About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search
00 PSoup V1.22 – Primordial Soup
Garvin Boyle | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017PSoup is an educational program in which evolution is demonstrated, on the desk-top, as you watch. Blind bugs evolve sophisticated heuristic search algorithms to be the best at finding food fast.
Cultural Dissemination: An Agent-Based Model with Social Influence
nhnguyen98 | Published Monday, July 26, 2021We study cultural dissemination in the context of an Axelrod-like agent-based model describing the spread of cultural traits across a society, with an added element of social influence. This modification produces absorbing states exhibiting greater variation in number and size of distinct cultural regions compared to the original Axelrod model, and we identify the mechanism responsible for this amplification in heterogeneity. We develop several new metrics to quantitatively characterize the heterogeneity and geometric qualities of these absorbing states. Additionally, we examine the dynamical approach to absorbing states in both our Social Influence Model as well as the Axelrod Model, which not only yields interesting insights into the differences in behavior of the two models over time, but also provides a more comprehensive view into the behavior of Axelrod’s original model. The quantitative metrics introduced in this paper have broad potential applicability across a large variety of agent-based cultural dissemination models.
Peer reviewed The OctoPINTS Model: Compliance and periodic fisheries closures (Beta)
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Tim M Daw Elizabeth Drury O'Neill Benedetta Veneroni Jineth Berrío-Martínez | Published Wednesday, April 20, 2022The purpose of the model is to explore how processes associated with compliance across different fishery actors’ social groups interplay with their acceptance of a fishery intervention, herein periodic closures of a small-scale octopus fishery. The model agents, entities and processes are designed based on stylized facts from literature and expert workshops on periodic closures in the Western Indian Ocean region, as well as fieldwork from Zanzibari villages that have implemented periodic octopus closures. The model is designed for scientists and decision-makers that are interested in understanding the complex interplay between fishers from different social groups, herein foot fisher men, foot fisher women and male skin divers or free divers within the periodic closure of an octopus species. Including various actions resulting from the restrictions, that is - opportunities that may be presented from restricting fishing in certain areas and during certain times. We are soon publishing an updated model with individual octopuses and their movement behaviors.
Wedding Doughnut
Eric Silverman Jason Hilton Jakub Bijak Viet Cao | Published Thursday, December 20, 2012 | Last modified Friday, September 20, 2013A reimplementation of the Wedding Ring model by Francesco Billari. We investigate partnership formation in an agent-based framework, and combine this with statistical demographic projections using real empirical data.
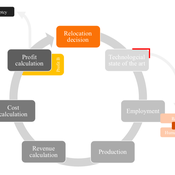
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
A Model to Unravel the Complexity of Rural Food Security
Stefano Balbi Samantha Dobbie | Published Monday, August 22, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018An ABM to simulate the behaviour of households within a village and observe the emerging properties of the system in terms of food security. The model quantifies food availability, access, utilisation and stability.
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Friendship Games Rev 1.0
David Dixon | Published Friday, October 07, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A friendship game is a kind of network game: a game theory model on a network. This is a NetLogo model of an agent-based adaptation of “‘Friendship-based’ Games” by PJ Lamberson. The agents reach an equilibrium that depends on the strategy played and the topology of the network.
Simulating Sustainability of Collective Awareness Platform for Sustainability and Social Innovation (CAPS)
Peter Gerbrands | Published Friday, May 08, 2020In an associated paper which focuses on analyzing the structure of several egocentric networks of collective awareness platforms for sustainable innovation (CAPS), this model is developed. It answers the question whether the network structure is determinative for the sustainability of the created awareness. Based on a thorough literature review a model is developed to explain and operationalize the concept of sustainability of a social network in terms of importance, effectiveness and robustness. By developing this agent-based model, the expected outcomes after the dissolution of the CAPS are predicted and compared with the results of a network with the same participants but with different ties. Twitter data from different CAPS is collected and used to feed the simulation. The results show that the structure of the network is of key importance for its sustainability. With this knowledge and the ability to simulate the results after network changes have taken place, CAPS can assess the sustainability of their legacy and actively steer towards a longer lasting potential for social innovation. The retrieved knowledge urges organizations like the European Commission to adopt a more blended approach focusing not only on solving societal issues but on building a community to sustain the initiated development.
Can ethnic tolerance curb self-reinforcing school segregation? A theoretical Agent Based Model
Lucas Sage Andreas Flache | Published Monday, August 10, 2020Schelling and Sakoda prominently proposed computational models suggesting that strong ethnic residential segregation can be the unintended outcome of a self-reinforcing dynamic driven by choices of individuals with rather tolerant ethnic preferences. There are only few attempts to apply this view to school choice, another important arena in which ethnic segregation occurs. In the current paper, we explore with an agent-based theoretical model similar to those proposed for residential segregation, how ethnic tolerance among parents can affect the level of school segregation. More specifically, we ask whether and under which conditions school segregation could be reduced if more parents hold tolerant ethnic preferences. We move beyond earlier models of school segregation in three ways. First, we model individual school choices using a random utility discrete choice approach. Second, we vary the pattern of ethnic segregation in the residential context of school choices systematically, comparing residential maps in which segregation is unrelated to parents’ level of tolerance to residential maps reflecting their ethnic preferences. Third, we introduce heterogeneity in tolerance levels among parents belonging to the same group. Our simulation experiments suggest that ethnic school segregation can be a very robust phenomenon, occurring even when about half of the population prefers mixed to segregated schools. However, we also identify a “sweet spot” in the parameter space in which a larger proportion of tolerant parents makes the biggest difference. This is the case when parents have moderate preferences for nearby schools and there is only little residential segregation. Further experiments are presented that unravel the underlying mechanisms.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search