction and operational stages of power plants.
Peer reviewed The dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance: A simulation of the self-organising task allocation process
Shaoni Wang | Published Tuesday, October 05, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance when focusing on self-organizing task allocation. For this, we develop a model that formalizes Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) theory into an ABM creating a framework to study the social dynamics that pertain to the mutual relations between the individual and group level of team performance. Specifically, it aims to answer how the three individual motivations of autonomy, competence, and belonging affect team performance.
The role of dispersal, selection intensity, and extirpation risk in resilience to climate change: a trait-based modeling approach
Jessica Mo P. David Polly | Published Monday, February 07, 2022This NetLogo model simulates trait-based biotic responses to climate change in an environmentally heterogeneous continent in an evolving clade, the species of which are each represented by local populations that disperse and interbreed; they also are subject to selection, genetic drift, and local extirpation. We simulated mammalian herbivores, whose success depends on tooth crown height, vegetation type, precipitation and grit. This model investigates the role of dispersal, selection, extirpation, and other factors contribute to resilience under three climate change scenarios.
ADAM: Agent-based Demand and Assignment Model
D Levinson | Published Monday, August 29, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The core algorithm is an agent-based model, which simulates travel patterns on a network based on microscopic decision-making by each traveler.
Displaying 10 of 810 results for "Jon Solera" clear search