MigrAgent (1.0.0)
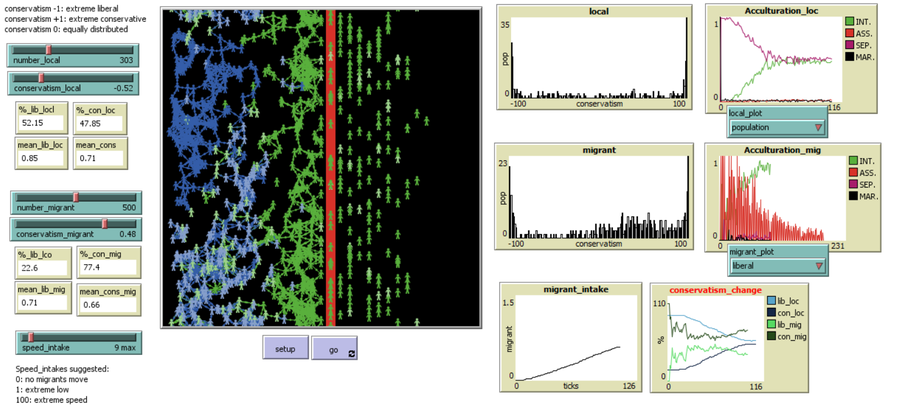
MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Release Notes
Sliders:
- number_local [0,1000]: number local agents
- conservatism_local [-1, +1]: mean normal distribution of conservatism agents (fixed standard deviation 0.45)
- number_migrant [0,1000]
- conservatism_migrant [-1, +1]: mean normal distribution of conservatism agents (fixed standard deviation 0.45)
- speed_intake [0, 100]: percentage of migrant agents moving together to host country
Associated Publications
Paolillo, R., & Jager, W. (2019). Simulating Acculturation Dynamics Between Migrants and Locals in Relation to Network Formation. Social Science Computer Review. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439318821678
This release is out-of-date. The latest version is
1.2.0
MigrAgent 1.0.0
Submitted by
Rocco Paolillo
Published Oct 05, 2018
Last modified Dec 05, 2024
MigrAgent simulates migration flows of a population from a home country to a host country and mutual adaptation of a migrant and local population post-migration. Agents accept interactions in intercultural networks depending on their degree of conservatism. Conservatism is a group-level parameter normally distributed within each ethnic group. Individual conservatism changes as function of reciprocity of interaction in intergroup experiences of acceptance or rejection.
The aim of MigrAgent is to unfold different outcomes of integration, assimilation, separation and marginalization in terms of networks as effect of different degrees of conservatism in each group and speed of migration flows.
Release Notes
Sliders:
- number_local [0,1000]: number local agents
- conservatism_local [-1, +1]: mean normal distribution of conservatism agents (fixed standard deviation 0.45)
- number_migrant [0,1000]
- conservatism_migrant [-1, +1]: mean normal distribution of conservatism agents (fixed standard deviation 0.45)
- speed_intake [0, 100]: percentage of migrant agents moving together to host country