About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 364 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Peer reviewed soslivestock model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral | Published Wednesday, May 28, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025The purpose of this model is to analyze how different management strategies affect the wellbeing, sustainability and resilience of an extensive livestock system under scenarios of climate change and landscape configurations. For this purpose, it simulates one cattle farming system, in which agents (cattle) move through the space using resources (grass). Three farmer profiles are considered: 1) a subsistence farmer that emphasizes self-sufficiency and low costs with limited attention to herd management practices, 2) a commercial farmer focused on profit maximization through efficient production methods, and 3) an environmental farmer that prioritizes conservation of natural resources and animal welfare over profit maximization. These three farmer profiles share the same management strategies to adapt to climate and resource conditions, but differ in their goals and decision-making criteria for when, how, and whether to implement those strategies. This model is based on the SequiaBasalto model (Dieguez Cameroni et al. 2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015), replicated in NetLogo by Soler-Navarro et al. (2023).
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each step begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of animals according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. Animals can be supplemented by the farmer in case of severe drought. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. This updated grass height value becomes the starting grass height for the next day. Cows then move to the next area with the highest grass height. After that, cattle prices are updated and cattle sales are held on the first day of fall. In the event of a severe drought, special sales are held. Finally, at the end of the day, the farm balance and the farmer’s effort are calculated.
An agent-based model of school enrollment process under educational competition
Yao Tong | Published Sunday, August 04, 2024Due to the role of education in promoting social status and facilitating upward social mobility, individuals and their families spare no effort to pursue better educational opportunities, especially in countries where education is highly competitive.
In China, the enrollment of senior high schools and universities mainly follows a ranking system based on students’ scores in national entrance exams (Zhongkao and Gaokao). Typically, students with higher scores have priority in choosing schools and endeavor to get into better senior high schools to increase their chances of entering a prestigious university.
However, students can only select “better” senior high schools based on their average Gaokao grades, which are strongly influenced by the initial performance (Zhongkao grades) of enrolled students. The true quality indicator of school education (schooling effect, defined as the grade improvement achieved through education at the senior high school) is unknowable. This raises the first question: will school rankings reflect the real educational quality of schools over decades of educational competition, or merely the initial quality of the students they enroll?
…
Wedding Doughnut
Eric Silverman Jason Hilton Jakub Bijak Viet Cao | Published Thursday, December 20, 2012 | Last modified Friday, September 20, 2013A reimplementation of the Wedding Ring model by Francesco Billari. We investigate partnership formation in an agent-based framework, and combine this with statistical demographic projections using real empirical data.
The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice
Guido Fioretti | Published Saturday, June 22, 2013We reconstruct Cohen, March and Olsen’s Garbage Can model of organizational choice as an agent-based model. We add another means for avoiding making decisions: buck-passing difficult problems to colleagues.
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
A minimal assumption based agent based simulation model of the emergence of technological innovation
Yuan Zhao Roland Ortt Bernhard Katzy | Published Sunday, October 19, 2014This simulation model is to simulate the emergence of technological innovation processes from the hypercycles perspective.
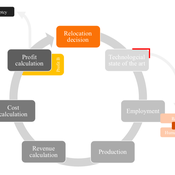
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
Peer reviewed Visibility of archaeological social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023The purpose of this model is to explore the impact of combining archaeological palimpsests with different methods of cultural transmission on the visibility of prehistoric social networks. Up until recently, Paleolithic archaeologists have relied on stylistic similarities of artifacts to reconstruct social networks. However, this method - which is successfully applied to more recent ceramic assemblages - may not be applicable to Paleolithic assemblages, as several of those consist of palimpsests of occupations. Therefore, this model was created to study how palimpsests of occupation affect our social network reconstructions.
The model simplifies inter-groups interactions between populations who share cultural traits as they produce artifacts. It creates a proxy archaeological record of artifacts with stylistic traits that can then be used to reconstruct interactions. One can thus use this model to compare the networks reconstructed through stylistic similarities with direct contact.
The S-uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Friday, March 17, 2023This version 2.1.0 of the uFunk model is about setting a business strategy (the S in the name) for an organization. A team of managers (or executives) meet and discuss various options on the strategy for the firm. There are three aspects that they have to agree on to set the strategic positioning of the organization.
The discussion is on market, stakeholders, and resources. The team (it could be a business strategy task force) considers various aspects of these three elements. The resources they use to develop the discussion can come from a traditional approach to strategy or from non-traditional means (e.g., so-called serious play, creativity and imagination techniques).
The S-uFunk 2.1.0 Model wants to understand to which extent cognitive means triggered by traditional and non-traditional resources affect the making of the strategy process.
Displaying 10 of 364 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search