About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Sjoukje A Osinga" clear search
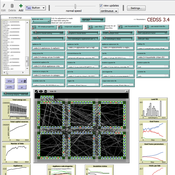
CEDSS is an agent-based model of domestic energy demand at the level of a small community.
A minimal assumption based agent based simulation model of the emergence of technological innovation
Yuan Zhao Roland Ortt Bernhard Katzy | Published Sunday, October 19, 2014This simulation model is to simulate the emergence of technological innovation processes from the hypercycles perspective.
A Simulation of Arab Spring Protests Informed by Qualitative Evidence
Bruce Edmonds Stephanie Dornschneider | Published Monday, April 29, 2019 | Last modified Friday, May 24, 2019The purpose of the simulation was to explore and better understand the process of bridging between an analysis of qualitative data and the specification of a simulation. This may be developed for more serious processes later but at the moment it is merely an illustration.
This exercise was done by Stephanie Dornschneider (School of Politics and International Relations, University College Dublin) and Bruce Edmonds to inform the discussion at the Lorentz workshop on “Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data using Social Simulation” at Leiden in April 2019. The qualitative data was collected and analysed by SD. The model specification was developed as the result of discussion by BE & SD. The model was programmed by BE. This is described in a paper submitted to Social Simulation 2019 and (to some extent) in the slides presented at the workshop.
The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries
Aaron Bramson Patrick Grim Daniel J Singer Jiin Jung William J. Berger Bennett Holman | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2023This model is linked to the paper “The Epistemic Role of Diversity in Juries: An Agent-Based Model”. There are many version of this model, but the current version focuses on the role of diversity in whether juries reach correct verdicts. Using this agent-based model, we argue that diversity can play at least four importantly different roles in affecting jury verdicts. (1) Where different subgroups have access to different information, equal representation can strengthen epistemic jury success. (2) If one subgroup has access to particularly strong evidence, epistemic success may demand participation by that group. (3) Diversity can also reduce the redundancy of the information on which a jury focuses, which can have a positive impact. (4) Finally, and most surprisingly, we show that limiting communication between diverse groups in juries can favor epistemic success as well.
GRASP world
Gert Jan Hofstede | Published Tuesday, April 16, 2019This agent-based model investigates group longevity in a population in a foundational way, using theory on social relations and culture. It is the first application of the GRASP meta-model for social agents, containing elements of Groups, Rituals, Affiliation, Status, and Power. It can be considered an exercise in artificial sociality: a culture-general, content-free base-line trust model from which to engage in more specific studies. Depending on cultural settings for individualism and power distance, as well as settings for xenophobia and for the increase of trust over group life, the GRASP world model generates a variety of patters. Number of groups ranges from one to many, composition from random to segregated, and pattern genesis from rapid to many hundreds of time steps. This makes GRASP world an instrument that plausibly models some basic elements of social structure in different societies.
A replication and extension of the Taylor's Simulation Model of Insurance Market Dynamics in C#
Rei England | Published Sunday, September 24, 2023A simple model is constructed using C# in order to to capture key features of market dynamics, while also producing reasonable results for the individual insurers. A replication of Taylor’s model is also constructed in order to compare results with the new premium setting mechanism. To enable the comparison of the two premium mechanisms, the rest of the model set-up is maintained as in the Taylor model. As in the Taylor example, homogeneous customers represented as a total market exposure which is allocated amongst the insurers.
In each time period, the model undergoes the following steps:
1. Insurers set competitive premiums per exposure unit
2. Losses are generated based on each insurer’s share of the market exposure
3. Accounting results are calculated for each insurer
…
This agent-based model (ABM), developed in NetLogo and available on the COMSES repository, simulates a stylized, competitive electricity market to explore the effects of carbon pricing policies under conditions of technological innovation. Unlike traditional models that treat innovation as exogenous, this ABM incorporates endogenous innovation dynamics, allowing clean technology costs to evolve based on cumulative deployment (Wright’s Law) or time (Moore’s Law). Electricity generation companies act as agents, making investment decisions across coal, gas, wind, and solar PV technologies based on expected returns and market conditions. The model evaluates three policy scenarios—No Policy, Emissions Trading System (ETS), and Carbon Tax—within a merit-order market framework. It is partially empirically grounded, using real-world data for technology costs and emissions caps. By capturing emergent system behavior, this model offers a flexible and transparent tool for analyzing the transition to low-carbon electricity systems.
Simulation of Self-enforcing Agreement in Cooperative Teams
Hang Xiong | Published Friday, April 01, 2016This is an agent-based model of the implementation of the self-enforcing agreement in cooperative teams.
An agent-based model to simulate meat consumption behaviour of consumers in Britain
Andrea Scalco | Published Friday, October 18, 2019The current rate of production and consumption of meat poses a problem both to peoples’ health and to the environment. This work aims to develop a simulation of peoples’ meat consumption behaviour in Britain using agent-based modelling. The agents represent individual consumers. The key variables that characterise agents include sex, age, monthly income, perception of the living cost, and concerns about the impact of meat on the environment, health, and animal welfare. A process of peer influence is modelled with respect to the agents’ concerns. Influence spreads across two eating networks (i.e. co-workers and household members) depending on the time of day, day of the week, and agents’ employment status. Data from a representative sample of British consumers is used to empirically ground the model. Different experiments are run simulating interventions of application of social marketing campaigns and a rise in price of meat. The main outcome is the average weekly consumption of meat per consumer. A secondary outcome is the likelihood of eating meat.
Replication of a Social-Links-Evolution-Model
Sascha Holzhauer | Published Wednesday, December 01, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013ReSolEvo File output version
Displaying 10 of 1115 results for "Sjoukje A Osinga" clear search