About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1123 results for "J A Cuesta" clear search
Peer reviewed Visibility of archaeological social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023The purpose of this model is to explore the impact of combining archaeological palimpsests with different methods of cultural transmission on the visibility of prehistoric social networks. Up until recently, Paleolithic archaeologists have relied on stylistic similarities of artifacts to reconstruct social networks. However, this method - which is successfully applied to more recent ceramic assemblages - may not be applicable to Paleolithic assemblages, as several of those consist of palimpsests of occupations. Therefore, this model was created to study how palimpsests of occupation affect our social network reconstructions.
The model simplifies inter-groups interactions between populations who share cultural traits as they produce artifacts. It creates a proxy archaeological record of artifacts with stylistic traits that can then be used to reconstruct interactions. One can thus use this model to compare the networks reconstructed through stylistic similarities with direct contact.
COMM-PDND: Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks
Lars Reinelt | Published Friday, September 08, 2023The Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks (COMM-PDND) is an agent-based model specifically created to examine the dynamics of perceived descriptive norms in the context of digital network structures. The model, developed as part of a master’s thesis titled “The Dynamics of Perceived Descriptive Norms in Digital Network Publics: An Agent-Based Simulation,” emphasizes the critical role of communication processes in norm formation. It focuses on the role of communicative interactions in shaping perceived descriptive norms.
The COMM-PDND is tuned to explore the effects of normative deviance in digital social networks. It provides functionalities for manipulating agents according to their network position, and has a versatile set of customizable parameters, making it adaptable to a wide range of research contexts.
An agent-based approach to weighted decision making in the spatially and temporally variable South African Paleoscape
Colin Wren | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016This model simulates a foraging system based on Middle Stone Age plant and shellfish foraging in South Africa.
Rangeland and evolution of management styles
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020Provided is a landscape of properties where pastoralists make decisions how much livestock they put on their property and how much to suppress fire from occuring. Rangelands can be grass dominated, or unproductive shrubb dominated. Overgrazing and fire suppresion lead to shrub dominated landscapes. What management strategies evolve, and how is this impacted by policies?
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/.
Do microfinance institutes help slum-dwellers in coping with frequent disasters? An Agent-Based Modelling study
Mitali Yeshwant Yeshwant Joshi | Published Friday, March 13, 2020The model aims to investigate the role of Microfinance Institutes (MFIs) in strengthening the coping capacity of slum-dwellers (residents) in case of frequent disasters. The main purpose of the model is system understanding. It aids in understanding the following research question: Are the microcredits provided by MFI to start a small business helpful in increasing coping capacity of a slum dweller for recovering from frequent and intense disasters?
Model of the social game associated to the production of potato seeds in a Venezuelan region
Christhophe Sibertin-Blanc Ravi Rojas Oswaldo Terán Lisbeth Alarcón Liccia Romero | Published Monday, April 27, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, November 22, 2015This work aims at describing and simulating the (social) game around the production of potato seeds in Venezuela. It shows the effect of the identification of some actors with the production of native potato seeds (e.g., Venezuelan State´s low ident)
External shocks, agent interactions, and endogenous feedbacks--investigating system resilience with a stylized land use model
Yang Chen | Published Tuesday, March 06, 2018The purpose of the presented ABM is to explore how system resilience is affected by external disturbances and internal dynamics by using the stylized model of an agricultural land use system.
We explore land system resilience with a stylized land use model in which agents’ land use activities are affected by external shocks, agent interactions, and endogenous feedbacks. External shocks are designed as yield loss in crops, which is ubiquitous in almost every land use system where perturbations can occur due to e.g. extreme weather conditions or diseases. Agent interactions are designed as the transfer of buffer capacity from farmers who can and are willing to provide help to other farmers within their social network. For endogenous feedbacks, we consider land use as an economic activity which is regulated by markets — an increase in crop production results in lower price (a negative feedback) and an agglomeration of a land use results in lower production costs for the land use type (a positive feedback).
The Evolution of Tribalism: A Social-Ecological Model of Cooperation and Inter-group Conflict Under Pastoralism
Nicholas Seltzer | Published Monday, January 21, 2019This study investigates a possible nexus between inter-group competition and intra-group cooperation, which may be called “tribalism.” Building upon previous studies demonstrating a relationship between the environment and social relations, the present research incorporates a social-ecological model as a mediating factor connecting both individuals and communities to the environment. Cyclical and non-cyclical fluctuation in a simple, two-resource ecology drive agents to adopt either “go-it-alone” or group-based survival strategies via evolutionary selection. Novelly, this simulation employs a multilevel selection model allowing group-level dynamics to exert downward selective pressures on individuals’ propensity to cooperate within groups. Results suggest that cooperation and inter-group conflict are co-evolved in a triadic relationship with the environment. Resource scarcity increases inter-group competition, especially when resources are clustered as opposed to widely distributed. Moreover, the tactical advantage of cooperation in the securing of clustered resources enhanced selective pressure on cooperation, even if that implies increased individual mortality for the most altruistic warriors. Troubling, these results suggest that extreme weather, possibly as a result of climate change, could exacerbate conflict in sensitive, weather-dependent social-ecologies—especially places like the Horn of Africa where ecologically sensitive economic modalities overlap with high-levels of diversity and the wide-availability of small arms. As well, global development and foreign aid strategists should consider how plans may increase the value of particular locations where community resources are built or aid is distributed, potentially instigating tribal conflict. In sum, these factors, interacting with pre-existing social dynamics dynamics, may heighten inter-ethnic or tribal conflict in pluralistic but otherwise peaceful communities.
For special issue submission in JASSS.
Sensitivity of a population submitted to floods to unknown upcoming floods and parameters of the dynamics
Sylvie Huet | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2021This work is a java implementation of a study of the viability of a population submitted to floods. The population derives some benefit from living in a certain environment. However, in this environment, floods can occur and cause damage. An individual protection measure can be adopted by those who wish and have the means to do so. The protection measure reduces the damage in case of a flood. However, the effectiveness of this measure deteriorates over time. Individual motivation to adopt this measure is boosted by the occurrence of a flood. Moreover, the public authorities can encourage the population to adopt this measure by carrying out information campaigns, but this comes at a cost. People’s decisions are modelled based on the Protection Motivation Theory (Rogers1975, Rogers 1997, Maddux1983) arguing that the motivation to protect themselves depends on their perception of risk, their capacity to cope with risk and their socio-demographic characteristics.
While the control designing proper informations campaigns to remain viable every time is computed in the work presented in https://www.comses.net/codebases/e5c17b1f-0121-4461-9ae2-919b6fe27cc4/releases/1.0.0/, the aim of the present work is to produce maps of probable viability in case the serie of upcoming floods is unknown as well as much of the parameters for the population dynamics. These maps are bi-dimensional, based on the value of known parameters: the current average wealth of the population and their actual or possible future annual revenues.
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
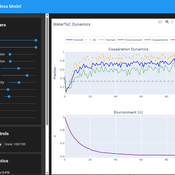
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
Displaying 10 of 1123 results for "J A Cuesta" clear search