About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 334 results for "Chelsea E Hunter" clear search
An agent-based approach to weighted decision making in the spatially and temporally variable South African Paleoscape
Colin Wren | Published Thursday, December 29, 2016This model simulates a foraging system based on Middle Stone Age plant and shellfish foraging in South Africa.
Cultural transmission in structured populations
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, November 13, 2024This structured population model is built to address how migration (or intergroup cultural transmission), copying error, and time-averaging affect regional variation in a single selectively neutral discrete cultural trait under different mechanisms of cultural transmission. The model allows one to quantify cultural differentiation between groups within a structured population (at equilibrium) as well as between regional assemblages of time-averaged archaeological material at two different temporal scales (1,000 and 10,000 ticks). The archaeological assemblages begin to accumulate only after a “burn-in” period of 10,000 ticks. The model includes two different representations of copying error: the infinite variants model of copying error and the finite model of copying error. The model also allows the user to set the variant ceiling value for the trait in the case of the finite model of copying error.
A language economics perspective on language spread: Simulating Language Dynamics in a Social Network
Marco Civico | Published Saturday, June 07, 2025This model examines language dynamics within a social network using simulation techniques to represent the interplay of language adoption, social influence, economic incentives, and language policies. The agent-based model (ABM) focuses on interactions between agents endowed with specific linguistic attributes, who engage in communication based on predefined rules. A key feature of our model is the incorporation of network analysis, structuring agent relationships as a dynamic network and leveraging network metrics to capture the evolving inter-agent connections over time. This integrative approach provides nuanced insights into emergent behaviors and system dynamics, offering an analytical framework that extends beyond traditional modeling approaches. By combining agent-based modeling with network analysis, the model sheds light on the underlying mechanisms governing complex language systems and can be effectively paired with sociolinguistic observational data.
ABM Simulation of Transition from Late Longshan Cultures to Early Erlitou Culture
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Within the archeological record for Bronze Age Chinese culture, there continues to be a gap in our understanding of the sudden rise of the Erlitou State from the previous late Longshan chiefdoms. In order to examine this period, I developed and used an agent-based model (ABM) to explore possible socio-politically relevant hypotheses for the gap between the demise of the late Longshan cultures and rise of the first state level society in East Asia. I tested land use strategy making and collective action in response to drought and flooding scenarios, the two plausible environmental hazards at that time. The model results show cases of emergent behavior where an increase in social complexity could have been experienced if a catastrophic event occurred while the population was sufficiently prepared for a different catastrophe, suggesting a plausible lead for future research into determining the life of the time period.
The ABM published here was originally developed in 2016 and its results published in the Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference.
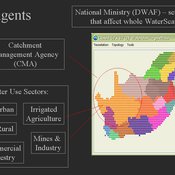
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Shared Norms and the Evolution of Ethnic Markers
Nathan Rollins | Published Friday, January 22, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The publication and mathematical model upon which this ABM is based shows one mechanism that can lead to stable behavioral and cultural traits between groups.
Charcoal Record Simulation Model (CharRec)
Grant Snitker | Published Monday, November 16, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, September 30, 2021This model (CharRec) creates simulated charcoal records, based on differing natural and anthropogenic patterns of ignitions, charcoal dispersion, and deposition.
Between Pleasure and Contentment: Evolutionary Dynamics of Some Possible Parameters of Happiness
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Saturday, March 12, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, March 16, 2016We build a computational model to investigate, in an evolutionary setting, a series of questions pertaining to happiness.
CEDSS is an agent-based model of domestic energy demand at the level of a small community.
Peer reviewed Visibility of archaeological social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023The purpose of this model is to explore the impact of combining archaeological palimpsests with different methods of cultural transmission on the visibility of prehistoric social networks. Up until recently, Paleolithic archaeologists have relied on stylistic similarities of artifacts to reconstruct social networks. However, this method - which is successfully applied to more recent ceramic assemblages - may not be applicable to Paleolithic assemblages, as several of those consist of palimpsests of occupations. Therefore, this model was created to study how palimpsests of occupation affect our social network reconstructions.
The model simplifies inter-groups interactions between populations who share cultural traits as they produce artifacts. It creates a proxy archaeological record of artifacts with stylistic traits that can then be used to reconstruct interactions. One can thus use this model to compare the networks reconstructed through stylistic similarities with direct contact.
Displaying 10 of 334 results for "Chelsea E Hunter" clear search