About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 175 results for "Woi Sok Oh" clear search
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
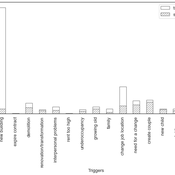
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
Peer reviewed JuSt-Social COVID-19
Jennifer Badham | Published Thursday, June 18, 2020 | Last modified Monday, March 29, 2021NetLogo model that allows scenarios concerning general social distancing, shielding of high-risk individuals, and informing contacts when symptomatic. Documentation includes a user manual with some simple scenarios, and technical information including descriptions of key procedures and parameter values.
Two agent-based models of cooperation in dynamic groups and fixed social networks
Carlos A. de Matos Fernandes | Published Thursday, January 20, 2022Both models simulate n-person prisoner dilemma in groups (left figure) where agents decide to C/D – using a stochastic threshold algorithm with reinforcement learning components. We model fixed (single group ABM) and dynamic groups (bad-barrels ABM). The purpose of the bad-barrels model is to assess the impact of information during meritocratic matching. In the bad-barrels model, we incorporated a multidimensional structure in which agents are also embedded in a social network (2-person PD). We modeled a random and homophilous network via a random spatial graph algorithm (right figure).
ReMoTe-S. Residential Mobility of Tenants in Switzerland: an agent-based model
Claudia Binder Anna Pagani Francesco Ballestrazzi Emanuele Massaro | Published Friday, April 01, 2022ReMoTe-S is an agent-based model of the residential mobility of Swiss tenants. Its goal is to foster a holistic understanding of the reciprocal influence between households and dwellings and thereby inform a sustainable management of the housing stock. The model is based on assumptions derived from empirical research conducted with three housing providers in Switzerland and can be used mainly for two purposes: (i) the exploration of what if scenarios that target a reduction of the housing footprint while accounting for households’ preferences and needs; (ii) knowledge production in the field of residential mobility and more specifically on the role of housing functions as orchestrators of the relocation process.
Open Peer Review Model
Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, May 24, 2021This is an agent-based model of a population of scientists alternatively authoring or reviewing manuscripts submitted to a scholarly journal for peer review. Peer-review evaluation can be either ‘confidential’, i.e. the identity of authors and reviewers is not disclosed, or ‘open’, i.e. authors’ identity is disclosed to reviewers. The quality of the submitted manuscripts vary according to their authors’ resources, which vary according to the number of publications. Reviewers can assess the assigned manuscript’s quality either reliably of unreliably according to varying behavioural assumptions, i.e. direct/indirect reciprocation of past outcome as authors, or deference towards higher-status authors.
Musical Chairs
Andreas Angourakis | Published Wednesday, February 03, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 11, 2016This Agent-Based model intends to explore the conditions for the emergence and change of land use patterns in Central Asian oases and similar contexts.
World of Cows - Exploring land-use policies for a dairy-farm world (teaching modeling complex human-environment systems)
Maria Haensel Thomas Michael Schmitt Jakob Bogenreuther | Published Wednesday, January 11, 2023In the “World of Cows”, dairy farmers run their farms and interact with each other, the surrounding agricultural landscape, and the economic and political framework. The model serves as an exemplary case of an interdependent human-environment system.
With the model, users can analyze the influence of policies and markets on land use decisions of dairy farms. The land use decisions taken by farms determine the delivered ecosystem services on the landscape level. Users can choose a combination of five policy options and how strongly market prices fluctuate. Ideally, the choice of policy options fulfills the following three “political goals” 1) dairy farming stays economically viable, 2) the provision of ecosystem services is secured, and 3) government spending on subsidies is as low as possible.
The model has been designed for students to practice agent-based modeling and analyze the impacts of land use policies.
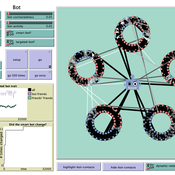
How do bots influence beliefs on social media? Why do beliefs propagated by social bots spread far and wide, yet does their direct influence appear to be limited?
This model extends Axelrod’s model for the dissemination of culture (1997), with a social bot agent–an agent who only sends information and cannot be influenced themselves. The basic network is a ring network with N agents connected to k nearest neighbors. The agents have a cultural profile with F features and Q traits per feature. When two agents interact, the sending agent sends the trait of a randomly chosen feature to the receiving agent, who adopts this trait with a probability equal to their similarity. To this network, we add a bot agents who is given a unique trait on the first feature and is connected to a proportion of the agents in the model equal to ‘bot-connectedness’. At each timestep, the bot is chosen to spread one of its traits to its neighbors with a probility equal to ‘bot-activity’.
The main finding in this model is that, generally, bot activity and bot connectedness are both negatively related to the success of the bot in spreading its unique message, in equilibrium. The mechanism is that very active and well connected bots quickly influence their direct contacts, who then grow too dissimilar from the bot’s indirect contacts to quickly, preventing indirect influence. A less active and less connected bot leaves more space for indirect influence to occur, and is therefore more successful in the long run.
Equity Constrained Dispatching Model of Emergency Medical Services
Sreekanth V K Ram Babu Roy | Published Thursday, September 08, 2016 | Last modified Monday, May 01, 2017Model for evaluating various ambulance dispatching policies of an equity constrained emergency medical services under bounded rationality.
We propose here a computational model of school segregation that is aligned with a corresponding Schelling-type model of residential segregation. To adapt the model for application to school segregation, we move beyond previous work by combining two preference arguments in modeling parents’ school choice, preferences for the ethnic composition of a school and preferences for minimizing the travelling distance to the school.
Displaying 10 of 175 results for "Woi Sok Oh" clear search