About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 7 of 227 results for "Abi Vanak" clear search
Learning Extension - RAGE RAngeland Grazing Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Cristina I. Apetrei Nikolay Khabarov Valeria Javalera Rincón | Published Saturday, July 22, 2023This is an extension of the original RAGE model (Dressler et al. 2018), where we add learning capabilities to agents, specifically learning-by-doing and social learning (two processes central to adaptive (co-)management).
The extension module is applied to smallholder farmers’ decision-making - here, a pasture (patch) is the private property of the household (agent) placed on it and there is no movement of the households. Households observe the state of the pasture and their neighrbours to make decisions on how many livestock to place on their pasture every year. Three new behavioural types are created (which cannot be combined with the original ones): E-RO (baseline behaviour), E-LBD (learning-by-doing) and E-RO-SL1 (social learning). Similarly to the original model, these three types can be compared regarding long-term social-ecological performance. In addition, a global strategy switching option (corresponding to double-loop learning) allows users to study how behavioural strategies diffuse in a heterogeneous population of learning and non-learning agents.
An important modification of the original model is that extension agents are heterogeneous in how they deal with uncertainty. This is represented by an agent property, called the r-parameter (household-risk-att in the code). The r-parameter is catch-all for various factors that form an agent’s disposition to act in a certain way, such as: uncertainty in the sensing (partial observability of the resource system), noise in the information received, or an inherent characteristic of the agent, for instance, their risk attitude.
COMM-PDND: Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks
Lars Reinelt | Published Friday, September 08, 2023The Communication-Based Model of Perceived Descriptive Norm Dynamics in Digital Networks (COMM-PDND) is an agent-based model specifically created to examine the dynamics of perceived descriptive norms in the context of digital network structures. The model, developed as part of a master’s thesis titled “The Dynamics of Perceived Descriptive Norms in Digital Network Publics: An Agent-Based Simulation,” emphasizes the critical role of communication processes in norm formation. It focuses on the role of communicative interactions in shaping perceived descriptive norms.
The COMM-PDND is tuned to explore the effects of normative deviance in digital social networks. It provides functionalities for manipulating agents according to their network position, and has a versatile set of customizable parameters, making it adaptable to a wide range of research contexts.
ReMoTe-S. Residential Mobility of Tenants in Switzerland: an agent-based model
Claudia Binder Anna Pagani Francesco Ballestrazzi Emanuele Massaro | Published Friday, April 01, 2022ReMoTe-S is an agent-based model of the residential mobility of Swiss tenants. Its goal is to foster a holistic understanding of the reciprocal influence between households and dwellings and thereby inform a sustainable management of the housing stock. The model is based on assumptions derived from empirical research conducted with three housing providers in Switzerland and can be used mainly for two purposes: (i) the exploration of what if scenarios that target a reduction of the housing footprint while accounting for households’ preferences and needs; (ii) knowledge production in the field of residential mobility and more specifically on the role of housing functions as orchestrators of the relocation process.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
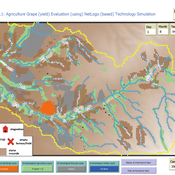
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Displaying 7 of 227 results for "Abi Vanak" clear search