About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 96 results for "B Dijkhuizen" clear search
03 MppLab V1.09 – Maximum Power Principle Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Using webs of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, we explore implications of the Maximum Power Principle. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
Rebel Group Protection Rackets
Gerd Wagner Luis Gustavo Nardin Kamil C. Klosek Frances Duffy | Published Wednesday, December 04, 2019System Narrative
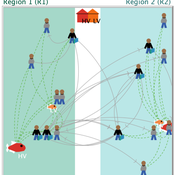
How do rebel groups control territory and engage with the local economy during civil war? Charles Tilly’s seminal War and State Making as Organized Crime (1985) posits that the process of waging war and providing governance resembles that of a protection racket, in which aspiring governing groups will extort local populations in order to gain power, and civilians or businesses will pay in order to ensure their own protection. As civil war research increasingly probes the mechanisms that fuel local disputes and the origination of violence, we develop an agent-based simulation model to explore the economic relationship of rebel groups with local populations, using extortion racket interactions to explain the dynamics of rebel fighting, their impact on the economy, and the importance of their economic base of support. This analysis provides insights for understanding the causes and byproducts of rebel competition in present-day conflicts, such as the cases of South Sudan, Afghanistan, and Somalia.
Model Description
The model defines two object types: RebelGroup and Enterprise. A RebelGroup is a group that competes for power in a system of anarchy, in which there is effectively no government control. An Enterprise is a local civilian-level actor that conducts business in this environment, whose objective is to make a profit. In this system, a RebelGroup may choose to extort money from Enterprises in order to support its fighting efforts. It can extract payments from an Enterprise, which fears for its safety if it does not pay. This adds some amount of money to the RebelGroup’s resources, and they can return to extort the same Enterprise again. The RebelGroup can also choose to loot the Enterprise instead. This results in gaining all of the Enterprise wealth, but prompts the individual Enterprise to flee, or leave the model. This reduces the available pool of Enterprises available to the RebelGroup for extortion. Following these interactions the RebelGroup can choose to AllocateWealth, or pay its rebel fighters. Depending on the value of its available resources, it can add more rebels or expel some of those which it already has, changing its size. It can also choose to expand over new territory, or effectively increase its number of potential extorting Enterprises. As a response to these dynamics, an Enterprise can choose to Report expansion to another RebelGroup, which results in fighting between the two groups. This system shows how, faced with economic choices, RebelGroups and Enterprises make decisions in war that impact conflict and violence outcomes.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
Modeling the Emergence of Riots
Andrew Crooks Bianica Pires | Published Wednesday, January 20, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 21, 2016The purpose of the model is to explore how the unique socioeconomic variables underlying Kibera, local interactions, and the spread of a rumor, may trigger a riot.
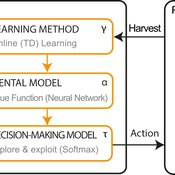
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
01a ModEco V2.05 – Model Economies – In C++
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, February 04, 2013 | Last modified Friday, April 14, 2017Perpetual Motion Machine - A simple economy that operates at both a biophysical and economic level, and is sustainable. The goal: to determine the necessary and sufficient conditions of sustainability, and the attendant necessary trade-offs.
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
Peer reviewed Small-Trade Model
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Blanca Gonzalez-Mon Örjan Bodin | Published Wednesday, July 28, 2021The purpose of this model is to understand the role of trade networks and their interaction with different fish resources, for fish provision. The model is developed based on a multi-methods approach, combining agent-based modeling, network analysis and qualitative data based on a small-scale fisheries study case. The model can be used to investigate both how trade network structures are embedded in a social-ecological context and the trade processes that occur within them, to analyze how they lead to emergent outcomes related to the resilience of fish provision. The model processes are informed by qualitative data analysis, and the social network analysis of an empirical fish trade network. The network analysis can be used to investigate diverse network structures to perform model experiments, and their influence on model outcomes.
The main outcomes we study are 1) the overexploitation of fish resources and 2) the availability and variability of fish provision to satisfy different market demands, and 3) individual traders’ fish supply at the micro-level. The model has two types of trader agents, seller and dealer. The model reveals that the characteristics of the trade networks, linked to different trader types (that have different roles in those networks), can affect the resilience of fish provision.
Displaying 10 of 96 results for "B Dijkhuizen" clear search