About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 52 results for "Iris Jmm Boumans" clear search
Peer reviewed General Housing Model
J M Applegate | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020The General Housing Model demonstrates a basic housing market with bank lending, renters, owners and landlords. This model was developed as a base to which students contributed additional functions during Arizona State University’s 2020 Winter School: Agent-Based Modeling of Social-Ecological Systems.
Peer reviewed Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders
J M Applegate | Published Saturday, September 11, 2021A curious aspect of the Covid-19 pandemic is the clustering of outbreaks. Evidence suggests that 80\% of people who contract the virus are infected by only 19% of infected individuals, and that the majority of infected individuals faile to infect another person. Thus, the dispersion of a contagion, $k$, may be of more use in understanding the spread of Covid-19 than the reproduction number, R0.
The Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders model, written in NetLogo, is an adaptation of the canonical Virus Transmission on a Network model and allows the exploration of various mitigation protocols such as testing and quarantines with both homogenous transmission and heterogenous transmission.
The model consists of a population of individuals arranged in a network, where both population and network degree are tunable. At the start of the simulation, a subset of the population is initially infected. As the model runs, infected individuals will infect neighboring susceptible individuals according to either homogenous or heterogenous transmission, where heterogenous transmission models super-spreaders. In this case, k is described as the percentage of super-spreaders in the population and the differing transmission rates for super-spreaders and non super-spreaders. Infected individuals either recover, at which point they become resistant to infection, or die. Testing regimes cause discovered infected individuals to quarantine for a period of time.
Peer reviewed Modern Wage Dynamics
J M Applegate | Published Sunday, June 05, 2022The Modern Wage Dynamics Model is a generative model of coupled economic production and allocation systems. Each simulation describes a series of interactions between a single aggregate firm and a set of households through both labour and goods markets. The firm produces a representative consumption good using labour provided by the households, who in turn purchase these goods as desired using wages earned, thus the coupling.
Each model iteration the firm decides wage, price and labour hours requested. Given price and wage, households decide hours worked based on their utility function for leisure and consumption. A labour market construct chooses the minimum of hours required and aggregate hours supplied. The firm then uses these inputs to produce goods. Given the hours actually worked, the households decide actual consumption and a market chooses the minimum of goods supplied and aggregate demand. The firm uses information gained through observing market transactions about consumption demand to refine their conceptions of the population’s demand.
The purpose of this model is to explore the general behaviour of an economy with coupled production and allocation systems, as well as to explore the effects of various policies on wage and production, such as minimum wage, tax credits, unemployment benefits, and universal income.
…
Peer reviewed Strategy with Externalities
J M Applegate Glenn Hoetker | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017The SWE models firms search behaviour as the performance landscape shifts. The shift represents society’s pricing of negative externalities, and the performance landscape is an NK structure. The model is written in NetLogo.
Peer reviewed Empathy & Power
J M Applegate Ned Wellman | Published Monday, November 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, December 21, 2017The purpose of this model is to explore the effects of different power structures on a cross-functional team’s prosocial decision making. Are certain power distributions more conducive to the team making prosocial decisions?
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
Peer reviewed AgModel
Isaac Ullah | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AgModel is an agent-based model of the forager-farmer transition. The model consists of a single software agent that, conceptually, can be thought of as a single hunter-gather community (i.e., a co-residential group that shares in subsistence activities and decision making). The agent has several characteristics, including a population of human foragers, intrinsic birth and death rates, an annual total energy need, and an available amount of foraging labor. The model assumes a central-place foraging strategy in a fixed territory for a two-resource economy: cereal grains and prey animals. The territory has a fixed number of patches, and a starting number of prey. While the model is not spatially explicit, it does assume some spatiality of resources by including search times.
Demographic and environmental components of the simulation occur and are updated at an annual temporal resolution, but foraging decisions are “event” based so that many such decisions will be made in each year. Thus, each new year, the foraging agent must undertake a series of optimal foraging decisions based on its current knowledge of the availability of cereals and prey animals. Other resources are not accounted for in the model directly, but can be assumed for by adjusting the total number of required annual energy intake that the foraging agent uses to calculate its cereal and prey animal foraging decisions. The agent proceeds to balance the net benefits of the chance of finding, processing, and consuming a prey animal, versus that of finding a cereal patch, and processing and consuming that cereal. These decisions continue until the annual kcal target is reached (balanced on the current human population). If the agent consumes all available resources in a given year, it may “starve”. Starvation will affect birth and death rates, as will foraging success, and so the population will increase or decrease according to a probabilistic function (perturbed by some stochasticity) and the agent’s foraging success or failure. The agent is also constrained by labor caps, set by the modeler at model initialization. If the agent expends its yearly budget of person-hours for hunting or foraging, then the agent can no longer do those activities that year, and it may starve.
Foragers choose to either expend their annual labor budget either hunting prey animals or harvesting cereal patches. If the agent chooses to harvest prey animals, they will expend energy searching for and processing prey animals. prey animals search times are density dependent, and the number of prey animals per encounter and handling times can be altered in the model parameterization (e.g. to increase the payoff per encounter). Prey animal populations are also subject to intrinsic birth and death rates with the addition of additional deaths caused by human predation. A small amount of prey animals may “migrate” into the territory each year. This prevents prey animals populations from complete decimation, but also may be used to model increased distances of logistic mobility (or, perhaps, even residential mobility within a larger territory).
…
The role of dispersal, selection intensity, and extirpation risk in resilience to climate change: a trait-based modeling approach
Jessica Mo P. David Polly | Published Monday, February 07, 2022This NetLogo model simulates trait-based biotic responses to climate change in an environmentally heterogeneous continent in an evolving clade, the species of which are each represented by local populations that disperse and interbreed; they also are subject to selection, genetic drift, and local extirpation. We simulated mammalian herbivores, whose success depends on tooth crown height, vegetation type, precipitation and grit. This model investigates the role of dispersal, selection, extirpation, and other factors contribute to resilience under three climate change scenarios.
Model of Rental Evictions in Phoenix During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Sean Bergin J M Applegate | Published Saturday, July 31, 2021 | Last modified Friday, October 15, 2021The purpose of this model is to explore the dynamics of residency and eviction for households renting in the greater Phoenix (Arizona) metropolitan area. The model uses a representative population of renters modified from American Community Survey (ACS) data that includes demographic, housing and economic information. Each month, households pay their subsistence, rental and utility bills. If a household is unable to pay their monthly rent or utility bill they apply for financial assistance. This model provides a platform to understand the impact of various economic shock upon households. Also, the model includes conditions that occurred as a result of the Covid-19 pandemic which allows for the study of eviction mitigation strategies that were employed, such as the eviction moratorium and stimulus payments. The model allows us to make preliminary predictions concerning the number of households that may be evicted once the moratorium on evictions ends and the long-term effects on the number of evicted households in the greater Phoenix area going forward.
Peer reviewed The Indus Village's Weather model: procedural generation of daily weather
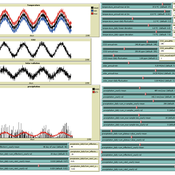
Andreas Angourakis | Published Tuesday, May 13, 2025Overview
The Weather model is a procedural generation model designed to create realistic daily weather data for socioecological simulations. It generates synthetic weather time series for solar radiation, temperature, and precipitation using algorithms based on sinusoidal and double logistic functions. The model incorporates stochastic variation to mimic unpredictable weather patterns and aims to provide realistic yet flexible weather inputs for exploring diverse climate scenarios.
The Weather model can be used independently or integrated into larger models, providing realistic weather patterns without extensive coding or data collection. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, enabling users to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and have greater confidence in their applications.
…
Displaying 10 of 52 results for "Iris Jmm Boumans" clear search