About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search
The Evolution of Cooperation in an Ecological Context
Oyita Udiani | Published Saturday, November 03, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the altruistic trait selection model described in Pepper & Smuts (2000, 2002).
An Agent-Based Model of Corruption: Micro Approach
Valery Dzutsati | Published Friday, January 30, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, September 27, 2015Endogenous social transition from a high-corruption state to a low-corruption state, replication of Hammond 2009
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
An Agent Based Model of International Capital Flows
Harvey Baldovino | Published Thursday, April 06, 2023This is a preliminary attempt in creating an Agent-Based Model of capital flows. This is based on the theory of capital flows based on interest-rate differentials. Foreign capital flows to a country with higher interest rates relative to another. The model shows how capital volatilty and wealth concentration are affected by the speed of capital flow, number of investors, magnitude of changes in interest rate due to capital flows and the interest differential threshold that investors set in deciding whether to move capital or not. Investors in the model are either “regional” investors (only investing in neighboring countries) and “global” investors (those who invest anywhere in the world).
In the future, the author hopes to extend this model to incorporate capital flow based on changes in macroeconomic fundamentals, exchange rate volatility, behavioral finance (for instance, herding behavior) and the presence of capital controls.
An Agent-Based Model for Skilled Workers Migration
Hassan Bashiri | Published Thursday, September 21, 2023This documentation provides an overview and explanation of the NetLogo simulation code for modeling skilled workers’ migration in Iran. The simulation aims to explore the dynamics of skilled workers’ migration and their transition through various states, including training, employment, and immigration.
The flow of elite and talent migration, or “brain drain,” is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for developing countries. The decision to migrate is made due to various factors including economic opportunities, political stability, social factors and personal circumstances.
Measuring individual interests in the field of immigration is a complex task that requires careful consideration of various factors. The agent-based model is a useful tool for understanding the complex factors that are involved in talent migration. By considering the various social, economic, and personal factors that influence migration decisions, policymakers can provide more effective strategies to retain skilled and talented labor and promote sustainable growth in developing countries. One of the main challenges in studying the flow of elite migration is the complexity of the decision-making process and a set of factors that lead to migration decisions. Agent-based modeling is a useful tool for understanding how individual decisions can lead to large-scale migration patterns.
HMODEL: an exploratory simulation of surface archaeological formation
Benjamin Davies Simon Holdaway Patricia Fanning | Published Thursday, November 30, 2017This model is used to simulate the influence of spatially and temporally variable sedimentary processes on the distribution of dated archaeological features in a surface context.
Peer reviewed OfficeMoves: Personalities and Performance in an Interdependent Environment
Alan Dugger | Published Thursday, June 11, 2020After a little work experience, we realize that different kinds of people prefer different work environments: some enjoy a fast-paced challenge; some want to get by; and, others want to show off.
From that experience, we also realize that different kinds of people affect their work environments differently: some increase the pace; some slow it down; and, others make it about themselves.
This model concerns how three different kinds of people affect their work environment and how that work environment affects them in return. The model explores how this circular relation between people’s preferences and their environment creates patterns of association and performance over time.
…
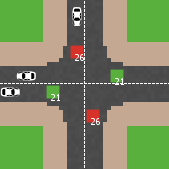
Modelling an intersection with traffic signal countdown timer
Eduard | Published Thursday, May 19, 2022Developed as a part of a project in the University of Augsburg, Institute of Geography, it simulates the traffic in an intersection or junction which uses either regular traffic lights or traffic lights with a countdown timer. The model tracks the average speed of cars before and after traffic lights as well as the throughput.
Nice Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Friday, February 05, 2016 | Last modified Friday, November 17, 2017The Nice Musical Chairs (NMC) model represent the competition for space between groups of stakeholders of farming and herding activities in the arid Afro-Eurasia.
Socio-hydrologicalModel_version_SESMO
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Paola Gomez Luis Bojorquez Fidel Serrano-Candela Hallie Eakin Yosune Miquelajauregui Rodrigo Garcia-Herrera | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We present here MEGADAPT_SESMO model. A hybrid, dynamic, spatially explicit, integrated model to simulate the vulnerability of urban coupled socio-ecological systems – in our case, the vulnerability of Mexico City to socio-hydrological risk.
Displaying 10 of 972 results for "M Van Den Hoven" clear search