About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search
Peer Review Game
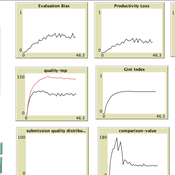
Giangiacomo Bravo Flaminio Squazzoni Francisco Grimaldo Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, April 30, 2018NetLogo software for the Peer Review Game model. It represents a population of scientists endowed with a proportion of a fixed pool of resources. At each step scientists decide how to allocate their resources between submitting manuscripts and reviewing others’ submissions. Quality of submissions and reviews depend on the amount of allocated resources and biased perception of submissions’ quality. Scientists can behave according to different allocation strategies by simply reacting to the outcome of their previous submission process or comparing their outcome with published papers’ quality. Overall bias of selected submissions and quality of published papers are computed at each step.
Automatic multi game chess
Julia Kasmire | Published Monday, July 22, 2019This model converts cleaned up versions of .pgn files (records of real chess games) and conversts them into files that record all of the events and “possible” events within a game of chess. This is intended to be a way to create sets of data that capture event sequences within the relatively complex but finite context of chess games as a proxy or “toy” data set. Although not a perfect correlation, these toy data sets are a first step in analysing complex and dynamic systems of events and possible events that happen in the real world.
Individual-based model to "Intraspecific trait variation in personality‐related movement behavior promotes coexistence" (Milles et al., 2020)
Alexander Milles | Published Monday, June 22, 2020The community consequences of intra-specific trait variation (ITV) are a current topic in ecological research. The effects of ITV on species coexistence have, yet, not sufficiently been understood. With this individual-based model we analyzed the effect of intra-specific variation in movement by mimicking variation found in ground-dwelling rodents and analyzing how such variation affects inter-specific differences in competitive ability (i.e. foraging efficiency) and temporary coexistence. The movement algorithm and behavioral plasticity was adapted from existing algorithms and current ecological literature. As a measure for temporary coexistence, we analyzed the time until one of the species went extinct.
Zombies
Jennifer Badham | Published Tuesday, June 08, 2021Zombies move toward humans and humans move (faster) away from zombies. They fight if they meet, and humans who lose become zombies.
WealthDistribRes
Romulus-Catalin Damaceanu | Published Friday, May 04, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model WealthDistribRes can be used to study the distribution of wealth in function of using a combination of resources classified in two renewable and nonrenewable.
Population aggregation in ancient arid environments
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, May 04, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The purpose of this model is to help understand how prehistoric societies adapted to the prehistoric American southwest landscape. In the American southwest there is a high degree of environmental var
Tiebout sorting
Marco Janssen | Published Thursday, January 24, 2019This Netlogo replication of Kollman, K., J.H. Miller and S.E. Page (1997) Political Institutions and Sorting in a Tiebout Model, American Economic Review 87(5): 977-992. The model consists of of citizens who can vote for partie and move to other jurisdictions if they expect their preferences are better served. Parties adjust their positions to increase their share in the elections.
Stylized Spatial-Social Subsystem based on Luhmann's theory (S4Luhmann)
Marcos Aurélio Santos da Silva | Published Saturday, April 06, 2019The model proposes a translation of some Luhmann’s concepts (social sub-system, perturbation, dissipation, social communication and power) into a model using a stylized spatial-society as a metaphor of a Luhmann’s social subsystem. The model has been used to improve the social theory understanding and to evaluate the effect of different parameterization in the global stabilization and individual/social power distribution.
Peer reviewed MIOvPOPsurveillance
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Monday, April 13, 2020MIOvPOPsurveillance is set up to simulate harvest-based chronic wasting disease (CWD) surveillance of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) populations in select Michigan Counties. New regions can be readily added, also the model can be readily adapted for other disease systems and used for informed-decision making during planning and implementation stages of disease surveillance in wildlife and free-ranging species.
Urban/Rural Adaptive Culture Model
Nick LaBerge | Published Sunday, July 19, 2020Contains python3 code used to replicate the culture model from the JASSS submission: “Modeling Cultural Dissemination and Divergence between Rural and Urban Regions.”
Displaying 10 of 1191 results for "Lee-Ann Sutherland" clear search