About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 226 results for "G M Leighton" clear search
Lake Anderson Revisited II
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Monday, June 28, 2021The purpose of this study is another agent-based replication of a System Dynamics model (Anderson,1973) where he analysed the dynamics of nutrient, biomass, oxygen and detritus in a model lake under conditions of artificial fertilising and policies to deal with the consequences of artificial fertilising.. A first replication (Möhring & Troitzsch,2001) added those agents to the original model that were necessary to move the role of the experimenter into the model, whereas this replication replaces the original lake with a collection of small elements between which biomass, nurtrents and oxygen are exchanged, adds rivers upstream and downstream as well as adjacent land divided into villages and populated with farms and industrial plants run by individual persons.
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
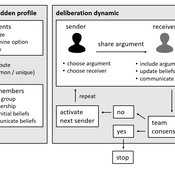
Agent-based model of team decision-making in hidden profile situations
Andreas Flache Jonas Stein Vincenz Frey | Published Thursday, April 20, 2023 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2023The model presented here is extensively described in the paper ‘Talk less to strangers: How homophily can improve collective decision-making in diverse teams’ (forthcoming at JASSS). A full replication package reproducing all results presented in the paper is accessible at https://osf.io/76hfm/.
Narrative documentation includes a detailed description of the model, including a schematic figure and an extensive representation of the model in pseudocode.
The model develops a formal representation of a diverse work team facing a decision problem as implemented in the experimental setup of the hidden-profile paradigm. We implement a setup where a group seeks to identify the best out of a set of possible decision options. Individuals are equipped with different pieces of information that need to be combined to identify the best option. To this end, we assume a team of N agents. Each agent belongs to one of M groups where each group consists of agents who share a common identity.
The virtual teams in our model face a decision problem, in that the best option out of a set of J discrete options needs to be identified. Every team member forms her own belief about which decision option is best but is open to influence by other team members. Influence is implemented as a sequence of communication events. Agents choose an interaction partner according to homophily h and take turns in sharing an argument with an interaction partner. Every time an argument is emitted, the recipient updates her beliefs and tells her team what option she currently believes to be best. This influence process continues until all agents prefer the same option. This option is the team’s decision.
Online Collaboration, Competing for Attention
M Manning | Published Wednesday, July 19, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, January 24, 2019This is a model of a community of online communities. Using mechanisms such as win-stay, lose-shift, and preferential attachment the model can reproduce similar patterns to those of the Stack Exchange network.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
Peer reviewed Emergent Firms Model
J M Applegate | Published Friday, July 13, 2018The Emergent Firm (EF) model is based on the premise that firms arise out of individuals choosing to work together to advantage themselves of the benefits of returns-to-scale and coordination. The Emergent Firm (EF) model is a new implementation and extension of Rob Axtell’s Endogenous Dynamics of Multi-Agent Firms model. Like the Axtell model, the EF model describes how economies, composed of firms, form and evolve out of the utility maximizing activity on the part of individual agents. The EF model includes a cash-in-advance constraint on agents changing employment, as well as a universal credit-creating lender to explore how costs and access to capital affect the emergent economy and its macroeconomic characteristics such as firm size distributions, wealth, debt, wages and productivity.
Peer reviewed General Housing Model
J M Applegate | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020The General Housing Model demonstrates a basic housing market with bank lending, renters, owners and landlords. This model was developed as a base to which students contributed additional functions during Arizona State University’s 2020 Winter School: Agent-Based Modeling of Social-Ecological Systems.
Peer reviewed Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders
J M Applegate | Published Saturday, September 11, 2021A curious aspect of the Covid-19 pandemic is the clustering of outbreaks. Evidence suggests that 80\% of people who contract the virus are infected by only 19% of infected individuals, and that the majority of infected individuals faile to infect another person. Thus, the dispersion of a contagion, $k$, may be of more use in understanding the spread of Covid-19 than the reproduction number, R0.
The Virus Transmission with Super-spreaders model, written in NetLogo, is an adaptation of the canonical Virus Transmission on a Network model and allows the exploration of various mitigation protocols such as testing and quarantines with both homogenous transmission and heterogenous transmission.
The model consists of a population of individuals arranged in a network, where both population and network degree are tunable. At the start of the simulation, a subset of the population is initially infected. As the model runs, infected individuals will infect neighboring susceptible individuals according to either homogenous or heterogenous transmission, where heterogenous transmission models super-spreaders. In this case, k is described as the percentage of super-spreaders in the population and the differing transmission rates for super-spreaders and non super-spreaders. Infected individuals either recover, at which point they become resistant to infection, or die. Testing regimes cause discovered infected individuals to quarantine for a period of time.
Displaying 10 of 226 results for "G M Leighton" clear search