No bio entered.
PaCE Austria Pilot Model
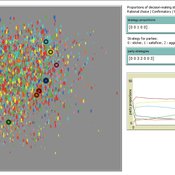
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, June 30, 2020The objective of building a social simulation in the Populism and Civic Engagement (PaCE) project is to study the phenomenon of populism by mapping individual level political behaviour and explain the influence of agents on, and their interdependence with the respective political parties. Voters, political parties and – to some extent – the media can be viewed as forming a complex adaptive system, in which parties compete for citizens’ votes, voters decide on which party to vote for based on their respective positions with regard to particular issues, and the media may influence the salience of issues in the public debate.
This is the first version of a model exploring voting behaviour in Austria. It focusses on modelling the interaction of voters and parties in a political landscape; the effects of the media are not yet represented. Austria was chosen as a case study because it has an established populist party (the “Freedom Party” FPO), which has even been part of the government over the years.
LaMEStModel
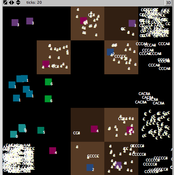
Ruth Meyer | Published Friday, October 12, 2018The Labour Markets and Ethnic Segmentation (LaMESt) Model is a model of a simplified labour market, where only jobs of the lowest skill level are considered. Immigrants of two different ethnicities (“Latino”, “Asian”) compete with a majority (“White”) and minority (“Black”) native population for these jobs. The model’s purpose is to investigate the effect of ethnically homogeneous social networks on the emergence of ethnic segmentation in such a labour market. It is inspired by Waldinger & Lichter’s study of immigration and the social organisation of labour in 1990’s Los Angeles.
DiDIY Factory
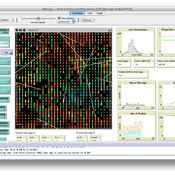
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, February 20, 2018The DiDIY-Factory model is a model of an abstract factory. Its purpose is to investigate the impact Digital Do-It-Yourself (DiDIY) could have on the domain of work and organisation.
DiDIY can be defined as the set of all manufacturing activities (and mindsets) that are made possible by digital technologies. The availability and ease of use of digital technologies together with easily accessible shared knowledge may allow anyone to carry out activities that were previously only performed by experts and professionals. In the context of work and organisations, the DiDIY effect shakes organisational roles by such disintermediation of experts. It allows workers to overcome the traditionally strict organisational hierarchies by having direct access to relevant information, e.g. the status of machines via real-time information systems implemented in the factory.
A simulation model of this general scenario needs to represent a more or less abstract manufacturing firm with supervisors, workers, machines and tasks to be performed. Experiments with such a model can then be run to investigate the organisational structure –- changing from a strict hierarchy to a self-organised, seemingly anarchic organisation.
DITCH --- A Model of Inter-Ethnic Partnership Formation
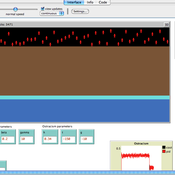
Ruth Meyer Laurence Lessard-Phillips Huw Vasey | Published Wednesday, November 05, 2014 | Last modified Tuesday, February 02, 2016The DITCH model has been developed to investigate partner selection processes, focusing on individual preferences, opportunities for contact, and group size to uncover how these may lead to differential rates of inter-ethnic marriage.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
Under development.