About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 359 results for "John C Moore" clear search
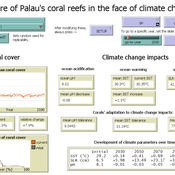
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Influence with over-confident agents
Juliette Rouchier Emily Tanimura | Published Wednesday, October 21, 2015Agents can influence each other if they are close enough in knowledge. The probability to convince with good knowledge and number of agents have an impact on the dissemination of knowledge.
Pedestrian Scramble
Sho Takami Rami Lake Dara Vancea | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025This is a model intended to demonstrate the function of scramble crossings and a more efficient flow of pedestrian traffic with the presence of diagonal crosswalks.
Gender differentiation model
Sylvie Huet | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, April 23, 2020This is a gender differentiation model in terms of reputations, prestige and self-esteem (presented in the paper https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0236840). The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) considering two groups.
This agent-based model studies how inequalities can be explained by the difference of open-mindness between two groups of interacting agents. We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. We study an heterogeneous population of two different groups: one more open to influence of others, taking less into account their perceived difference of esteem, called L; a second one less prone to it, called S, who designed the credibility they give to others strongly based on how higher or lower valued than themselves they perceive them.
We show that a mixed population always turns in favor to some agents belonging to the group of less open-minded agents S, and harms the other group: (1) the average group self-opinion or reputation of S is always better than the one of L; (2) the higher rank in terms of reputation are more frequently occupied by the S agents while the L agents occupy more the bottom rank; (3) the properties of the dynamics of differentiation between the two groups are similar to the properties of the glass ceiling effect proposed by Cotter et al (2001).
Netlogo Profiler code example
Colin Wren | Published Wednesday, March 04, 2015This is a very simple foraging model used to illustrate the features of Netlogo’s Profiler extension.
Diffusion of innovations
Marco Janssen | Published Tuesday, January 14, 20203 simple models to illustrate diffusion of innovations.
The models are discussed in Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling by Marco Janssen. For more information see https://intro2abm.com/
A Toy Model for the Abilene Paradox
Victor Sahin | Published Monday, June 17, 2019 | Last modified Sunday, July 14, 2019This version adds a Maslowian entropy to each agent decision based on Kendrick et. al. Rudimentary implementation assumes agents with lower scores are more likely to make decisions autonomously rather than sociotropically.
Livestock drought insurance model
Birgit Müller Felix John Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Russell Toth | Published Tuesday, December 19, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 14, 2018The model analyzes the economic and ecological effects of a provision of livestock drought insurance for dryland pastoralists. More precisely, it yields qualitative insights into how long-term herd and pasture dynamics change through insurance.
Pollution-development Tradeoffs in Nigeria--an Agent-based Model
Christopher Thron | Published Thursday, June 03, 2021Like many developing countries, Nigeria is faced with a number of tradeoffs that pit rapid economic development against environmental preservation. Environmentally sustainable, “green” economic development is slower, more costly, and more difficult than unrestricted, unregulated economic growth. The mathematical model that we develop in this code suggests that widespread public awareness of environmental issues is insufficient to prevent the tendency towards sacrificing the environment for the sake of growth. Even if people have an understanding of negative impacts and always choose to act in their own self-interest, they may still act collectively in such a way as to bring down the quality of life for the entire society. We conclude that additional actions must be taken besides raising public awareness of the environmental problem.
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Displaying 10 of 359 results for "John C Moore" clear search