About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 11 results environmental change clear search
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
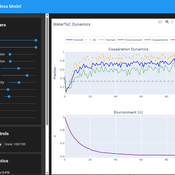
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
LogoClim: WorldClim in NetLogo
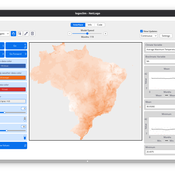
Daniel Vartanian Leandro Garcia Aline Martins de Carvalho Aline | Published Thursday, July 03, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, September 16, 2025LogoClim is a NetLogo model for simulating and visualizing global climate conditions. It allows researchers to integrate high-resolution climate data into agent-based models, supporting reproducible research in ecology, agriculture, environmental sciences, and other fields that rely on climate data.
The model utilizes raster data to represent climate variables such as temperature and precipitation over time. It incorporates historical data (1951-2024) and future climate projections (2021-2100) derived from global climate models under various Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs, O’Neill et al., 2017). All climate inputs come from WorldClim 2.1, a widely used source of high-resolution, interpolated climate datasets based on weather station observations worldwide (Fick & Hijmans, 2017).
LogoClim follows the FAIR Principles for Research Software (Barker et al., 2022) and is openly available on the CoMSES Network and GitHub. See the Logônia model for an example of its integration into a full NetLogo simulation.
A formalized implementation of Halstead and O’Shea’s Bad Year Economics. The agent population uses one of four resilience strategies in an attempt to cope with a dynamic environment of stresses and shocks.
Peer reviewed The Megafauna Hunting Pressure Model
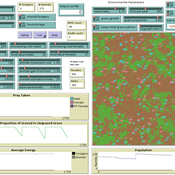
Isaac Ullah Miriam C. Kopels | Published Friday, February 16, 2024 | Last modified Friday, October 11, 2024The Megafaunal Hunting Pressure Model (MHPM) is an interactive, agent-based model designed to conduct experiments to test megaherbivore extinction hypotheses. The MHPM is a model of large-bodied ungulate population dynamics with human predation in a simplified, but dynamic grassland environment. The overall purpose of the model is to understand how environmental dynamics and human predation preferences interact with ungulate life history characteristics to affect ungulate population dynamics over time. The model considers patterns in environmental change, human hunting behavior, prey profitability, herd demography, herd movement, and animal life history as relevant to this main purpose. The model is constructed in the NetLogo modeling platform (Version 6.3.0; Wilensky, 1999).
PopComp
Andre Costopoulos | Published Thursday, December 10, 2020PopComp by Andre Costopoulos 2020
andre.costopoulos@ualberta.ca
Licence: DWYWWI (Do whatever you want with it)
I use Netlogo to build a simple environmental change and population expansion and diffusion model. Patches have a carrying capacity and can host two kinds of populations (APop and BPop). Each time step, the carrying capacity of each patch has a given probability of increasing or decreasing up to a maximum proportion.
…
Change and Senescence
André Martins | Published Tuesday, November 10, 2020Agers and non-agers agent compete over a spatial landscape. When two agents occupy the same grid, who will survive is decided by a random draw where chances of survival are proportional to fitness. Agents have offspring each time step who are born at a distance b from the parent agent and the offpring inherits their genetic fitness plus a random term. Genetic fitness decreases with time, representing environmental change but effective non-inheritable fitness can increase as animals learn and get bigger.
Managing networked landscapes: conservation in fragmented, regionally connected world
Jacopo A. Baggio Michael Schoon Sechindra Vallury | Published Monday, December 09, 2019Exploring how learning and social-ecological networks influence management choice set and their ability to increase the likelihood of species coexistence (i.e. biodiversity) on a fragmented landscape controlled by different managers.
Peer reviewed FishMob: Interactions between fisher mobility and spatial resource heterogeneity
Emilie Lindkvist | Published Wednesday, October 16, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, June 23, 2020Migration or other long-distance movement into other regions is a common strategy of fishers and fishworkers living and working on the coast to adapt to environmental change. This model attempts to understand the general dynamics of fisher mobility for over larger spatial scales. The model can be used for investigating the complex interplay that exists between mobility and fish stock heterogeneity across regions, and the associated outcomes of mobility at the system level.
The model design informed by the example of small-scale fisheries in the Gulf of California, Mexico but implements theoretical and stylized facts and can as such be used for different archetypical cases. Our methodological approach for designing the model aims to account for the complex causation, emergence and interdependencies in small-scale fisheries to explain the phenomenon of sequential overexploitation, i.e., overexploiting one resource after another. The model is intended to be used as a virtual laboratory to investigate when and how different levels of mobile fishers affect exploitation patterns of fisheries resources.
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
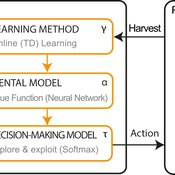
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
Displaying 10 of 11 results environmental change clear search