About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 942 results for "Wilfried van Sark" clear search
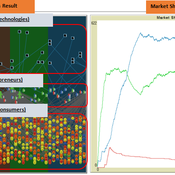
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
Rebel Group Protection Rackets
Gerd Wagner Luis Gustavo Nardin Kamil C. Klosek Frances Duffy | Published Wednesday, December 04, 2019System Narrative
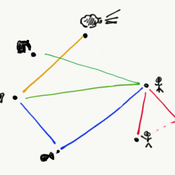
How do rebel groups control territory and engage with the local economy during civil war? Charles Tilly’s seminal War and State Making as Organized Crime (1985) posits that the process of waging war and providing governance resembles that of a protection racket, in which aspiring governing groups will extort local populations in order to gain power, and civilians or businesses will pay in order to ensure their own protection. As civil war research increasingly probes the mechanisms that fuel local disputes and the origination of violence, we develop an agent-based simulation model to explore the economic relationship of rebel groups with local populations, using extortion racket interactions to explain the dynamics of rebel fighting, their impact on the economy, and the importance of their economic base of support. This analysis provides insights for understanding the causes and byproducts of rebel competition in present-day conflicts, such as the cases of South Sudan, Afghanistan, and Somalia.
Model Description
The model defines two object types: RebelGroup and Enterprise. A RebelGroup is a group that competes for power in a system of anarchy, in which there is effectively no government control. An Enterprise is a local civilian-level actor that conducts business in this environment, whose objective is to make a profit. In this system, a RebelGroup may choose to extort money from Enterprises in order to support its fighting efforts. It can extract payments from an Enterprise, which fears for its safety if it does not pay. This adds some amount of money to the RebelGroup’s resources, and they can return to extort the same Enterprise again. The RebelGroup can also choose to loot the Enterprise instead. This results in gaining all of the Enterprise wealth, but prompts the individual Enterprise to flee, or leave the model. This reduces the available pool of Enterprises available to the RebelGroup for extortion. Following these interactions the RebelGroup can choose to AllocateWealth, or pay its rebel fighters. Depending on the value of its available resources, it can add more rebels or expel some of those which it already has, changing its size. It can also choose to expand over new territory, or effectively increase its number of potential extorting Enterprises. As a response to these dynamics, an Enterprise can choose to Report expansion to another RebelGroup, which results in fighting between the two groups. This system shows how, faced with economic choices, RebelGroups and Enterprises make decisions in war that impact conflict and violence outcomes.
Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers
Antonio Franco | Published Wednesday, July 13, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 02, 2018The code for the paper “Social norms and the dominance of Low-doers”
Catch Me if You Can: Using a Threshold Model to Simulate Support for Presidential Candidates in the Invisible Primary
Elizabeth Stiles | Published Wednesday, November 14, 2018We use a threshold model to drive our simulated network analysis testing public support for candidates in invisible primaries. We assign voter thresholds for candidates and vary number of voters, attachment to candidates and decay. Results of the algorithm show effects of size of lead, attachment and size of decay.
RBM - A Relation-based model - a fishery implementation
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Anja Klein Tilman Hertz | Published Monday, March 17, 2025The Relation-Based Model (RBM) purpose is to operationalise (a form of) process-relational (PR) thinking to serve as a thinking tool for process-relational thinking among social-ecological system (SES) researchers. The development of this model itself has been a ‘Proof of concept’- exercise to see whether we actually represent process-relational thinking in a methodology that is entity-based (ABM).
The target of the agent-based model is to show the emergence, change and disappearance of fishing assemblages (focusing on processes of self-organisation) in a Mexican fishery using a process-relational view. From this view, a fishery is regarded as an assemblage in which fishing can be enabled, fishing can occur, and fish can be bought/sold. These core doings - or sub-assemblages or capacities - maintain the assemblage. Each (sub)assemblage reflects different actualisations of constellations of relations and elements (buyers, fishers, fuel, permits, vessels and wind). The RBM thereby reflects an artificial fishery in which agents (elements) and their links (relations) engage in (enabling) fishing and buying/selling.
Spatial rangeland model
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 22, 2019 | Last modified Friday, March 04, 2022Spatial explicit model of a rangeland system, based on Australian conditions, where grass, woody shrubs and fire compete fore resources. Overgrazing can cause the system to flip from a healthy state to an unproductive shrub state. With the model one can explore the consequences of different movement rules of the livestock on the resilience of the system.
The model is discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/.
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Pandemic package
Peter Cotton | Published Friday, April 24, 2020 | Last modified Friday, May 08, 2020Pandemic (pip install pandemic)
An agent model in which commuting, compliance, testing and contagion parameters drive infection in a population of thousands of millions. Agents follow Ornstein-Uhlenbeck processes in the plane and collisions drive transmission. Results are stored at SwarmPrediction.com for further analysis, and can be retrieved by anyone.
This is a very simple simulation that in a special case can be shown to be approximated by a compartmental model with time varying infection rate.
A preliminary extension of the Hemelrijk 1996 model of reciprocal behavior to include feeding
Sean Barton | Published Monday, December 13, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A more complete description of the model can be found in Appendix I as an ODD protocol. This model is an expansion of the Hemelrijk (1996) that was expanded to include a simple food seeking behavior.
FOUR SEASONS
Lars G Spang | Published Tuesday, March 28, 2017Butterflies (turtles) goes through metamorphism and moves to corresponding patches each season of the year. The number of years and seasons are monitored.
A test-bed ecological model
Bruce Edmonds | Published Sunday, May 04, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, May 15, 2019This is a multi-patch meta-population ecological model. It intended as a test-bed in which to test the impact of humans with different kinds of social structure.
Displaying 10 of 942 results for "Wilfried van Sark" clear search