About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search
Models for assessing empowerment through public policies in rural areas in Brazil
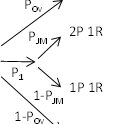
Marcos Aurélio Santos da Silva | Published Monday, April 08, 2019Brazil has initiated two territorial public policies for a rural sustainable development, the National Program for Sustainable Development of the Rural Territories (PRONAT) and Citizenship Territory Program (PTC). These public policies aims, as a condition for its effectiveness, the equilibrium of the power relations between actors which participate in the Collegiate for Territorial Development (CODETER) of each Rural Territory. Our research studies the hypotheses that, in the Rural Territories submitted to the PRONAT and PTC public policies, the power and reciprocity relations between actors engaged in the CODETER effectively have evolved in favor of the civil society representatives to the detriment of the public powers, notably the mayors.
The SocLab approach has been applied in two case studies and four models representing the Southern Rural Territory of Sergipe (TRSS) and the São Francisco Rural Territory (TRBSF) were designed for two referential periods, 2008-2012 and 2013-2017. These models were developed to evaluate the empowerment of the civil society in these rural territories due to thes two public policies, PRONAT and PTC.
Peer reviewed An IBM of a fishing fleet exploiting a pelagic resource and with a fisher management system. A preliminary version.
Paul Hart | Published Tuesday, March 19, 2024A fisher directed management system was describeded by Hart (2021). It was proposed that fishers should only be allowed to exploit a resource if they collaborated in a resource management system for which they would own and be collectively responsible for. As part of the system fishers would need to follow the rules of exploitation set by the group and provide a central unit with data with which to monitor the fishery. Any fisher not following the rules would at first be fined but eventually expelled from the fishery if he/she continued to act selfishly. This version of the model establishes the dynamics of a fleet of vessels and controls overfishing by imposing fines on fishers whose income is low and who are tempted to keep fishing beyond the set quota which is established each year depending on the abundance of the fish stock. This version will later be elaborated to have interactions between the fishers including pressure to comply with the norms set by the group and which could lead to a stable management system.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
The impact of potential crowd behaviours on emergency evacuation: an evolutionary game theoretic approach
Azhar Mohd Ibrahim | Published Monday, July 30, 2018Crowd dynamics have important applications in evacuation management systems relevant to organizing safer large scale gatherings. For crowd safety, it is very important to study the evolution of potential crowd behaviours by simulating the crowd evacuation process. Planning crowd control tasks by studying the impact of crowd behaviour evolution towards evacuation could mitigate the possibility of crowd disasters. During a typical emergency evacuation scenario, conflict among agents occurs when agents intend to move to the same location as a result of the interaction with their nearest neighbours. The effect of the agent response towards their neighbourhood is vital in order to understand the effect of variation of crowd behaviour on the whole environment. In this work, we model crowd motion subject to exit congestion under uncertainty conditions in a continuous space via computer simulations. We model best-response, risk-seeking, risk-averse and risk-neutral behaviours of agents via certain game theoretic notions. We perform computer simulations with heterogeneous populations in order to study the effect of the evolution of agent behaviours towards egress flow under threat conditions. Our simulation results show the relation between the local crowd pressure and the number of injured agents. We observe that when the proportion of agents in a population of risk-seeking agents is increased, the average crowd pressure, average local density and the number of injured agents increases. Besides that, based on our simulation results, we can infer that crowd disasters could be prevented if the agent population consists entirely of risk-averse and risk-neutral agents despite circumstances that lead to threats.
Peer reviewed TRANSOPE: a multi-agent model to simulate outsourcing networks in road freight transport.
Aitor Salas-Peña Blanca Rosa Cases Gutiérrez | Published Friday, October 21, 2022A road freight transport (RFT) operation involves the participation of several types of companies in its execution. The TRANSOPE model simulates the subcontracting process between 3 types of companies: Freight Forwarders (FF), Transport Companies (TC) and self-employed carriers (CA). These companies (agents) form transport outsourcing chains (TOCs) by making decisions based on supplier selection criteria and transaction acceptance criteria. Through their participation in TOCs, companies are able to learn and exchange information, so that knowledge becomes another important factor in new collaborations. The model can replicate multiple subcontracting situations at a local and regional geographic level.
The succession of n operations over d days provides two types of results: 1) Social Complex Networks, and 2) Spatial knowledge accumulation environments. The combination of these results is used to identify the emergence of new logistics clusters. The types of actors involved as well as the variables and parameters used have their justification in a survey of transport experts and in the existing literature on the subject.
As a result of a preferential selection process, the distribution of activity among agents shows to be highly uneven. The cumulative network resulting from the self-organisation of the system suggests a structure similar to scale-free networks (Albert & Barabási, 2001). In this sense, new agents join the network according to the needs of the market. Similarly, the network of preferential relationships persists over time. Here, knowledge transfer plays a key role in the assignment of central connector roles, whose participation in the outsourcing network is even more decisive in situations of scarcity of transport contracts.
Peer reviewed Yards
srailsback Emily Minor Soraida Garcia Philip Johnson | Published Thursday, November 02, 2023This is a model of plant communities in urban and suburban residential neighborhoods. These plant communities are of interest because they provide many benefits to human residents and also provide habitat for wildlife such as birds and pollinators. The model was designed to explore the social factors that create spatial patterns in biodiversity in yards and gardens. In particular, the model was originally developed to determine whether mimicry behaviors–-or neighbors copying each other’s yard design–-could produce observed spatial patterns in vegetation. Plant nurseries and socio-economic constraints were also added to the model as other potential sources of spatial patterns in plant communities.
The idea for the model was inspired by empirical patterns of spatial autocorrelation that have been observed in yard vegetation in Chicago, Illinois (USA), and other cities, where yards that are closer together are more similar than yards that are farther apart. The idea is further supported by literature that shows that people want their yards to fit into their neighborhood. Currently, the yard attribute of interest is the number of plant species, or species richness. Residents compare the richness of their yards to the richness of their neighbors’ yards. If a resident’s yard is too different from their neighbors, the resident will be unhappy and change their yard to make it more similar.
The model outputs information about the diversity and identity of plant species in each yard. This can be analyzed to look for spatial autocorrelation patterns in yard diversity and to explore relationships between mimicry behaviors, yard diversity, and larger scale diversity.
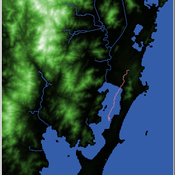
Shellmound Mobility
Henrique de Sena Kozlowski | Published Saturday, June 15, 2024Least Cost Path (LCP) analysis is a recurrent theme in spatial archaeology. Based on a cost of movement image, the user can interpret how difficult it is to travel around in a landscape. This kind of analysis frequently uses GIS tools to assess different landscapes. This model incorporates some aspects of the LCP analysis based on GIS with the capabilities of agent-based modeling, such as the possibility to simulate random behavior when moving. In this model the agent will travel around the coastal landscape of Southern Brazil, assessing its path based on the different cost of travel through the patches. The agents represent shellmound builders (sambaquieiros), who will travel mainly through the use of canoes around the lagoons.
How it works?
When the simulation starts the hiker agent moves around the world, a representation of the lagoon landscape of the Santa Catarina state in Southern Brazil. The agent movement is based on the travel cost of each patch. This travel cost is taken from a cost surface raster created in ArcMap to represent the different cost of movement around the landscape. Each tick the agent will have a chance to select the best possible patch to move in its Field of View (FOV) that will take it towards its target destination. If it doesn’t select the best possible patch, it will randomly choose one of the patches to move in its FOV. The simulation stops when the hiker agent reaches the target destination. The elevation raster file and the cost surface map are based on a 1 Arc-second (30m) resolution SRTM image, scaled down 5 times. Each patch represents a square of 150m, with an area of 0,0225km². The dataset uses a UTM Sirgas 2000 22S projection system. There are four different cost functions available to use. They change the cost surface used by the hikers to navigate around the world.
Peer reviewed Garbage can model Excel reconstruction
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, August 19, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, July 30, 2019Reconstruction of the original code M. Cohen, J. March, and J. Olsen garbage can model, realized by means of Microsoft Office Excel 2010
Peer reviewed NetLogo model of USA mass shootings
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, September 24, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, April 14, 2020Is the mass shooter a maniac or a relatively normal person in a state of great stress? According to the FBI report (Silver, J., Simons, A., & Craun, S. (2018). A Study of the Pre-Attack Behaviors of Active Shooters in the United States Between 2000 – 2013. Federal Bureau of Investigation, U.S. Department of Justice,Washington, D.C. 20535.), only 25% of the active shooters were known to have been diagnosed by a mental health professional with a mental illness of any kind prior to the offense.
The main objects of the model are the humans and the guns. The main factors influencing behavior are the population size, the number of people with mental disabilities (“psycho” in the model terminology) per 100,000 population, the total number of weapons (“guns”) in the population, the availability of guns for humans, the intensity of stressors affecting humans and the threshold level of stress, upon reaching which a person commits an act of mass shooting.
The key difference (in the model) between a normal person and a psycho is that a psycho accumulates stressors and, upon reaching a threshold level, commits an act of mass shooting. A normal person is exposed to stressors, but reaching the threshold level for killing occurs only when the simultaneous effect of stressors on him exceeds this level.
The population dynamics are determined by the following factors: average (normally distributed) life expectancy (“life_span” attribute of humans) and population growth with the percentage of newborns set by the value of the TickReprRatio% slider of the current population volume from 16 to 45 years old.Thus, one step of model time corresponds to a year.
An agent-based model for assessing strategies of adaptation to climate and tourism demand changes in an alpine destination
Stefano Balbi Marco Alberti | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model is then used for assessing three hypothetical and contrasted infrastructure-oriented adaptation strategies for the winter tourism industry, that have been previously discussed with local stakeholders, as possible alternatives to the “business-as-usual” situation.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search