About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 273 results for "Eckhard Auch" clear search
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
How information propagation in hybrid spaces affects decision-making: using ABM to simulate Covid-19 vaccine uptake
Fuzhen Yin | Published Wednesday, March 13, 2024Abstract: The notion of physical space has long been central in geographical theories. However, the widespread adoption of information and communication technologies (ICTs) has freed human dynamics from purely physical to also relational and cyber spaces. While researchers increasingly recognize such shifts, rarely have studies examined how the information propagates in these hybrid spaces (i.e., physical, relational, and cyber). By exploring the vaccine opinion dynamics through agent-based modeling, this study is the first that combines all hybrid spaces and explores their distinct impacts on human dynamics from an individual’s perspective. Our model captures the temporal dynamics of vaccination progress with small errors (MAE=2.45). Our results suggest that all hybrid spaces are indispensable in vaccination decision making. However, in our model, most of the agents tend to give more emphasis to the information that is spread in the physical instead of other hybrid spaces. Our study not only sheds light on human dynamics research but also offers a new lens to identifying vaccinated individuals which has long been challenging in disease-spread models. Furthermore, our study also provides responses for practitioners to develop vaccination outreach policies and plan for future outbreaks.
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
The tragedy of the park: an agent-based model on endogenous and exogenous institutions for the management of a forest.
Elena Vallino | Published Wednesday, March 27, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, April 26, 2018I model a forest and a community of loggers. Agents follow different kinds of rules in order to log. I compare the impact of endogenous and of exogenous institutions on the state of the forest and on the profit of the users, representing different scenarios of participatory conservation projects.
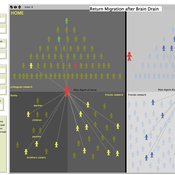
RETURN MIGRATION AFTER BRAIN DRAIN: A SIMULATION APPROACH
Alessandro Pluchino Alessio Emanuele Biondo Andrea Rapisarda | Published Friday, June 21, 2013This model, realized on the NetLogo platform, compares utility levels at home and abroad to simulate agents’ migration and their eventual return. Our model is based on two fundamental individual features, i.e. risk aversion and initial expectation, which characterize the dynamics of different agents according to the evolution of their social contacts.
Model of the social game associated to the production of potato seeds in a Venezuelan region
Christhophe Sibertin-Blanc Ravi Rojas Oswaldo Terán Lisbeth Alarcón Liccia Romero | Published Monday, April 27, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, November 22, 2015This work aims at describing and simulating the (social) game around the production of potato seeds in Venezuela. It shows the effect of the identification of some actors with the production of native potato seeds (e.g., Venezuelan State´s low ident)
07 EffLab_V5.07 NL
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, October 07, 2019EffLab was built to support the study of the efficiency of agents in an evolving complex adaptive system. In particular:
- There is a definition of efficiency used in ecology, and an analogous definition widely used in business. In ecological studies it is called EROEI (energy returned on energy invested), or, more briefly, EROI (pronounced E-Roy). In business it is called ROI (dollars returned on dollars invested).
- In addition, there is the more well-known definition of efficiency first described by Sadi Carnot, and widely used by engineers. It is usually represented by the Greek letter ‘h’ (pronounced as ETA). These two measures of efficiency bear a peculiar relationship to each other: EROI = 1 / ( 1 - ETA )
In EffLab, blind seekers wander through a forest looking for energy-rich food. In this multi-generational world, they live and reproduce, or die, depending on whether they can find food more effectively than their contemporaries. Data is collected to measure their efficiency as they evolve more effective search patterns.
…
Non-attentional visual information transmission in groups under predation
J. Fransje Weerden, van | Published Wednesday, March 25, 2020Our aim is to show effects of group living when only low-level cognition is assumed, such as pattern recognition needed for normal functioning, without assuming individuals have knowledge about others around them or warn them actively.
The model is of a group of vigilant foragers staying within a patch, under attack by a predator. The foragers use attentional scanning for predator detection, and flee after detection. This fleeing action constitutes a visual cue to danger, and can be received non-attentionally by others if it occurs within their limited visual field. The focus of this model is on the effectiveness of this non-attentional visual information reception.
A blind angle obstructing cue reception caused by behaviour can exist in front, morphology causes a blind angle in the back. These limitations are represented by two visual field shapes. The scan for predators is all-around, with distance-dependent detection; reception of flight cues is limited by visual field shape.
Initial parameters for instance: group sizes, movement, vision characteristics for predator detection and for cue reception. Captures (failure), number of times the information reached all individuals at the same time (All-fled, success), and several other effects of the visual settings are recorded.
An agent-based model of building occupant behavior during load shedding
Handi Chandra Putra | Published Thursday, May 21, 2020Load shedding enjoys increasing popularity as a way to reduce power consumption in buildings during hours of peak demand on the electricity grid. This practice has well known cost saving and reliability benefits for the grid, and the contracts utilities sign with their “interruptible” customers often pass on substantial electricity cost savings to participants. Less well-studied are the impacts of load shedding on building occupants, hence this study investigates those impacts on occupant comfort and adaptive behaviors. It documents experience in two office buildings located near Philadelphia (USA) that vary in terms of controllability and the set of adaptive actions available to occupants. An agent-based model (ABM) framework generalizes the case-study insights in a “what-if” format to support operational decision making by building managers and tenants. The framework, implemented in EnergyPlus and NetLogo, simulates occupants that have heterogeneous
thermal and lighting preferences. The simulated occupants pursue local adaptive actions such as adjusting clothing or using portable fans when central building controls are not responsive, and experience organizational constraints, including a corporate dress code and miscommunication with building managers. The model predicts occupant decisions to act fairly well but has limited ability to predict which specific adaptive actions occupants will select.
Displaying 10 of 273 results for "Eckhard Auch" clear search