About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 204 results for "M Vavier" clear search
Peer reviewed A Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE)-informed ABM for pedestrian evacuation in different constricted spaces
Jiaqi Ge Yiyu Wang Alexis Comber | Published Wednesday, October 11, 2023This BNE-informed ABM ultimately aims to provide a more realistic description of complicated pedestrian behaviours especially in high-density and life-threatening situations. Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) was adopted to reproduce interactive decision-making process among rational and game-playing agents. The implementations of 3 behavioural models, which are Shortest Route (SR) model, Random Follow (RF) model, and BNE model, make it possible to simulate emergent patterns of pedestrian behaviours (e.g. herding and self-organised queuing behaviours, etc.) in emergency situations.
According to the common features of previous mass trampling accidents, a series of simulation experiments were performed in space with 3 types of barriers, which are Horizontal Corridors, Vertical Corridors, and Random Squares, standing for corridors, bottlenecks and intersections respectively, to investigate emergent behaviours of evacuees in varied constricted spatial environments. The output of this ABM has been available at https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/9v4byyvgxh/1.
This is the final version of the model. To simulate the normative dynamics we used the EmIL (EMergence In the Loop) Framework which was kindly provided by Ulf Lotzmann. http://cfpm.org/EMIL-D5.1.pdf
Resource distribution effects on optimal foraging theory
Marco Janssen Kim Hill | Published Friday, January 27, 2017The original Ache model is used to explore different distributions of resources on the landscape and it’s effect on optimal strategies of the camps on hunting and camp movement.
Model of communication between two groups of managers in the course of project implementation
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Monday, December 07, 2020This is a simulation model of communication between two groups of managers in the course of project implementation. The “world” of the model is a space of interaction between project participants, each of which belongs either to a group of work performers or to a group of customers. Information about the progress of the project is publicly available and represents the deviation Earned value (EV) from the planned project value (cost baseline).
The key elements of the model are 1) persons belonging to a group of customers or performers, 2) agents that are communication acts. The life cycle of persons is equal to the time of the simulation experiment, the life cycle of the communication act is 3 periods of model time (for the convenience of visualizing behavior during the experiment). The communication act occurs at a specific point in the model space, the coordinates of which are realized as random variables. During the experiment, persons randomly move in the model space. The communication act involves persons belonging to a group of customers and a group of performers, remote from the place of the communication act at a distance not exceeding the value of the communication radius (MaxCommRadius), while at least one representative from each of the groups must participate in the communication act. If none are found, the communication act is not carried out. The number of potential communication acts per unit of model time is a parameter of the model (CommPerTick).
The managerial sense of the feedback is the stimulating effect of the positive value of the accumulated communication complexity (positive background of the project implementation) on the productivity of the performers. Provided there is favorable communication (“trust”, “mutual understanding”) between the customer and the contractor, it is more likely that project operations will be performed with less lag behind the plan or ahead of it.
The behavior of agents in the world of the model (change of coordinates, visualization of agents’ belonging to a specific communicative act at a given time, etc.) is not informative. Content data are obtained in the form of time series of accumulated communicative complexity, the deviation of the earned value from the planned value, average indicators characterizing communication - the total number of communicative acts and the average number of their participants, etc. These data are displayed on graphs during the simulation experiment.
The control elements of the model allow seven independent values to be varied, which, even with a minimum number of varied values (three: minimum, maximum, optimum), gives 3^7 = 2187 different variants of initial conditions. In this case, the statistical processing of the results requires repeated calculation of the model indicators for each grid node. Thus, the set of varied parameters and the range of their variation is determined by the logic of a particular study and represents a significant narrowing of the full set of initial conditions for which the model allows simulation experiments.
…
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
SLUCEII LUXE (Land Use in an eXurban Environment)
Qingxu Huang Rick L Riolo Shipeng Sun Derek Robinson Dawn Parker Tatiana Filatova Meghan Hutchins Dan Brown | Published Tuesday, September 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, October 22, 2022LUXE is a land-use change model featuring different levels of land market implementation. It integrates utility measures, budget constraints, competitive bidding, and market interactions to model land-use change in exurban environment.
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
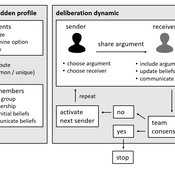
Agent-based model of team decision-making in hidden profile situations
Andreas Flache Jonas Stein Vincenz Frey | Published Thursday, April 20, 2023 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2023The model presented here is extensively described in the paper ‘Talk less to strangers: How homophily can improve collective decision-making in diverse teams’ (forthcoming at JASSS). A full replication package reproducing all results presented in the paper is accessible at https://osf.io/76hfm/.
Narrative documentation includes a detailed description of the model, including a schematic figure and an extensive representation of the model in pseudocode.
The model develops a formal representation of a diverse work team facing a decision problem as implemented in the experimental setup of the hidden-profile paradigm. We implement a setup where a group seeks to identify the best out of a set of possible decision options. Individuals are equipped with different pieces of information that need to be combined to identify the best option. To this end, we assume a team of N agents. Each agent belongs to one of M groups where each group consists of agents who share a common identity.
The virtual teams in our model face a decision problem, in that the best option out of a set of J discrete options needs to be identified. Every team member forms her own belief about which decision option is best but is open to influence by other team members. Influence is implemented as a sequence of communication events. Agents choose an interaction partner according to homophily h and take turns in sharing an argument with an interaction partner. Every time an argument is emitted, the recipient updates her beliefs and tells her team what option she currently believes to be best. This influence process continues until all agents prefer the same option. This option is the team’s decision.
Parental choices, children's skills, and skill inequality: An agent-based model implemented in Python
Andrés Cardona | Published Thursday, October 30, 2014The model explores the emergence of inequality in cognitive and socio-emotional skills at the societal level within and across generations that results from differences in parental investment behavior during childhood and adolescence.
Peer reviewed Lithic Raw Material Procurement and Provisioning
Jonathan Paige | Published Friday, March 06, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015This model simulates the lithic raw material use and provisioning behavior of a group that inhabits a permanent base camp, and uses stone tools.
Displaying 10 of 204 results for "M Vavier" clear search