About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
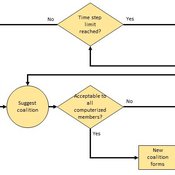
Human-in-the-loop Experiment of the Strategic Coalition Formation using the glove game
Andrew Collins | Published Monday, November 23, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 22, 2022The purpose of the model is to collect information on human decision-making in the context of coalition formation games. The model uses a human-in-the-loop approach, and a single human is involved in each trial. All other agents are controlled by the ABMSCORE algorithm (Vernon-Bido and Collins 2020), which is an extension of the algorithm created by Collins and Frydenlund (2018). The glove game, a standard cooperative game, is used as the model scenario.
The intent of the game is to collection information on the human players behavior and how that compares to the computerized agents behavior. The final coalition structure of the game is compared to an ideal output (the core of the games).
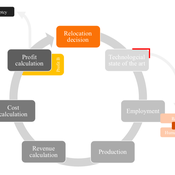
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
Bayesian Updating Opinion Shared Uncertainty Model.
Johnathan Adams | Published Monday, November 16, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 14, 2021This is an opinion dynamics model which extends the model found in (Martins 2009). The previous model had an unshared uncertainty assumption in agent-to-agent interaction this model relaxes that assumption. The model only supports a fully connect network where every agent has an equal likelihood of interacting with every other agent at any given time step. The model is highly modular so different social network paradigm can easier be implemented.
Seeding for information transmission in social networks
Beatrice Nöldeke Ulrike Grote Etti Winter | Published Tuesday, November 03, 2020This model simulates different seeding strategies for information diffusion in a social network adjusted to a case study area in rural Zambia. It systematically evaluates different criteria for seed selection (centrality measures and hierarchy), number of seeds, and interaction effects between seed selection criteria and set size.
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
This model investigates how anti-conformist intentions could be related to some biases on the perception of attitudes. It starts from two case studies, related to the adoption of organic farming, that show anti-conformist intentions. It proposes an agent-based model which computes an intention based on the Theory of Reasoned Action and assumes some biases in the perception of others’ attitudes according to the Social Judgement Theory.
It investigates the conditions on the model parameter values for which the simulations reproduce the features observed in the case studies. The results suggest that perception biases are indeed likely to contribute to anti-conformist intentions.
Leviathan model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Thursday, September 17, 2020 | Last modified Monday, September 06, 2021The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017). We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters.
We show that the inequality of reputations among agents have a negative effect on the opinions about the agents of low status.The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the agent, the more detrimental the interactions are for the opinions about this agent, especially when gossip is activated, while the interactions always tend to increase the opinions about agents of high status.
The uFUNK Model
Davide Secchi | Published Monday, August 31, 2020The agent-based simulation is set to work on information that is either (a) functional, (b) pseudo-functional, (c) dysfunctional, or (d) irrelevant. The idea is that a judgment on whether information falls into one of the four categories is based on the agent and its network. In other words, it is the agents who interprets a particular information as being (a), (b), (c), or (d). It is a decision based on an exchange with co-workers. This makes the judgment a socially-grounded cognitive exercise. The uFUNK 1.0.2 Model is set on an organization where agent-employee work on agent-tasks.
Peer reviewed Gregarious Behavior, Human Colonization and Social Differentiation Agent-Based Model
Gert Jan Hofstede Mark R Kramer Sebastian Fajardo Andrés Bernal Martijn de Vries | Published Thursday, August 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, October 29, 2020Studies of colonization processes in past human societies often use a standard population model in which population is represented as a single quantity. Real populations in these processes, however, are structured with internal classes or stages, and classes are sometimes created based on social differentiation. In this present work, information about the colonization of old Providence Island was used to create an agent-based model of the colonization process in a heterogeneous environment for a population with social differentiation. Agents were socially divided into two classes and modeled with dissimilar spatial clustering preferences. The model and simulations assessed the importance of gregarious behavior for colonization processes conducted in heterogeneous environments by socially-differentiated populations. Results suggest that in these conditions, the colonization process starts with an agent cluster in the largest and most suitable area. The spatial distribution of agents maintained a tendency toward randomness as simulation time increased, even when gregariousness values increased. The most conspicuous effects in agent clustering were produced by the initial conditions and behavioral adaptations that increased the agent capacity to access more resources and the likelihood of gregariousness. The approach presented here could be used to analyze past human colonization events or support long-term conceptual design of future human colonization processes with small social formations into unfamiliar and uninhabited environments.
Displaying 10 of 477 results social clear search