About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search
Opinion Dynamics Under Intergroup Conflict Escalation
Meysam Alizadeh Alin Coman Michael Lewis Katia Sycara | Published Friday, March 14, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, October 29, 2014We develop an agent-based model to explore the effect of perceived intergroup conflict escalation on the number of extremists. The proposed model builds on the 2D bounded confidence model proposed by Huet et al (2008).
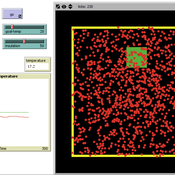
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
Collective Behavior of In-group Favoritism
Meysam Alizadeh Andrew Crooks Claudio Cioffi-Revilla | Published Tuesday, September 01, 2015We investigate the interplay of homophily, differentiation, and in-group cooperation mechanisms on the formation of opinion clusters and emergence of radical opinions.
The Informational Dynamics of Regime Change
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Saturday, October 07, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, January 14, 2020We model the epistemic dynamics preceding political uprising. Before deciding whether to start protests, agents need to estimate the amount of discontent with the regime. This model simulates the dynamics of group knowledge about general discontent.
Exploring the Effects of Link Recommendations on Social Networks
Andrew Crooks Ciara Sibley | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020The purpose of this model is explore how “friend-of-friend” link recommendations, which are commonly used on social networking sites, impact online social network structure. Specifically, this model generates online social networks, by connecting individuals based upon varying proportions of a) connections from the real world and b) link recommendations. Links formed by recommendation mimic mutual connection, or friend-of-friend algorithms. Generated networks can then be analyzed, by the included scripts, to assess the influence that different proportions of link recommendations have on network properties, specifically: clustering, modularity, path length, eccentricity, diameter, and degree distribution.
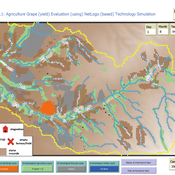
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
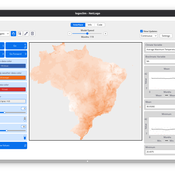
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
COMM-PDND: Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks
Lars Reinelt | Published Friday, September 08, 2023The Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks (COMM-PDND) is an agent-based model specifically created to examine the dynamics of perceived descriptive norms in the context of digital network structures. The model, developed as part of a master’s thesis titled “The Dynamics of Perceived Descriptive Norms in Digital Network Publics: An Agent-Based Simulation,” emphasizes the critical role of communication processes in norm formation. It focuses on the role of communicative interactions in shaping perceived descriptive norms.
The COMM-PDND is tuned to explore the effects of normative deviance in digital social networks. It provides functionalities for manipulating agents according to their network position, and has a versatile set of customizable parameters, making it adaptable to a wide range of research contexts.
Effect of communication in irrigation games
Jacopo A. Baggio Marco Janssen | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, August 09, 2017The model includes different formulations how agents make decisions in irrigation games and this is compared with empirical data. The aim is to test different theoretical models, especially explaining effect of communication.
Walk Away in groups
Athena Aktipis | Published Thursday, March 17, 2016This NetLogo model implements the Walk Away strategy in a spatial public goods game, where individuals have the ability to leave groups with insufficient levels of cooperation.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search