About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 373 results for "Puqing Wang" clear search
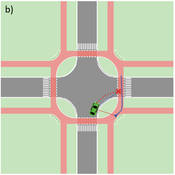
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
MASTOC - A Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of The Commons
Julia Schindler | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013MASTOC is a replication of the Tragedy of the Commons by G. Hardin, programmed in NetLogo 4.0.4, based on behavioral game theory and Nash solution.
A Mathematical Model of The Beer Game
Hakan Yasarcan Mert Edali | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014This is the R code of the mathematical model that includes the decision making formulations for artificial agents. This code corresponds to equations 1-70 given in the paper “A Mathematical Model of The Beer Game”.
Multistate modeling extended by behavioral rules
Frans Willekens Sabine Zinn Matthias Leuchter Anna Klabunde | Published Wednesday, August 03, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 13, 2018Toolkit to specify demographic multistate model with a behavioural element linking intentions to behaviour
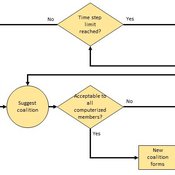
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
Multi-Hazard Coastal Agent-Based Model (MHCABM)
Andrew Allison | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021MHCABM is an agent-based, multi-hazard risk interaction model with an integrated applied dynamic adaptive pathways planning component. It is designed to explore the impacts of climate change adaptation decisions on the form and function of a coastal human-environment system, using as a case study an idealised patch based representation of the Mount North-Omanu area of Tauranga city, New Zealand. The interacting hazards represented are erosion, inundation, groundwater intrusion driven by intermittent heavy rainfall / inundations (storm) impacts, and sea level rise.
MUGS - Model of Urban Green Spaces
Stefano Picascia | Published Friday, September 17, 2021Abstract model investigating the determinants of inter- and intra-urban inequality in contact with nature. We explore the plausibility of a social integration hypothesis - whereby the primary factor in decisions to visit Urban Green Spaces (UGS) is an assessment of who else is likely to be using the space at the same time, and the assessment runs predominantly along class lines. The model simulates four cities in Scotland and shows the conditions under which the mechanisms theorised are sufficient to reproduce observed inequalities in UGS usage.
epiworldR Type: Fast Agent-Based Epi Models
George G. Vega Yon Derek Meyer | Published Monday, August 26, 2024A flexible framework for Agent-Based Models (ABM), the ‘epiworldR’ package provides methods for prototyping disease outbreaks and transmission models using a ‘C++’ backend, making it very fast. It supports multiple epidemiological models, including the Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible (SIS), Susceptible-Infected-Removed (SIR), Susceptible-Exposed-Infected-Removed (SEIR), and others, involving arbitrary mitigation policies and multiple-disease models. Users can specify infectiousness/susceptibility rates as a function of agents’ features, providing great complexity for the model dynamics. Furthermore, ‘epiworldR’ is ideal for simulation studies featuring large populations.
Comparing agent-based models on experimental data of irrigation games
Marco Janssen Jacopo A. Baggio | Published Tuesday, July 02, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 03, 2013Comparing 7 alternative models of human behavior and assess their performance on a high resolution dataset based on individual behavior performance in laboratory experiments.
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
Displaying 10 of 373 results for "Puqing Wang" clear search