About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search
Risk perception of individuals and the transmission dynamics of COVID-19
Sara Shahin Moghadam Franziska klügel | Published Tuesday, June 27, 2023The purpose of this model is to explore the influence of integrating individuals’ behavioral dynamics in an agent-based model of COVID-19, on the dynamics of disease transmission. The model is an agent-based extention of an established large-scale Individual-based model called STRIDE. Four risk factors determine the individual’s perception of the risk and how they behave accordingly. It is assumed that individuals with higher levels of risk perception adopt higher levels of contact reduction in their daily routines. Individuals can assign different weights to any of the four different risk factors, i.e., the modeler can model different populations and explore how the transmission dynamics vary among them.
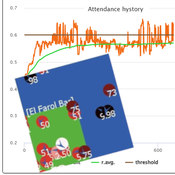
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
Using Agent-Based Modelling and Reinforcement Learning to Study Hybrid Threats
kpadur | Published Friday, September 20, 2024Hybrid attacks coordinate the exploitation of vulnerabilities across domains to undermine trust in authorities and cause social unrest. Whilst such attacks have primarily been seen in active conflict zones, there is growing concern about the potential harm that can be caused by hybrid attacks more generally and a desire to discover how better to identify and react to them. In addressing such threats, it is important to be able to identify and understand an adversary’s behaviour. Game theory is the approach predominantly used in security and defence literature for this purpose. However, the underlying rationality assumption, the equilibrium concept of game theory, as well as the need to make simplifying assumptions can limit its use in the study of emerging threats. To study hybrid threats, we present a novel agent-based model in which, for the first time, agents use reinforcement learning to inform their decisions. This model allows us to investigate the behavioural strategies of threat agents with hybrid attack capabilities as well as their broader impact on the behaviours and opinions of other agents.
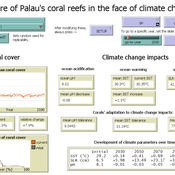
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Agent-based Modelling of Unsustainable and Sustainable Norms Under Resource Constraints
Fachrizal Sinaga Adrian Thomas Sufyan Fawwad | Published Monday, November 24, 2025This model explores the coupled dynamics of social norm diffusion and finite resource depletion. Extending the “Affordance Landscape” framework by Kaaronen & Strelkovskii (2020), this simulation investigates how resource scarcity and regeneration rates influence the adoption of pro-environmental behaviours.
The model addresses the gap by linking behavioural norms to a depleting common-pool resource. It tests whether sustainable norms can diffuse rapidly enough to prevent ecological collapse and identifies “tipping points” where resource scarcity acts as a driver for behavioural change.
Peer reviewed A Model of Global Diversity and Local Consensus in Status Beliefs
André Grow Andreas Flache Rafael Wittek | Published Wednesday, March 01, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, October 25, 2017This model makes it possible to explore how network clustering and resistance to changing existing status beliefs might affect the spontaneous emergence and diffusion of such beliefs as described by status construction theory.
Managing ecological disturbances: Learning and the structure of social-ecological networks
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018The aim of this model is to explore and understand the factors driving adoption of treatment strategies for ecological disturbances, considering payoff signals, learning strategies and social-ecological network structure
Simulation of the Effects of Disorganization on Goals and Problem Solving
Dinuka Herath | Published Sunday, August 13, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, August 13, 2017This is a model of the occurrence of disorganization and its impact on individual goal setting and problem-solving. This model therefore, explores the effects of disorganization on goal achievement.
SMILI-T: Small-scale fisheries institutions and local interactions for transformations
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Tuesday, January 09, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 26, 2021This model examines how financial and social top-down interventions interplay with the internal self-organizing dynamics of a fishing community. The aim is to transform from hierarchical fishbuyer-fisher relationship into fishing cooperatives.
Talent vs Luck: the role of randomness in success and failure
Alessandro Pluchino Alessio Emanuele Biondo Andrea Rapisarda | Published Monday, July 16, 2018The largely dominant meritocratic paradigm of highly competitive Western cultures is rooted on the belief that success is due mainly, if not exclusively, to personal qualities such as talent, intelligence, skills, smartness, efforts, willfulness, hard work or risk taking. Sometimes, we are willing to admit that a certain degree of luck could also play a role in achieving significant material success. But, as a matter of fact, it is rather common to underestimate the importance of external forces in individual successful stories. It is very well known that intelligence (or, more in general, talent and personal qualities) exhibits a Gaussian distribution among the population, whereas the distribution of wealth - often considered a proxy of success - follows typically a power law (Pareto law), with a large majority of poor people and a very small number of billionaires. Such a discrepancy between a Normal distribution of inputs, with a typical scale (the average talent or intelligence), and the scale invariant distribution of outputs, suggests that some hidden ingredient is at work behind the scenes. In a recent paper, with the help of this very simple agent-based model realized with NetLogo, we suggest that such an ingredient is just randomness. In particular, we show that, if it is true that some degree of talent is necessary to be successful in life, almost never the most talented people reach the highest peaks of success, being overtaken by mediocre but sensibly luckier individuals. As to our knowledge, this counterintuitive result - although implicitly suggested between the lines in a vast literature - is quantified here for the first time. It sheds new light on the effectiveness of assessing merit on the basis of the reached level of success and underlines the risks of distributing excessive honors or resources to people who, at the end of the day, could have been simply luckier than others. With the help of this model, several policy hypotheses are also addressed and compared to show the most efficient strategies for public funding of research in order to improve meritocracy, diversity and innovation.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search