About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 194 results for "Ingo Wolf" clear search
Peer reviewed Reduced Mobility Transition Model (R-MoTMo)
Gesine A. Steudle Sarah Wolf Steffen Fürst | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2022The Mobility Transition Model (MoTMo) is a large scale agent-based model to simulate the private mobility demand in Germany until 2035. Here, we publish a very much reduced version of this model (R-MoTMo) which is designed to demonstrate the basic modelling ideas; the aim is by abstracting from the (empirical, technological, geographical, etc.) details to examine the feed-backs of individual decisions on the socio-technical system.
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with Brown and Green capital (ABRam-BG)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez | Published Monday, December 09, 2024The purpose of the ABRam-BG model is to study belief dynamics as a potential driver of green (growth) transitions and illustrate their dynamics in a closed, decentralized economy populated by utility maximizing agents with an environmental attitude. The model is built using the ABRam-T model (for model visit: https://doi.org/10.25937/ep45-k084) and introduces two types of capital – green (low carbon intensity) and brown (high carbon intensity) – with their respective technological progress levels. ABRam-BG simulates a green transition as an emergent phenomenon resulting from well-known opinion dynamics along the economic process.
Survival analysis and Population viability analysis of the Northern Bald Ibis
Stephanie Kramer-Schadt Cédric Scherer Viktoriia Radchuk Sinah Drenske Corinna Esterer Ingo Kowarik Johannes Fritz | Published Thursday, August 04, 2022This is the full repository to run the survival analysis (in R) and run the population viability model and its analysis (NetLogo + R) of the Northern Bald Ibis (NBI) presented in the study
On the road to self-sustainability: Reintroduced migratory European Northern Bald Ibises (Geronticus eremita) still need management interventions for population viability
by Sinah Drenske, Viktoriia Radchuk, Cédric Scherer, Corinna Esterer, Ingo Kowarik, Johannes Fritz, Stephanie Kramer-Schadt
…
Peer reviewed FishCensus
Miguel Pais | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, February 09, 2017The FishCensus model simulates underwater visual census methods, where a diver estimates the abundance of fish. A separate model is used to shape species behaviours and save them to a file that can be shared and used by the counting model.
Peer reviewed ACross (Academic Collaboration, Research, Output, and System Simulation)
Wenhan Feng Bayi Li | Published Saturday, June 28, 2025The primary purpose of this model is to explain the dynamic processes within university-centered collaboration networks, with a particular focus on the complex transformation of academic knowledge into practical projects. Based on investigations of actual research projects and a thorough literature review, the model integrates multiple drivers and influencing factors to explore how these factors affect the formation and evolution of collaboration networks under different parameter scenarios. The model places special emphasis on the impact of disciplinary attributes, knowledge exchange, and interdisciplinary collaboration on the dynamics of collaboration networks, as well as the complex mechanisms of network structure, system efficiency, and interdisciplinary interactions during project formation.
Specifically, the model aims to:
- Simulate how university research departments drive the formation of research projects through knowledge creation.
- Investigate how the dynamics of collaboration networks influence the transformation of innovative hypotheses into matured projects.
- Examine the critical roles of knowledge exchange and interdisciplinary collaboration in knowledge production and project formation.
- Provide both quantitative and qualitative insights into the interactions among academia, industry, and project outputs.
BehaviorSpace tutorial model
Colin Wren | Published Wednesday, March 23, 2016This is based off my previous Profiler tutorial model, but with an added tutorial on converting it into a model usable with BehaviorSpace, and creating a BehaviorSpace experiment.
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
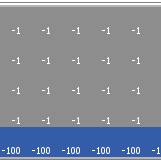
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
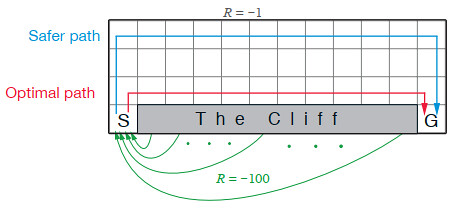
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
Lake Anderson Revisited II
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Monday, June 28, 2021The purpose of this study is another agent-based replication of a System Dynamics model (Anderson,1973) where he analysed the dynamics of nutrient, biomass, oxygen and detritus in a model lake under conditions of artificial fertilising and policies to deal with the consequences of artificial fertilising.. A first replication (Möhring & Troitzsch,2001) added those agents to the original model that were necessary to move the role of the experimenter into the model, whereas this replication replaces the original lake with a collection of small elements between which biomass, nurtrents and oxygen are exchanged, adds rivers upstream and downstream as well as adjacent land divided into villages and populated with farms and industrial plants run by individual persons.
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with endogenous technical progress (ABRam-T)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez Malika Tokpanova | Published Wednesday, February 14, 2024 | Last modified Monday, February 19, 2024The Agent-Based Ramsey growth model is designed to analyze and test a decentralized economy composed of utility maximizing agents, with a particular focus on understanding the growth dynamics of the system. We consider farms that adopt different investment strategies based on the information available to them. The model is built upon the well-known Ramsey growth model, with the introduction of endogenous technical progress through mechanisms of learning by doing and knowledge spillovers.
Displaying 10 of 194 results for "Ingo Wolf" clear search