About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 321 results for "J Hall" clear search
Inquisitiveness in ad hoc teams
Davide Secchi | Published Sunday, October 18, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, June 11, 2020This model builds on inquisitiveness as a key individual disposition to expand the bounds of their rationality. It represents a system where teams are formed around problems and inquisitive agents integrate competencies to find ‘emergent’ solutions.
Narragansett Bay (RI) Recreational Fishery ABM
Tyler Pavlowich Anne Innes-Gold Margaret Heinichen M. Conor McManus Jason McNamee Jeremy Collie Austin Humphries | Published Monday, June 21, 2021This model is based on the Narragansett Bay, RI recreational fishery. The two types of agents are piscivorous fish and fishers (shore and boat fishers are separate “breeds”). Each time step represents one week. Open season is weeks 1-26, assuming fishing occurs during half the year. At each weekly time step, fish agents grow, reproduce, and die. Fisher agents decide whether or not to fish based on their current satisfaction level, and those that do go fishing attempt to catch a fish. If they are successful, they decide whether to keep or release the fish. In our publication, this model was linked to an Ecopath with Ecosim food web model where the commercial harvest of forage fish affected the biomass of piscivorous fish - which then became the starting number of piscivorous fish for this ABM. The number of fish caught in a season of this ABM was converted to a fishing pressure and input back into the food web model.
PalaeoDiet : Rabbit hunting during the Upper Palaeolithic
Liliana Perez Samuel Seuru Ariane Burke | Published Thursday, October 06, 2022Zooarchaeological evidences indicate that rabbit hunting became prevalent during the Upper Palaeolithic in the Iberian Peninsula.
The purpose of the ABM is to test if warren hunting using nets as a collective strategy can explain the introduction of rabbits in the human diet in the Iberian Peninsula during this period. It is analyzed whether this hunting strategy has an impact on human diet breadth by affecting the relative abundance of other main taxa in the dietary spectrum.
Model validity is measured by comparing simulated diet breadth to the observed diet breadth in the zooarchaeological record.
The agent-based model is explicitly grounded on the Diet Breadth Model (DBM), from the Optimal Foraging Theory (OFT).
…
Modeling Arabian Upraise, a System Dynamics Approach: Egypt case study
Morteza Nazari | Published Wednesday, October 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A System Dynamics Model to anticipate insurgent movements and policy design to handle them .
Cliff Walking with Q-Learning NetLogo Extension
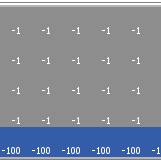
Kevin Kons Fernando Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2019This model implements a classic scenario used in Reinforcement Learning problem, the “Cliff Walking Problem”. Consider the gridworld shown below (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018). This is a standard undiscounted, episodic task, with start and goal states, and the usual actions causing movement up, down, right, and left. Reward is -1 on all transitions except those into the region marked “The Cliff.” Stepping into this region incurs a reward of -100 and sends the agent instantly back to the start (SUTTON; BARTO, 2018).
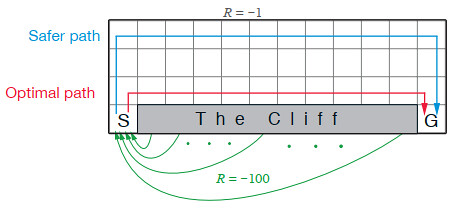
The problem is solved in this model using the Q-Learning algorithm. The algorithm is implemented with the support of the NetLogo Q-Learning Extension
Human-in-the-loop Experiment of the Strategic Coalition Formation using the glove game
Andrew Collins | Published Monday, November 23, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 22, 2022The purpose of the model is to collect information on human decision-making in the context of coalition formation games. The model uses a human-in-the-loop approach, and a single human is involved in each trial. All other agents are controlled by the ABMSCORE algorithm (Vernon-Bido and Collins 2020), which is an extension of the algorithm created by Collins and Frydenlund (2018). The glove game, a standard cooperative game, is used as the model scenario.
The intent of the game is to collection information on the human players behavior and how that compares to the computerized agents behavior. The final coalition structure of the game is compared to an ideal output (the core of the games).
An agent based model of a population subject to floods
Bruno Bonté Katrin Erdlenbruch | Published Wednesday, September 22, 2021This model allows simulating the impacts of floods on a population. Floods are described by their intensity (flood height) and date of occurrence. Households are more or less severely hit by floods according to their geographical situation. Impacts are measured in terms of reductions in household wealth. Households may take up protection measures against floods, depending on their individual characteristics, a social network and information campaigns. If such measures are taken, flood impacts (wealth reduction) are less severe. Information campaigns increase the probability that households adopt protection measures. Two types of information campaigns are modeled: top-down policies which are the same for all households, people-centered policies, which adapt to the individual characteristics of each household.
Network Behaviour Diffusion
Jennifer Badham | Published Saturday, October 02, 2021This model implements two types of network diffusion from an initial group of activated nodes. In complex contagion, a node is activated if the proportion of neighbour nodes that are already activated exceeds a given threshold. This is intended to represented the spread of health behaviours. In simple contagion, an activated node has a given probability of activating its inactive neighbours and re-tests each time step until all of the neighbours are activated. This is intended to represent information spread.
A range of networks are included with the model from secondary school friendship networks. The proportion of nodes initially activated and the method of selecting those nodes are controlled by the user.
A simple agent-based spatial model of the economy
Bernardo Alves Furtado Isaque Daniel Rocha Eberhardt | Published Thursday, March 10, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 22, 2016The modeling includes citizens, bounded into families; firms and governments; all of them interacting in markets for goods, labor and real estate. The model is spatial and dynamic.
01b ModEco NLG V1.39 – Model Economies – The PMM
Garvin Boyle | Published Friday, April 14, 2017It is very difficult to model a sustainable intergenerational biophysical/financial economy. ModEco NLG is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
Displaying 10 of 321 results for "J Hall" clear search