About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1105 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Peer reviewed MIOvPOPsurveillance
Aniruddha Belsare | Published Monday, April 13, 2020MIOvPOPsurveillance is set up to simulate harvest-based chronic wasting disease (CWD) surveillance of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) populations in select Michigan Counties. New regions can be readily added, also the model can be readily adapted for other disease systems and used for informed-decision making during planning and implementation stages of disease surveillance in wildlife and free-ranging species.
The NetLogo HIV Spread Model Exploring Impact of PrEP Indication Guidelines
Uri Wilensky Wouter Vermeer Arthur Hjorth | Published Friday, June 05, 2020This agent-based model was built as part of a replication effort of Jeness et al.’s work (linked below). The model simulates an MSM sexual activity network for the purpose of modeling the effects of respectively PrEP and ART on HIV prevention. The purpose of the model is to explore the differences between differerent interpretations of the NIH Indication Guidelines for PrEP.
An epidemiological-economic agent-based model of Huanglongbing and Asian citrus psyllid control in California
Jonathan Kaplan | Published Wednesday, June 01, 2022This model simulates economic and epidemiological interaction between citrus production and the disease Huanglongbing (HLB), which is vectored by the Asian citrus psyllid. The model is used to evaluate area-wide coordinated spraying when free-riding is possible given individuals’ beliefs in other grower participation in area-wide spraying and in the information provided by extension on the threat as HLB spread.
ABM Code: Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries
Diego Leal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2025The code and data in this repository are associated with the article titled: “Locating Cultural Holes Brokers in Diffusion Dynamics across Bright Symbolic Boundaries.” The NetLogo code (version 6.4.0) is designed to be a standalone piece of code although it uses the ‘nw’ and ‘matrix’ extensions that come integrated with NetLogo 6.4.0. The code was ran on a Windows 10 x 64 machine.
Social Nets Emergence Model
Di Wang | Published Wednesday, March 21, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates the interactions and dynamic trust changes between people which results in social group emergence and evolution.
Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model
Szymon Talaga Andrzej Nowak | Published Tuesday, September 17, 2019This is code repository for the paper “Homophily as a process generating social networks: insights from Social Distance Attachment model”.
It provides all information, code and data necessary to replicate all the simulations and analyses presented in the paper.
This document contains the overall instruction as well as description of the content of the repository.
Details regarding particular stages are documented within source files as comments.
Opinion dynamics model for prediction markets
Valerio Restocchi | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We introduce a model of prediction markets that uses opinion dynamics as its underlying mechanism for price formation. We base the opinion dynamics on the Deffuant model of bounded rationality. We have used this model to show that price formation in prediction markets can be robustly explained by opinion dynamics, and that the model can also explain phase transitions depending on just two parameters.
Peer reviewed Credit and debt market of low-income families
Márton Gosztonyi | Published Tuesday, December 12, 2023 | Last modified Friday, January 19, 2024The purpose of the Credit and debt market of low-income families model is to help the user examine how the financial market of low-income families works.
The model is calibrated based on real-time data which was collected in a small disadvantaged village in Hungary it contains 159 households’ social network and attributes data.
The simulation models the households’ money liquidity, expenses and revenue structures as well as the formal and informal loan institutions based on their network connections. The model forms an intertwined system integrated in the families’ local socioeconomic context through which families handle financial crises and overcome their livelihood challenges from one month to another.
The simulation-based on the abstract model of low-income families’ financial survival system at the bottom of the pyramid, which was described in following the papers:
…
Peer reviewed ABM Overtourism Santa Marta
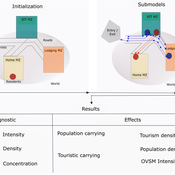
Janwar Moreno | Published Monday, October 23, 2023This model presents the simulation model of a city in the context of overtourism. The study area is the city of Santa Marta in Colombia. The purpose is to illustrate the spatial and temporal distribution of population and tourists in the city. The simulation analyzes emerging patterns that result from the interaction between critical components in the touristic urban system: residents, urban space, touristic sites, and tourists. The model is an Agent-Based Model (ABM) with the GAMA software. Also, it used public input data from statistical centers, geographical information systems, tourist websites, reports, and academic articles. The ABM includes assessing some measures used to address overtourism. This is a field of research with a low level of analysis for destinations with overtourism, but the ABM model allows it. The results indicate that the city has a high risk of overtourism, with spatial and temporal differences in the population distribution, and it illustrates the effects of two management measures of the phenomenon on different scales. Another interesting result is the proposed tourism intensity indicator (OVsm), taking into account that the tourism intensity indicators used by the literature on overtourism have an overestimation of tourism pressures.
A Replication of Rolf Zieglers Kula Ring Simulation
Rhian Stotts | Published Tuesday, December 16, 2008 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a simulation of the ceremonial exchange network in Papua New Guinea called the Kula Ring. In the Kula Ring, there are two types of gifts that travel in opposite directions: armshells co
Displaying 10 of 1105 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search