About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search
Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM)
Andrew Collins | Published Thursday, April 03, 2025The Agent-Based Model for Multiple Team Membership (ABMMTM) simulates design teams searching for viable design solutions, for a large design project that requires multiple design teams that are working simultaneously, under different organizational structures; specifically, the impact of multiple team membership (MTM). The key mechanism under study is how individual agent-level decision-making impacts macro-level project performance, specifically, wage cost. Each agent follows a stochastic learning approach, akin to simulated annealing or reinforcement learning, where they iteratively explore potential design solutions. The agent evaluates new solutions based on a random-walk exploration, accepting improvements while rejecting inferior designs. This iterative process simulates real-world problem-solving dynamics where designers refine solutions based on feedback.
As a proof-of-concept demonstration of assessing the macro-level effects of MTM in organizational design, we developed this agent-based simulation model which was used in a simulation experiment. The scenario is a system design project involving multiple interdependent teams of engineering designers. In this scenario, the required system design is split into three separate but interdependent systems, e.g., the design of a satellite could (trivially) be split into three components: power source, control system, and communication systems; each of three design team is in charge of a design of one of these components. A design team is responsible for ensuring its proposed component’s design meets the design requirement; they are not responsible for the design requirements of the other components. If the design of a given component does not affect the design requirements of the other components, we call this the uncoupled scenario; otherwise, it is a coupled scenario.
The Evolution of Tribalism: A Social-Ecological Model of Cooperation and Inter-group Conflict Under Pastoralism
Nicholas Seltzer | Published Monday, January 21, 2019This study investigates a possible nexus between inter-group competition and intra-group cooperation, which may be called “tribalism.” Building upon previous studies demonstrating a relationship between the environment and social relations, the present research incorporates a social-ecological model as a mediating factor connecting both individuals and communities to the environment. Cyclical and non-cyclical fluctuation in a simple, two-resource ecology drive agents to adopt either “go-it-alone” or group-based survival strategies via evolutionary selection. Novelly, this simulation employs a multilevel selection model allowing group-level dynamics to exert downward selective pressures on individuals’ propensity to cooperate within groups. Results suggest that cooperation and inter-group conflict are co-evolved in a triadic relationship with the environment. Resource scarcity increases inter-group competition, especially when resources are clustered as opposed to widely distributed. Moreover, the tactical advantage of cooperation in the securing of clustered resources enhanced selective pressure on cooperation, even if that implies increased individual mortality for the most altruistic warriors. Troubling, these results suggest that extreme weather, possibly as a result of climate change, could exacerbate conflict in sensitive, weather-dependent social-ecologies—especially places like the Horn of Africa where ecologically sensitive economic modalities overlap with high-levels of diversity and the wide-availability of small arms. As well, global development and foreign aid strategists should consider how plans may increase the value of particular locations where community resources are built or aid is distributed, potentially instigating tribal conflict. In sum, these factors, interacting with pre-existing social dynamics dynamics, may heighten inter-ethnic or tribal conflict in pluralistic but otherwise peaceful communities.
For special issue submission in JASSS.
A Computational Model of Workers Protest
Jae-Woo Kim | Published Friday, May 13, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013We present an agent-based model of worker protest informed by Epstein (2002). Workers have varying degrees of grievance depending on the difference between their wage and the average of their neighbors. They protest with probabilities proportional to grievance, but are inhibited by the risk of being arrested – which is determined by the ratio of coercive agents to probable rebels in the local area. We explore the effect of similarity perception on the dynamics of collective behavior. If […]
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
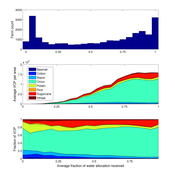
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
Agent-based model for centralized student admission process
Connie Wang Shu-Heng Chen Bin-Tzong Chi | Published Wednesday, November 04, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to match students and schools using real-world student admission mechanisms. The mechanisms in this model are serial dictatorship, deferred acceptance, the Boston mechanism, Chinese Parallel, and the Taipei mechanism.
Modeling Asian-Papuan Admixture during the Neolithic Expansion across Island Southeast Asia
Murray Cox François Vallée | Published Friday, December 09, 2016This Repast Simphony model simulates genomic admixture during the farming expansion of human groups from mainland Asia into the Papuan dominated islands of Southeast Asia during the Neolithic period.
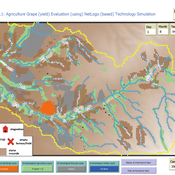
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
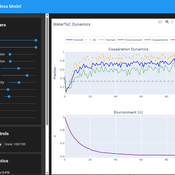
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
Peer reviewed Strategy with Externalities
J M Applegate Glenn Hoetker | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017The SWE models firms search behaviour as the performance landscape shifts. The shift represents society’s pricing of negative externalities, and the performance landscape is an NK structure. The model is written in NetLogo.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search