About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 22 results industry clear search
Industrial Cooperation and the Hydrogen Transition
Amineh Ghorbani Renske van 't Veer Emre Ates Zofia Lukszo | Published Tuesday, September 23, 2025An Agent Based Model that explores the deployment of hydrogen among a regional industrial cluster in the Netherlands, consisting of 15 companies. The companies seek to decarbonize by replacing their natural gas by hydrogen.
The model integrates technical characteristics as well as company motivations to transition to hydrogen. The baseline model only considers individual investments where company can locally produce hydrogen. If they reach the backbone threshold, companies can also consider buying hydrogen through a connection to the national hydrogen network. The second scenario considers that companies can participate in a joint investment to get an electrolyzer to locally produce the hydrogen.
Two experiments look at the impact of the sectoral configuration and at the impact of subsidy conditions on the region’s hydrogen transition
Peer reviewed ACross (Academic Collaboration, Research, Output, and System Simulation)
Wenhan Feng Bayi Li | Published Saturday, June 28, 2025The primary purpose of this model is to explain the dynamic processes within university-centered collaboration networks, with a particular focus on the complex transformation of academic knowledge into practical projects. Based on investigations of actual research projects and a thorough literature review, the model integrates multiple drivers and influencing factors to explore how these factors affect the formation and evolution of collaboration networks under different parameter scenarios. The model places special emphasis on the impact of disciplinary attributes, knowledge exchange, and interdisciplinary collaboration on the dynamics of collaboration networks, as well as the complex mechanisms of network structure, system efficiency, and interdisciplinary interactions during project formation.
Specifically, the model aims to:
- Simulate how university research departments drive the formation of research projects through knowledge creation.
- Investigate how the dynamics of collaboration networks influence the transformation of innovative hypotheses into matured projects.
- Examine the critical roles of knowledge exchange and interdisciplinary collaboration in knowledge production and project formation.
- Provide both quantitative and qualitative insights into the interactions among academia, industry, and project outputs.
U-TRANS Modelling Urban Transition with Coupled Housing and Labour Markets
Bernardo Furtado Jiaqi Ge | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We develop an agent-based model (U-TRANS) to simulate the transition of an abstract city under an industrial revolution. By coupling the labour and housing markets, we propose a holistic framework that incorporates the key interacting factors and micro processes during the transition. Using U-TRANS, we look at five urban transition scenarios: collapse, weak recovery, transition, enhanced training and global recruit, and find the model is able to generate patterns observed in the real world. For example, We find that poor neighbourhoods benefit the most from growth in the new industry, whereas the rich neighbourhoods do better than the rest when the growth is slow or the situation deteriorates. We also find a (subtle) trade-off between growth and equality. The strategy to recruit a large number of skilled workers globally will lead to higher growth in GDP, population and human capital, but it will also entail higher inequality and market volatility, and potentially create a divide between the local and international workers. The holistic framework developed in this paper will help us better understand urban transition and detect early signals in the process. It can also be used as a test-bed for policy and growth strategies to help a city during a major economic and technological revolution.
Peer reviewed Viable North Sea (ViNoS): A NetLogo Agent-based Model of German Small-scale Fisheries
Wolfgang Nikolaus Probst Jieun Seo Jürgen Scheffran Carsten Lemmen Sascha Hokamp Verena Mühlberger Serra Örey | Published Thursday, May 25, 2023 | Last modified Tuesday, December 05, 2023Viable North Sea (ViNoS) is an Agent-based Model of the German North Sea Small-scale Fisheries in a Social-Ecological Systems framework focussing on the adaptive behaviour of fishers facing regulatory, economic, and resource changes. Small-scale fisheries are an important part both of the cultural perception of the German North Sea coast and of its fishing industry. These fisheries are typically family-run operations that use smaller boats and traditional fishing methods to catch a variety of bottom-dwelling species, including plaice, sole, and brown shrimp. Fisheries in the North Sea face area competition with other uses of the sea – long practiced ones like shipping, gas exploration and sand extractions, and currently increasing ones like marine protection and offshore wind farming. German authorities have just released a new maritime spatial plan implementing the need for 30% of protection areas demanded by the United Nations High Seas Treaty and aiming at up to 70 GW of offshore wind power generation by 2045. Fisheries in the North Sea also have to adjust to the northward migration of their established resources following the climate heating of the water. And they have to re-evaluate their economic balance by figuring in the foreseeable rise in oil price and the need for re-investing into their aged fleet.
Peer reviewed SIM-VOLATILE: Adoption of emerging circular technologies in the waste-treatment sector
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Wednesday, December 14, 2022The SIM-VOLATILE model is a technology adoption model at the population level. The technology, in this model, is called Volatile Fatty Acid Platform (VFAP) and it is in the frame of the circular economy. The technology is considered an emerging technology and it is in the optimization phase. Through the adoption of VFAP, waste-treatment plants will be able to convert organic waste into high-end products rather than focusing on the production of biogas. Moreover, there are three adoption/investment scenarios as the technology enables the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), single-cell oils (SCO), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). However, due to differences in the processing related to the products, waste-treatment plants need to choose one adoption scenario.
In this simulation, there are several parameters and variables. Agents are heterogeneous waste-treatment plants that face the problem of circular economy technology adoption. Since the technology is emerging, the adoption decision is associated with high risks. In this regard, first, agents evaluate the economic feasibility of the emerging technology for each product (investment scenarios). Second, they will check on the trend of adoption in their social environment (i.e. local pressure for each scenario). Third, they combine these two economic and social assessments with an environmental assessment which is their environmental decision-value (i.e. their status on green technology). This combination gives the agent an overall adaptability fitness value (detailed for each scenario). If this value is above a certain threshold, agents may decide to adopt the emerging technology, which is ultimately depending on their predominant adoption probabilities and market gaps.
Peer reviewed Labor and environment in global value chains: An evolutionary policy study with a three-sector and two-region agent-based macroeconomic model
Lena Gerdes Manuel Scholz-Wäckerle Bernhard Rengs | Published Wednesday, December 22, 2021With this model, we investigate resource extraction and labor conditions in the Global South as well as implications for climate change originating from industry emissions in the North. The model serves as a testbed for simulation experiments with evolutionary political economic policies addressing these issues. In the model, heterogeneous agents interact in a self-organizing and endogenously developing economy. The economy contains two distinct regions – an abstract Global South and Global North. There are three interlinked sectors, the consumption good–, capital good–, and resource production sector. Each region contains an independent consumption good sector, with domestic demand for final goods. They produce a fictitious consumption good basket, and sell it to the households in the respective region. The other sectors are only present in one region. The capital good sector is only found in the Global North, meaning capital goods (i.e. machines) are exclusively produced there, but are traded to the foreign as well as the domestic market as an intermediary. For the production of machines, the capital good firms need labor, machines themselves and resources. The resource production sector, on the other hand, is only located in the Global South. Mines extract resources and export them to the capital firms in the North. For the extraction of resources, the mines need labor and machines. In all three sectors, prices, wages, number of workers and physical capital of the firms develop independently throughout the simulation. To test policies, an international institution is introduced sanctioning the polluting extractivist sector in the Global South as well as the emitting industrial capital good producers in the North with the aim of subsidizing innovation reducing environmental and social impacts.
Peer reviewed A Macroeconomic Model of a Closed Economy
Ian Stuart | Published Saturday, May 08, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, June 23, 2021This model/program presents a “three industry model” that may be particularly useful for macroeconomic simulations. The main purpose of this program is to demonstrate a mechanism in which the relative share of labor shifts between industries.
Care has been taken so that it is written in a self-documenting way so that it may be useful to anyone that might build from it or use it as an example.
This model is not intended to match a specific economy (and is not calibrated to do so) but its particular minimalist implementation may be useful for future research/development.
…
TunaFisher ABM
Guus Ten Broeke | Published Wednesday, January 13, 2021TunaFisher ABM simulates the decisions of fishing companies and fishing vessels of the Philippine tuna purse seinery operating in the Celebes and Sulu Seas.
High fishing effort remains in many of the world’s fisheries, including the Philippine tuna purse seinery, despite a variety of policies that have been implemented to reduce it. These policies have predominantly focused on models of cause and effect which ignore the possibility that the intended outcomes are altered by social behavior of autonomous agents at lower scales.
This model is a spatially explicit Agent-based Model (ABM) for the Philippine tuna purse seine fishery, specifically designed to include social behavior and to study its effects on fishing effort, fish stock and industry profit. The model includes economic and social factors of decision making by companies and fishing vessels that have been informed by interviews.
…
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
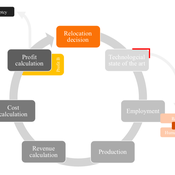
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
Displaying 10 of 22 results industry clear search